The flavonoid morin restores blood pressure and lipid metabolism in DOCA-salt hypertensive rats
- PMID: 22781105
- PMCID: PMC6837552
- DOI: 10.1179/1351000212Y.0000000015
The flavonoid morin restores blood pressure and lipid metabolism in DOCA-salt hypertensive rats
Abstract
Objective: This study was undertaken to investigate the antihypertensive and antihyperlipedimic potential of morin against deoxycorticosterone acetate (DOCA)-salt hypertensive rats.
Methods: Hypertension was induced in uninephrectomized rats (UNX) by weekly twice subcutaneous injection of DOCA (25 mg/kg) and 1% NaCl in the drinking water for six consecutive weeks. Morin (50 mg/kg) was administered to DOCA-salt rats orally using an intragastric tube daily for a period of 6 weeks.
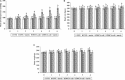
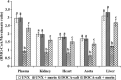
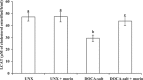
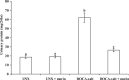
Results: The DOCA-salt hypertensive rats showed significant elevation in mean arterial pressure (MAP), heart rate (HR) and reduction in body weight. A significant increase in the concentrations of plasma and tissue (liver, kidney, heart, and aorta) lipids such as total cholesterol, triglycerides, free fatty acids, phospholipids, plasma low-density and very low-density lipoproteins cholesterol, and a decrease in the concentration of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol were noticed in DOCA-salt hypertensive rats. Also, the levels of urinary protein and the activity of 3-hydroxy 3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase in the plasma and tissues were increased, and lecithin cholesterol acyl transferase activity in the plasma was decreased in DOCA-salt rats. Morin supplementation (50 mg/kg) throughout the experimental period restored all the above parameters significantly.
Conclusion: Morin has a potential role in attenuating severe hypertension and hyperlipedimia.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Morin attenuates blood pressure and oxidative stress in deoxycorticosterone acetate-salt hypertensive rats: a biochemical and histopathological evaluation.Metabolism. 2012 Aug;61(8):1087-99. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2011.12.012. Epub 2012 Mar 3. Metabolism. 2012. PMID: 22386933
-
Diosmin, a bioflavonoid reverses alterations in blood pressure, nitric oxide, lipid peroxides and antioxidant status in DOCA-salt induced hypertensive rats.Eur J Pharmacol. 2012 Mar 15;679(1-3):81-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.12.040. Epub 2012 Jan 12. Eur J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22266490
-
Effect of morin, a flavonoid against DOCA-salt hypertensive rats: a dose dependent study.Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2012 Jun;2(6):443-8. doi: 10.1016/S2221-1691(12)60073-2. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2012. PMID: 23569947 Free PMC article.
-
Antihyperlipidemic effect of Melothria maderaspatana leaf extracts on DOCA-salt induced hypertensive rats.Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2012 Jun;5(6):434-9. doi: 10.1016/S1995-7645(12)60074-1. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2012. PMID: 22575974
-
Antihypertensive effects of the essential oil of Alpinia zerumbet and its main constituent, terpinen-4-ol, in DOCA-salt hypertensive conscious rats.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2003 Jun;17(3):323-30. doi: 10.1046/j.1472-8206.2003.00150.x. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12803571
Cited by
-
Antioxidant Phytochemicals for the Prevention and Treatment of Chronic Diseases.Molecules. 2015 Nov 27;20(12):21138-56. doi: 10.3390/molecules201219753. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 26633317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phytochemicals as Potential Lead Molecules against Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(32):5199-5221. doi: 10.2174/0109298673275501231213063902. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38213177 Review.
-
The effect of Opuntia ficus-indica juice supplementation on oxidative stress, cardiovascular parameters, and biochemical markers following yo-yo Intermittent recovery test.Food Sci Nutr. 2017 Dec 6;6(2):259-268. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.529. eCollection 2018 Mar. Food Sci Nutr. 2017. PMID: 29564091 Free PMC article.
-
Morin Ameliorates Myocardial Injury in Diabetic Rats via Modulation of Autophagy, Apoptosis, Inflammation, and Oxidative Stress.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024 Dec 27;17:4867-4882. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S476867. eCollection 2024. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024. PMID: 39742288 Free PMC article.
-
Nitrooleic Acid Attenuates Lipid Metabolic Disorders and Liver Steatosis in DOCA-Salt Hypertensive Mice.PPAR Res. 2015;2015:480348. doi: 10.1155/2015/480348. Epub 2015 Mar 11. PPAR Res. 2015. PMID: 25861250 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization Available from http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs317/en/ [accessed 31 January 2011].
-
- Chapman MJ, Sposito AC. Hypertension and dyslipidemia in obesity and insulin resistance: pathophysiology, impact on atherosclerotic disease and pharmacotherapy. Pharmacol Ther 2008;117:354–73. - PubMed
-
- Wong ND, Lopez V, Tang S, Williams GR. Prevalence, treatment, and control of combined hypertension and hypercholesterolemia in the United States. Am J Cardiol 2006;98:204–8. - PubMed
-
- Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL Jr, et al. Seventh report of the Joint National Committee on prevention, detection, evaluation, treatment of high blood pressure. Hypertens 2003;42:1206–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
