Electrophysiological effects of single point transcutaneous 650 and 808 nm laser irradiation of rat sciatic nerve: a study of relevance for low-level laser therapy and laser acupuncture
- PMID: 22779441
- PMCID: PMC3423878
- DOI: 10.1089/pho.2012.3248
Electrophysiological effects of single point transcutaneous 650 and 808 nm laser irradiation of rat sciatic nerve: a study of relevance for low-level laser therapy and laser acupuncture
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this study was to evaluate effects of transcutaneous 650 and 808 nm laser irradiation (LI) to a single point overlying rat sciatic nerve; a comparison to four point LI and relevance to the clinical application of low-level laser therapy (LLLT) and laser acupuncture (LA).
Background data: Transcutaneous LI inhibits somatosensory and motor conduction when delivered to four points overlying sciatic nerve; however, effects of the same total energy delivered to a single point over the nerve, equating to laser acupuncture, are undefined.
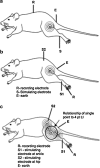
Methods: Transcutaneous 808 nm, 450 mW, (13.5 or 54 J) continuous wave (cw) mode or 650 nm, 35 mW, (1.1 or 4.4 J), cw LI or sham LI, was applied for 30 or 120 sec to a single point overlying the midpoint of rat sciatic nerve. Somatosensory evoked potentials (SSEPs) and compound muscle action potentials (CMAPs) were then recorded after 10 and 20 min, and after 24 and 48 h.
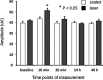
Results: 120 sec of 808 nm LI increased SSEP amplitudes only at 10 min, with no effect of 30 or 120 sec at other time points on SSEPs or on CMAPs. LI 650 nm for 30 or 120 sec did not alter SSEPs or CMAPs at any time point.
Conclusions: Localized transcutaneous 808 LI to a single point overlying sciatic nerve increases SSEP amplitudes when compared with delivery of the same total energy to four points, which causes decreased SSEP amplitudes and conduction block. Therefore, the area and duration of delivery are important, independent variables with implications for clinical delivery of both LLLT and LA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibitory effects of visible 650-nm and infrared 808-nm laser irradiation on somatosensory and compound muscle action potentials in rat sciatic nerve: implications for laser-induced analgesia.J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2011 Jun;16(2):130-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1529-8027.2011.00337.x. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2011. PMID: 21692912
-
No effect of GA-AS (904 nm) laser irradiation on the intact skin of the injured rat sciatic nerve.Lasers Med Sci. 2003;18(2):83-8. doi: 10.1007/s10103-003-0258-6. Lasers Med Sci. 2003. PMID: 12928817
-
Low-level laser irradiation improves functional recovery and nerve regeneration in sciatic nerve crush rat injury model.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 13;9(8):e103348. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0103348. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25119457 Free PMC article.
-
Low-level laser therapy for chronic non-specific low back pain: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.Acupunct Med. 2016 Oct;34(5):328-341. doi: 10.1136/acupmed-2015-011036. Epub 2016 May 20. Acupunct Med. 2016. PMID: 27207675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of photobiomodulation on experimental models of peripheral nerve injury.Lasers Med Sci. 2017 Dec;32(9):2155-2165. doi: 10.1007/s10103-017-2359-7. Epub 2017 Oct 23. Lasers Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 29063472 Review.
Cited by
-
Laser Acupuncture Exerts Neuroprotective Effects via Regulation of Creb, Bdnf, Bcl-2, and Bax Gene Expressions in the Hippocampus.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:7181637. doi: 10.1155/2017/7181637. Epub 2017 Mar 20. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017. PMID: 28408940 Free PMC article.
-
Near-Infrared Photobiomodulation of the Peripheral Nerve Inhibits the Neuronal Firing in a Rat Spinal Dorsal Horn Evoked by Mechanical Stimulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 25;24(3):2352. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032352. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768673 Free PMC article.
-
The Clinical Effects of Laser Acupuncture on Hospitalized Patients With Severe COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial.J Lasers Med Sci. 2023 May 8;14:e14. doi: 10.34172/jlms.2023.14. eCollection 2023. J Lasers Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37583492 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical efficacy of lasers in the management of recurrent aphthous ulcers of oral cavity: a systematic review of randomized control trials.Lasers Med Sci. 2025 Jan 28;40(1):49. doi: 10.1007/s10103-024-04268-9. Lasers Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39870970
-
Effects of different wavelengths of invasive laser acupuncture on chronic non-specific low back pain: a study protocol for a pilot randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Feb 5;22(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05038-6. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33546748 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maiman T. Stimulated optical radiation in ruby. Nature. 1960;187:493.
-
- Baxter G.C. Walsh D.M. Allen J.M. Lowe A.S. Bell A.J. Effects of low intensity infrared laser irradiation upon conduction in the human median nerve in vivo. Exp. Physiol. 1994;79:227–234. - PubMed
-
- Cambier D. Blom K. Witvrouw E. Ollevier G. De Muynck M. Vanderstraeten G. The influence of low intensity infrared laser irradiation on conduction characteristics of peripheral nerve: A randomised, controlled, double blind study on the sural nerve. Lasers Med. Sci. 2000;15:195–200.
-
- Snyder–Mackler L. Bork C.E. Effect of helium-neon laser irradiation on peripheral sensory nerve latency. Phys. Ther. 1988;68:223–225. - PubMed
-
- Naeser M.A. Photobiomodulation of pain in carpal tunnel syndrome: review of seven laser therapy studies. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2006;24:101–110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

