Dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase/nitric oxide synthase pathway in liver and kidney: protective effect of cyanidin 3-O-β-D-glucoside on ochratoxin-A toxicity
- PMID: 22778905
- PMCID: PMC3386635
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins4050353
Dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase/nitric oxide synthase pathway in liver and kidney: protective effect of cyanidin 3-O-β-D-glucoside on ochratoxin-A toxicity
Abstract
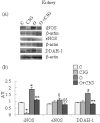
The aim of the present study was to evaluate the effect of long-term cyanidin 3-O-β-D-glucoside (C3G) and/or Ochratoxin A (OTA)-exposure on dimethylarginine dimethylamino hydrolase/nitric oxide synthase (DDAH/NOS) pathway in rats. The experiments were performed in rats supplemented with C3G (1 g/kg feed), OTA (200 ppb), and OTA + C3G. After 4 weeks of daily treatment, liver and kidneys were processed for eNOS, iNOS and DDAH-1 Western blotting, nitrite levels evaluation and DDAH activity determination. Results show that OTA is able to induce iNOS both in kidney and liver, whereas OTA is able to induce eNOS and DDAH-1 overexpression and DDAH activation only in kidney, resulting in increased nitrite levels. In kidney of OTA + C3G fed rats, iNOS, eNOS and DDAH-1 expression were less pronounced compared with those observed in the OTA-treated group. Coherent with the decreased iNOS, eNOS and DDAH-1 expression a decrease in nitrite levels and DDAH activity was observed in the OTA + C3G group. Results demonstrate that C3G is able to counteract the deleterious effects of chronic consumption of OTA and also suggest a possible involvement of iNOS-eNOS-DDAH impairment in OTA nephrocarcinogenity.
Keywords: DDAH; NOS; cyanidin-3-O-β-glucoside; kidney; ochratoxin-A.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Toxicity of ochratoxin a and its modulation by antioxidants: a review.Toxins (Basel). 2013 Oct 11;5(10):1742-66. doi: 10.3390/toxins5101742. Toxins (Basel). 2013. PMID: 24152986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective effect of cyanidin 3-O-beta-D-glucoside on ochratoxin A-mediated damage in the rat.Br J Nutr. 2007 Nov;98(5):937-43. doi: 10.1017/S0007114507756908. Epub 2007 Jun 12. Br J Nutr. 2007. PMID: 17562227
-
Heme oxygenase induction by cyanidin-3-O-beta-glucoside in cultured human endothelial cells.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2007 May;51(5):580-6. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.200600204. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2007. PMID: 17440991
-
Role of ADMA/DDAH-1 and iNOS/eNOS signaling in the gastroprotective effect of tadalafil against indomethacin-induced gastric injury.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Jun;150:113026. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113026. Epub 2022 Apr 28. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 35658250
-
Dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase (DDAH): expression, regulation, and function in the cardiovascular and renal systems.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007 Dec;293(6):H3227-45. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00998.2007. Epub 2007 Oct 12. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17933965 Review.
Cited by
-
Ochratoxin A: Molecular Interactions, Mechanisms of Toxicity and Prevention at the Molecular Level.Toxins (Basel). 2016 Apr 15;8(4):111. doi: 10.3390/toxins8040111. Toxins (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27092524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ochratoxin A and Kidney Oxidative Stress: The Role of Nutraceuticals in Veterinary Medicine-A Review.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Jun 9;14(6):398. doi: 10.3390/toxins14060398. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35737059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toxicity of ochratoxin a and its modulation by antioxidants: a review.Toxins (Basel). 2013 Oct 11;5(10):1742-66. doi: 10.3390/toxins5101742. Toxins (Basel). 2013. PMID: 24152986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Anti-Leukemic Activity of Natural Compounds.Molecules. 2021 May 5;26(9):2709. doi: 10.3390/molecules26092709. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34063044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The use of plant extracts and their phytochemicals for control of toxigenic fungi and mycotoxins.Heliyon. 2020 Oct 22;6(10):e05291. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05291. eCollection 2020 Oct. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 33134582 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Clark H.A., Snedeker S.M. Ochratoxin A: Its cancer risk and potential for exposure. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2006;9:265–296. - PubMed
-
- Jörgensen K., Rasmussen G., Thorup I. Ochratoxin A in Danish cereals 1986–1992 and daily intake by the Danish population. Food Addit. Contam. 1996;13:95–104. - PubMed
-
- Pfohl-Leszkowicz A., Manderville R.A. Ochratoxin A: An overview on toxicity and carcinogenicity in animals and humans. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007;51:61–99. - PubMed
-
- Vrabcheva T., Petkova-Bocharova T., Grosso F., Nikolov I., Chernozemsky I.N., Castegnaro M., Dragacci S. Analysis of ochratoxin A in foods consumed by in habitants from an area with balkan endemic nephropathy: A 1 month follow-up study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004;52:2404–2410. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

