What we know and would like to know about CDKL5 and its involvement in epileptic encephalopathy
- PMID: 22779007
- PMCID: PMC3385648
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/728267
What we know and would like to know about CDKL5 and its involvement in epileptic encephalopathy
Abstract
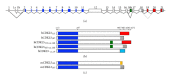
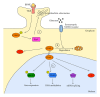
In the last few years, the X-linked serine/threonine kinase cyclin-dependent kinase-like 5 (CDKL5) has been associated with early-onset epileptic encephalopathies characterized by the manifestation of intractable epilepsy within the first weeks of life, severe developmental delay, profound hypotonia, and often the presence of some Rett-syndrome-like features. The association of CDKL5 with neurodevelopmental disorders and its high expression levels in the maturing brain underscore the importance of this kinase for proper brain development. However, our present knowledge of CDKL5 functions is still rather limited. The picture that emerges from the molecular and cellular studies suggests that CDKL5 functions are important for regulating both neuronal morphology through cytoplasmic signaling pathways and activity-dependent gene expression in the nuclear compartment. This paper surveys the current state of CDKL5 research with emphasis on the clinical symptoms associated with mutations in CDKL5, the different mechanisms regulating its functions, and the connected molecular pathways. Finally, based on the available data we speculate that CDKL5 might play a role in neuronal plasticity and we adduce and discuss some possible arguments supporting this hypothesis.
Figures


References
-
- Montini E, Andolfi G, Caruso A, et al. Identification and characterization of a novel serine-threonine kinase gene from the Xp22 region. Genomics. 1998;51(3):427–433. - PubMed
-
- Williamson SL, Giudici L, Kilstrup-Nielsen C, et al. A novel transcript of cyclin-dependent kinase-like 5 (CDKL5) has an alternative C-terminus and is the predominant transcript in brain. Human Genetics. 2011:1–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

