Moringa oleifera hydroethanolic extracts effectively alleviate acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in experimental rats through their antioxidant nature
- PMID: 22781444
- PMCID: PMC6268890
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules17078334
Moringa oleifera hydroethanolic extracts effectively alleviate acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in experimental rats through their antioxidant nature
Abstract
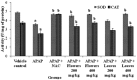
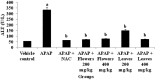
The aim of the study was to investigate the in vitro antioxidant properties Moringa oleifera Lam. (MO) extracts and its curative role in acetaminophen (APAP)-induced toxic liver injury in rats caused by oxidative damage. The total phenolic content and antioxidant properties of hydroethanolic extracts of different MO edible parts were investigated by employing an established in vitro biological assay. In the antihepatotoxic study, either flowers or leaves extract (200 mg/kg or 400 mg/kg, i.p) were administered an hour after APAP administration, respectively. N-Acetylcysteine was used as the positive control against APAP-induced hepatotoxicity. The levels of liver markers such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and the levels of oxidative damage markers including malondialdehyde (MDA), 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) protein adduct, reduced glutathione (GSH), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) were analysed and compared between experimental groups. Among MO edible parts the flower extracts contain the highest total phenolic content and antioxidant capacity, followed by leaves extract. The oxidative marker MDA, as well as 4-HNE protein adduct levels were elevated and GSH, SOD and CAT were significantly decreased in groups treated with hepatotoxin. The biochemical liver tissue oxidative markers measured in the rats treated with MO flowers and leaves hydroethanolic extracts showed a significant (p < 0.05) reduction in the severity of the liver damage. The results of this study strongly indicate the therapeutic properties of MO hydroethanolic extracts against acute liver injury and thereby scientifically support its traditional use.
Figures

References
-
- Choi J.H., Kim D.W., Yun N., Choi J.S., Islam M.N., Kim Y.S., Lee S.M. Protective effects of hyperoside against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver damage in mice. J. Nat. Prod. 2011;74:1055–1060. - PubMed
-
- Huang B., Ban X., He J., Tong J., Tian J., Wang Y. Hepatoprotective and antioxidant activity of ethanolic extracts of edible lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.) leaves. Food Chem. 2010;120:873–878. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.11.020. - DOI
-
- Fakurazi S., Hairuszah I., Nanthini U. Moringa oleifera Lam prevents acetaminophen induced liver injury through restoration of glutathione level. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008;46:2611–2615. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

