Emerging PPARγ-Independent Role of PPARγ Ligands in Lung Diseases
- PMID: 22778711
- PMCID: PMC3385049
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/705352
Emerging PPARγ-Independent Role of PPARγ Ligands in Lung Diseases
Abstract
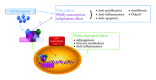
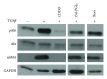
Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor (PPAR)-γ is a nuclear hormone receptor that is activated by multiple agonists including thiazolidinediones, prostaglandins, and synthetic oleanolic acids. Many PPARγ ligands are under investigation as potential therapies for human diseases. These ligands modulate multiple cellular pathways via both PPARγ-dependent and PPARγ-independent mechanisms. Here, we review the role of PPARγ and PPARγ ligands in lung disease, with emphasis on PPARγ-independent effects. PPARγ ligands show great promise in moderating lung inflammation, as antiproliferative agents in combination to enhance standard chemotherapy in lung cancer and as treatments for pulmonary fibrosis, a progressive fatal disease with no effective therapy. Some of these effects occur when PPARγ is pharmaceutically antagonized or genetically PPARγ and are thus independent of classical PPARγ-dependent transcriptional control. Many PPARγ ligands demonstrate direct binding to transcription factors and other proteins, altering their function and contributing to PPARγ-independent inhibition of disease phenotypes. These PPARγ-independent mechanisms are of significant interest because they suggest new therapeutic uses for currently approved drugs and because they can be used as probes to identify novel proteins and pathways involved in the pathogenesis or treatment of disease, which can then be targeted for further investigation and drug development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The antifibrogenic potential of PPARgamma ligands in pulmonary fibrosis.J Investig Med. 2008 Feb;56(2):534-8. doi: 10.2310/JIM.0b013e31816464e9. J Investig Med. 2008. PMID: 18317437 Review.
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma ligands induce heme oxygenase-1 in lung fibroblasts by a PPARgamma-independent, glutathione-dependent mechanism.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009 Nov;297(5):L912-9. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00148.2009. Epub 2009 Sep 4. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19734319 Free PMC article.
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonists as insulin sensitizers: from the discovery to recent progress.Curr Top Med Chem. 2008;8(17):1483-507. doi: 10.2174/156802608786413474. Curr Top Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 19075761 Review.
-
Combined treatment with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) gamma ligands and gamma radiation induces apoptosis by PPARγ-independent up-regulation of reactive oxygen species-induced deoxyribonucleic acid damage signals in non-small cell lung cancer cells.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013 Apr 1;85(5):e239-48. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.11.040. Epub 2013 Jan 17. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013. PMID: 23332223
-
Up-regulation of p21 gene expression by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in human lung carcinoma cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Mar 15;10(6):1911-9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-03-0985. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15041706
Cited by
-
Peroxisomes and Oxidative Stress: Their Implications in the Modulation of Cellular Immunity During Mycobacterial Infection.Front Microbiol. 2019 Jun 14;10:1121. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01121. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31258517 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel QSAR Models for Molecular Initiating Event Modeling in Two Intersecting Adverse Outcome Pathways Based Pulmonary Fibrosis Prediction for Biocidal Mixtures.Toxics. 2021 Mar 16;9(3):59. doi: 10.3390/toxics9030059. Toxics. 2021. PMID: 33809804 Free PMC article.
-
Chinese Herbs and Repurposing Old Drugs as Therapeutic Agents in the Regulation of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Pulmonary Diseases.J Inflamm Res. 2021 Mar 4;14:657-687. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S293135. eCollection 2021. J Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 33707963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PPARγ and the Innate Immune System Mediate the Resolution of Inflammation.PPAR Res. 2015;2015:549691. doi: 10.1155/2015/549691. Epub 2015 Dec 2. PPAR Res. 2015. PMID: 26713087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Naringenin interferes with the anti-diabetic actions of pioglitazone via pharmacodynamic interactions.J Nat Med. 2017 Apr;71(2):442-448. doi: 10.1007/s11418-016-1063-4. Epub 2016 Dec 3. J Nat Med. 2017. PMID: 27915399
References
-
- Desvergne B, Wahli W. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: nuclear control of metabolism. Endocrine Reviews. 1999;20(5):649–688. - PubMed
-
- Berger J, Moller DE. The mechanisms of action of PPARs. Annual Review of Medicine. 2002;53:409–435. - PubMed
-
- Noy N. Ligand specificity of nuclear hormone receptors: sifting through promiscuity. Biochemistry. 2007;46(47):13461–13467. - PubMed
-
- Willson TM, Wahli W. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor agonists. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology. 1997;1(2):235–241. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

