Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: promises for diagnosis and treatment of multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 22778862
- PMCID: PMC3369738
- DOI: 10.1021/cn100100e
Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: promises for diagnosis and treatment of multiple sclerosis
Abstract
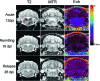
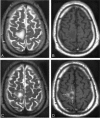
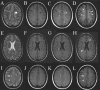
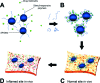
Smart superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) are the most promising candidate for theragnosis (i.e., diagnosis and treatment) of multiple sclerosis. A deep understanding of the dynamics of the in vivo neuropathology of multiple sclerosis can be achieved by improving the efficiency of various medical techniques (e.g., positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance imaging) using multimodal SPIONs. In this Review, recent advances and challenges in the development of smart SPIONs for theragnostic applications are comprehensively described. In addition, critical outlines of emerging developments are provided from the points of view of both clinicians and nanotechnologists.
Keywords: Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles; multimodality; multiple sclerosis; neuropathology; theragnosis.
Figures

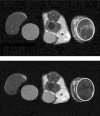
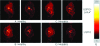

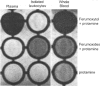
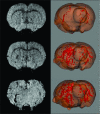
References
-
- Young I. R.; Hall A. S.; Pallis C. A.; Legg N. J.; Bydder G. M.; Steiner R. E. (1981) Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging of the brain in multiple sclerosis. Lancet 2, 1063–1066. - PubMed
-
- Sahraian M. A.; Eshaghi A. (2010) Role of MRI in diagnosis and treatment of multiple sclerosis. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 112, 609–615. - PubMed
-
- McDonald W. I.; Compston A.; Edan G.; Goodkin D.; Hartung H. P.; Lublin F. D. (2001) Recommended diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guidelines from the International Panel on the Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 50, 121–127. - PubMed
-
- Polman C. H.; Reingold S. C.; Edan G.; Filippi M.; Hartung H. P.; Kappos L. (2005) Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2005 revisions to the “McDonald Criteria”. Ann. Neurol. 58, 840–846. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

