Cardioprotective Activity of Methanol Extract of fruit of Trichosanthes cucumerina on Doxorubicin-induced Cardiotoxicity in Wistar Rats
- PMID: 22778516
- PMCID: PMC3388762
- DOI: 10.4103/0971-6580.97218
Cardioprotective Activity of Methanol Extract of fruit of Trichosanthes cucumerina on Doxorubicin-induced Cardiotoxicity in Wistar Rats
Abstract
Aim and objective: The objective was to determine the activity of methanol extract of fruit of Trichosanthes cucumerina in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats.
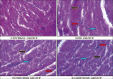
Materials and methods: The methanol extract of fruit of T. cucumerina was prepared. Male Wistar rats were divided in four groups. Group I was vehicle control. Group II animals received doxorubicin 4 mg/kg i.p. on days 21, 28, 35, and 42. Group III and IV animals were treated with methanol extract of T. cucumerina (500 and 1000 mg/kg, respectively) for 49 days. Doxorubicin was administered on days 21, 28, 35, and 42 days. The parameters of study were body weight, serum biomarkers, ECG, blood pressure, and left ventricular function. At the end of the study, the histology of heart, liver, and kidney was carried out.
Results: Cardiac toxicity by doxorubicin was manifested as body weight loss, elevated serum LDH and CK-MB, increased ST, QT and QRS complex, reduced blood pressure, and left ventricular function. The methanol extract of T. cucumerina significantly decreased LDH and CK-MB, reduced ST, QT interval and QRS complex, increased heart rate, restored blood pressure, and left ventricular function. Doxorubicin caused liver and kidney necrosis, cellular infiltration, and vascular changes that indicated injury.
Conclusion: T. cucumerina (1000 mg/kg) reduced the severity of doxorubicin-induced cardiac damage especially in heart. It is concluded that doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity is reduced by pretreatment with methanol extract of fruit of T. cucumerina.
Keywords: Cardiotoxicity; Trichosanthes cucumerina; doxorubicin.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Al-Majed AA, Gdo AM, Al-Shabanah OA, Mansour MA. Alpha-lipolic acid ameliorate myocardial toxicity induced by doxorubicin. Pharmacol Res. 2002;46:499–503. - PubMed
-
- Arawwawala M, Thabrew I, Arambewela L, Handunnetti S. Anti-inflammatory activity of Trichosanthese cucumerina Linn. in rats. J Ethanopharmacol. 2010;131:538–43. - PubMed
-
- Arawwala M, Thabrew I, Arambewela L. Gastroprotective activity of Trichosanthese cucumerina in rats. J Ethanopharmacol. 2010;127:750–54. - PubMed
-
- Ateşşahin A, Karahan I, Türk G, Gür S, Yilmaz S, Ceribaşi AO. Protective role of lycopene on cisplatin-induced changes in spermcharacteristics, testicular damage and oxidative stress in rats. Reprod Toxicol. 2006;21:42–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous