From sequencer to supercomputer: an automatic pipeline for managing and processing next generation sequencing data
- PMID: 22779037
- PMCID: PMC3392054
From sequencer to supercomputer: an automatic pipeline for managing and processing next generation sequencing data
Abstract
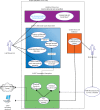
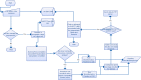
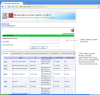
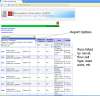
Next Generation Sequencing is highly resource intensive. NGS Tasks related to data processing, management and analysis require high-end computing servers or even clusters. Additionally, processing NGS experiments requires suitable storage space and significant manual interaction. At The Ohio State University's Biomedical Informatics Shared Resource, we designed and implemented a scalable architecture to address the challenges associated with the resource intensive nature of NGS secondary analysis built around Illumina Genome Analyzer II sequencers and Illumina's Gerald data processing pipeline. The software infrastructure includes a distributed computing platform consisting of a LIMS called QUEST (http://bisr.osumc.edu), an Automation Server, a computer cluster for processing NGS pipelines, and a network attached storage device expandable up to 40TB. The system has been architected to scale to multiple sequencers without requiring additional computing or labor resources. This platform provides demonstrates how to manage and automate NGS experiments in an institutional or core facility setting.
Figures


References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
