Involvement of inflammation and adverse vascular remodelling in the blood pressure raising effect of repeatedly heated palm oil in rats
- PMID: 22778962
- PMCID: PMC3388444
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/404025
Involvement of inflammation and adverse vascular remodelling in the blood pressure raising effect of repeatedly heated palm oil in rats
Abstract
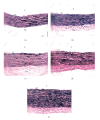
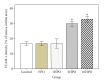
Oil thermoxidation during deep frying generates harmful oxidative free radicals that induce inflammation and increase the risk of hypertension. This study aimed to investigate the effect of repeatedly heated palm oil on blood pressure, aortic morphometry, and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) expression in rats. Male Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into five groups: control, fresh palm oil (FPO), one-time-heated palm oil (1HPO), five-time-heated palm oil (5HPO), or ten-time-heated palm oil (10HPO). Feeding duration was six months. Blood pressure was measured at baseline and monthly using tail-cuff method. After six months, the rats were sacrificed and the aortic arches were dissected for morphometric and immunohistochemical analyses. FPO group showed significantly lower blood pressure than all other groups. Blood pressure was increased significantly in 5HPO and 10HPO groups. The aortae of 5HPO and 10HPO groups showed significantly increased thickness and area of intima-media, circumferential wall tension, and VCAM-1 than other groups. Elastic lamellae were disorganised and fragmented in 5HPO- and 10HPO-treated rats. VCAM-1 expression showed a significant positive correlation with blood pressure. In conclusion, prolonged consumption of repeatedly heated palm oil causes blood pressure elevation, adverse remodelling, and increased VCAM-1, which suggests a possible involvement of inflammation.
Figures



References
-
- Abdullah A, Suondoh MS, Xuan CS, et al. Level of awareness amongst the general public regarding usage of repeatedly heated cooking oil in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. International Medical Journal. 2010;17(4):310–311.
-
- Williams MJA, Sutherland WHF, McCormick MP, De Jong SA, Walker RJ, Wilkins GT. Impaired endothelial function following a meal rich in used cooking fat. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 1999;33(4):1050–1055. - PubMed
-
- Soriguer F, Rojo-Martínez G, Dobarganes MC, et al. Hypertension is related to the degradation of dietary frying oils. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2003;78(6):1092–1097. - PubMed
-
- Leong XF, Aishah A, Nor Aini U, Das S, Jaarin K. Heated palm oil causes rise in blood pressure and cardiac changes in heart muscle in experimental rats. Archives of Medical Research. 2008;39(6):567–572. - PubMed
-
- Harrison DG, Gongora MC, Guzik TJ, Widder J. Oxidative stress and hypertension. Journal of the American Society of Hypertension. 2007;1(1):30–44. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

