The perception and identification of facial emotions in individuals with autism spectrum disorders using the Let's Face It! Emotion Skills Battery
- PMID: 22780332
- PMCID: PMC3505257
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.2012.02571.x
The perception and identification of facial emotions in individuals with autism spectrum disorders using the Let's Face It! Emotion Skills Battery
Abstract
Background: Although impaired social-emotional ability is a hallmark of autism spectrum disorder (ASD), the perceptual skills and mediating strategies contributing to the social deficits of autism are not well understood. A perceptual skill that is fundamental to effective social communication is the ability to accurately perceive and interpret facial emotions. To evaluate the expression processing of participants with ASD, we designed the Let's Face It! Emotion Skills Battery (LFI! Battery), a computer-based assessment composed of three subscales measuring verbal and perceptual skills implicated in the recognition of facial emotions.
Methods: We administered the LFI! Battery to groups of participants with ASD and typically developing control (TDC) participants that were matched for age and IQ.
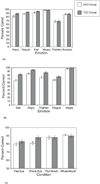
Results: On the Name Game labeling task, participants with ASD (N = 68) performed on par with TDC individuals (N = 66) in their ability to name the facial emotions of happy, sad, disgust and surprise and were only impaired in their ability to identify the angry expression. On the Matchmaker Expression task that measures the recognition of facial emotions across different facial identities, the ASD participants (N = 66) performed reliably worse than TDC participants (N = 67) on the emotions of happy, sad, disgust, frighten and angry. In the Parts-Wholes test of perceptual strategies of expression, the TDC participants (N = 67) displayed more holistic encoding for the eyes than the mouths in expressive faces whereas ASD participants (N = 66) exhibited the reverse pattern of holistic recognition for the mouth and analytic recognition of the eyes.
Conclusion: In summary, findings from the LFI! Battery show that participants with ASD were able to label the basic facial emotions (with the exception of angry expression) on par with age- and IQ-matched TDC participants. However, participants with ASD were impaired in their ability to generalize facial emotions across different identities and showed a tendency to recognize the mouth feature holistically and the eyes as isolated parts.
© 2012 The Authors. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry © 2012 Association for Child and Adolescent Mental Health.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that they have no competing or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Brief report: accuracy and response time for the recognition of facial emotions in a large sample of children with autism spectrum disorders.J Autism Dev Disord. 2014 Sep;44(9):2363-8. doi: 10.1007/s10803-014-2084-z. J Autism Dev Disord. 2014. PMID: 24634064
-
Using computerized games to teach face recognition skills to children with autism spectrum disorder: the Let's Face It! program.J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2010 Aug;51(8):944-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.2010.02258.x. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2010. PMID: 20646129 Clinical Trial.
-
Specific impairment of face-processing abilities in children with autism spectrum disorder using the Let's Face It! skills battery.Autism Res. 2008 Dec;1(6):329-40. doi: 10.1002/aur.56. Autism Res. 2008. PMID: 19360688 Free PMC article.
-
Measuring change in facial emotion recognition in individuals with autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review.Autism. 2020 Oct;24(7):1607-1628. doi: 10.1177/1362361320925334. Epub 2020 Jun 18. Autism. 2020. PMID: 32551983 Free PMC article.
-
Age-related changes in emotion recognition across childhood: A meta-analytic review.Psychol Bull. 2024 Sep;150(9):1094-1117. doi: 10.1037/bul0000442. Psychol Bull. 2024. PMID: 39298231 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring emotional expression recognition in aging adults using the Moving Window Technique.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 18;13(10):e0205341. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0205341. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30335767 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodal Evidence of Atypical Processing of Eye Gaze and Facial Emotion in Children With Autistic Traits.Front Hum Neurosci. 2022 Feb 15;16:733852. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2022.733852. eCollection 2022. Front Hum Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35242018 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental plateau in visual object processing from adolescence to adulthood in autism.Brain Cogn. 2014 Oct;90:124-34. doi: 10.1016/j.bandc.2014.06.004. Epub 2014 Jul 12. Brain Cogn. 2014. PMID: 25019999 Free PMC article.
-
Face Processing and Social Functioning in Pediatric Brain Tumor Survivors.J Pediatr Psychol. 2021 Oct 18;46(10):1267-1275. doi: 10.1093/jpepsy/jsab067. J Pediatr Psychol. 2021. PMID: 34313751 Free PMC article.
-
From early markers to neuro-developmental mechanisms of autism.Dev Rev. 2014 Sep;34(3):189-207. doi: 10.1016/j.dr.2014.05.003. Dev Rev. 2014. PMID: 25187673 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adolphs R, Sears L, Piven J. Abnormal processing of social information from faces in autism. Journal of Cogntiive Neuroscience. 2001;13:232–240. - PubMed
-
- Bolte S, Poustka F. The recognition of facial affect in autistic and schizophrenic subjects and their first-degree relatives. Psychological Medicine. 2003;33:907–915. - PubMed
-
- Burack JA, Iarocci G, Flanagan TD, Bowler DM. On mosaics and melting pots: conceptual considerations of comparison and matching strategies. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders. 2004;34(1):65–73. - PubMed
-
- Campbell R, Lawrence K, Mandy W, Mitra C, Jeyakuma L, Skuse D. Meanings in motion and faces: developmental associations between the processing of intention from geometrical animations and gaze detection accuracy. Developmental Psychopathology. 2006;18:99–118. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

