Baseline levels of soluble CD14 and CD16+56- natural killer cells are negatively associated with response to interferon/ribavirin therapy during HCV-HIV-1 coinfection
- PMID: 22782948
- PMCID: PMC3501153
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jis434
Baseline levels of soluble CD14 and CD16+56- natural killer cells are negatively associated with response to interferon/ribavirin therapy during HCV-HIV-1 coinfection
Abstract
Disease progression of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) is associated with immune activation. Activation indices are higher during coinfection of hepatitis C virus (HCV) and HIV. The effect of immune activation on interferon α (IFN-α) therapy response is unknown. We evaluated soluble CD14 (sCD14) and natural killer (NK)-cell subsets at baseline, and during pegIFN-α2a/ribavirin therapy in HCV-HIV coinfection. The sCD14 level increased during therapy. Baseline sCD14 positively correlated with baseline HCV level and CD16(+)56(-) NK-cell frequency, and both sCD14 and CD16(+)56(-) NK cells correlated negatively with magnitude of HCV decline. IL28B genotype was associated with therapy response but not sCD14 or CD16(+)56(-) NK frequency. Markers of innate immune activation predict poor host response to IFN-α-based HCV therapy during HCV-HIV coinfection.
Figures
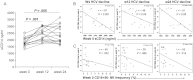
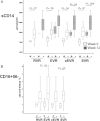
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- I01 BX001894/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- UM1 AI069501/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK068361/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI082151/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 069501/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI073963/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 36219/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI069195/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 68636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI036219/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069501/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI066957/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 082151/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 68634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI067094/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI-068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

