In vivo evaluation of limiting brain penetration of probes for α(2C)-adrenoceptor using small-animal positron emission tomography
- PMID: 22778842
- PMCID: PMC3368684
- DOI: 10.1021/cn1000364
In vivo evaluation of limiting brain penetration of probes for α(2C)-adrenoceptor using small-animal positron emission tomography
Abstract
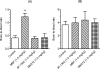
To evaluate in vivo brain penetration of α(2C)-adrenoceptor (α(2C)-AR) antagonists as a therapeutic agent, we synthesized two new (11)C-labeled selective α(2C)-AR antagonists 4-(6,7-dimethoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolin-2-yl)methyl-2-aryl-7-methoxybenzofuran ([(11)C]MBF) and acridin-9-yl-[4-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)phenyl]amine ([(11)C]JP-1302) as α(2C)-AR-selective positron emission tomography (PET) probes. The radiochemical yield, specific activity, and radiochemical purity of these probes was appropriate for injection. To evaluate whether the brain penetration of these probes is related to the function of two major drug efflux transporters, P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP), we performed PET studies using wild-type and P-gp/Bcrp knockout mice. In wild-type mice, the radioactivity level after injection with [(11)C]MBF initially increased and effluxed immediately from the brain, whereas that with [(11)C]JP-1302 was distributed throughout the brain. However, the regional distribution of radioactivity after injection with [(11)C]JP-1302 in the brain was different from that of α(2C)-ARs. In P-gp/Bcrp knockout mice, uptake of [(11)C]MBF was approximately 3.7-fold higher and that of [(11)C]JP-1302 was approximately 1.6-fold higher than those in wild-type mice. These results indicate that brain penetration of the two PET probes was affected by modulation of P-gp and Bcrp functions.
Keywords: 11C; 4-(6,7-dimethoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolin-2-yl)methyl-2-aryl-7-methoxybenzofuran (MBF); P-glycoprotein (P-gp); acridin-9-yl-[4-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)phenyl]amine (JP-1302); breast cancer resistance protein (Bcrp); α2C-Adrenoceptor.
Figures


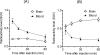



Similar articles
-
Evaluation of limiting brain penetration related to P-glycoprotein and breast cancer resistance protein using [(11)C]GF120918 by PET in mice.Mol Imaging Biol. 2011 Feb;13(1):152-60. doi: 10.1007/s11307-010-0313-1. Mol Imaging Biol. 2011. PMID: 20379788
-
P-glycoprotein and breast cancer resistance protein influence brain distribution of dasatinib.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009 Sep;330(3):956-63. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.154781. Epub 2009 Jun 2. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009. PMID: 19491323
-
The effect of breast cancer resistance protein and P-glycoprotein on the brain penetration of flavopiridol, imatinib mesylate (Gleevec), prazosin, and 2-methoxy-3-(4-(2-(5-methyl-2-phenyloxazol-4-yl)ethoxy)phenyl)propanoic acid (PF-407288) in mice.Drug Metab Dispos. 2009 May;37(5):946-55. doi: 10.1124/dmd.108.024489. Epub 2009 Feb 18. Drug Metab Dispos. 2009. PMID: 19225039
-
O-[11C]methyl derivative of 6,7-dimethoxy-2-(4-methoxy-biphenyl-4-yl-methyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-isoquinoline.2012 Nov 5 [updated 2013 Jan 31]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2012 Nov 5 [updated 2013 Jan 31]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 23390669 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Radioligands targeting P-glycoprotein and other drug efflux proteins at the blood-brain barrier.J Labelled Comp Radiopharm. 2013 Mar-Apr;56(3-4):68-77. doi: 10.1002/jlcr.2993. J Labelled Comp Radiopharm. 2013. PMID: 24285312 Review.
Cited by
-
Preclinical in vitro and in vivo evaluation of [11C]ORM-13070 as PET ligand for alpha-2C adrenergic receptor occupancy using PET imaging in non-human primates.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2025 Apr;45(4):677-689. doi: 10.1177/0271678X241291949. Epub 2024 Oct 31. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2025. PMID: 39479946 Free PMC article.
-
Application of cross-species PET imaging to assess neurotransmitter release in brain.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015 Nov;232(21-22):4129-57. doi: 10.1007/s00213-015-3938-6. Epub 2015 Apr 30. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015. PMID: 25921033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PET Radiotracers for CNS-Adrenergic Receptors: Developments and Perspectives.Molecules. 2020 Sep 3;25(17):4017. doi: 10.3390/molecules25174017. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32899124 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gottesman M. M.; Fojo T.; Bates S. E. (2002) Multidrug resistance in cancer: Role of ATP-dependent transporters. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2, 48–58. - PubMed
-
- Borst P.; Oude Elferink R. (2002) Mammalian ABC transporters in health and disease. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 71, 537–592. - PubMed
-
- Doze P.; Van Waarde A.; Elsinga P. H.; Hendrikse N. H.; Vaalburg W. (2000) Enhanced cerebral uptake of receptor ligands by modulation of P-glycoprotein function in the blood-brain barrier. Synapse 36, 66–74. - PubMed
-
- Passchier J.; vanWaarde A.; Doze P.; Elsinga P. H.; Vaalburg W. (2000) Influence of P-glycoprotein on brain uptake of [18F]MPPF in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 407, 273–280. - PubMed
-
- Elsinga P. H.; Hendrikse N. H.; Bart J.; Vaalburg W.; van Waarde A. (2004) PET studies on P-glycoprotein function in the blood-brain barrier: How it affects uptake and binding of drugs within the CNS. Curr. Pharm. Des. 10, 1493–1503. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

