Effects of a single nucleotide polymorphism in the chicken NK-lysin gene on antimicrobial activity and cytotoxicity of cancer cells
- PMID: 22783018
- PMCID: PMC3409721
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1209161109
Effects of a single nucleotide polymorphism in the chicken NK-lysin gene on antimicrobial activity and cytotoxicity of cancer cells
Abstract
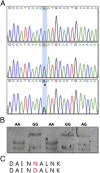
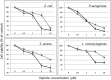
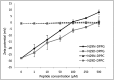
NK-lysin is an effector protein of the innate immune system and an important component of host protection. We isolated a SNP in the NK-lysin coding sequence among different chicken breeds. This A to G substitution at the position 271 nucleotide in the ORF results in an Asn (N) to Asp (D) amino acid alteration. We synthesized two 30-aa peptides (N29N and N29D) to compare the biological activity of the helix 2-loop-helix 3 region of NK-lysin resulting from the polymorphic gene. Both peptides were found to be cytotoxic in bacteria and tumor cell cultures at micromolar concentrations. The N29N peptide, however, exhibited greater antibacterial and anticancer activity than the N29D peptide. Circular dichroism spectroscopy of the two peptides in negatively charged single unilamellar vesicles showed spectra typical of α-helical peptides. The helical profile of N29D was reduced substantially compared with that of N29N. However, no structural change was observed in neutral vesicles. ζ-Potential measurements of liposomes incubated with increasing peptide concentrations allowed surface charge neutralization with a negatively charged lipid, but not with a zwitterionic lipid. This result suggests that a difference in electrostatic interaction between lipid membranes and the helical peptides results from the polymorphic gene and is subsequently an important factor in cell lytic activity of variant NK-lysin peptides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mapping and genotypic analysis of the NK-lysin gene in chicken.Genet Sel Evol. 2014 Jul 7;46(1):43. doi: 10.1186/1297-9686-46-43. Genet Sel Evol. 2014. PMID: 25001618 Free PMC article.
-
Chicken NK-lysin is an alpha-helical cationic peptide that exerts its antibacterial activity through damage of bacterial cell membranes.Poult Sci. 2014 Apr;93(4):864-70. doi: 10.3382/ps.2013-03670. Poult Sci. 2014. PMID: 24706963
-
Effect of a single polymorphism in the Japanese quail NK-lysin gene on antimicrobial activity.Anim Sci J. 2016 Jan;87(1):143-6. doi: 10.1111/asj.12515. Epub 2015 Oct 16. Anim Sci J. 2016. PMID: 26472627
-
NK-lysin, structure and function of a novel effector molecule of porcine T and NK cells.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1996 Nov;54(1-4):123-6. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2427(96)05677-2. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1996. PMID: 8988855 Review.
-
Using genomics to identify novel antimicrobials.Rev Sci Tech. 2016 Apr;35(1):95-103. doi: 10.20506/rst.35.1.2420. Rev Sci Tech. 2016. PMID: 27217171 Review.
Cited by
-
From oncolytic peptides to oncolytic polymers: A new paradigm for oncotherapy.Bioact Mater. 2023 Aug 14;31:206-230. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.08.007. eCollection 2024 Jan. Bioact Mater. 2023. PMID: 37637082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mapping and genotypic analysis of the NK-lysin gene in chicken.Genet Sel Evol. 2014 Jul 7;46(1):43. doi: 10.1186/1297-9686-46-43. Genet Sel Evol. 2014. PMID: 25001618 Free PMC article.
-
AvBD1 nucleotide polymorphisms, peptide antimicrobial activities and microbial colonisation of the broiler chicken gut.BMC Genomics. 2017 Aug 18;18(1):637. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-4034-6. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28821240 Free PMC article.
-
Response of immunoglobulin M in gut mucosal immunity of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) infected with Aeromonas hydrophila.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 17;13:1037517. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1037517. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36466906 Free PMC article.
-
NKLP27: a teleost NK-lysin peptide that modulates immune response, induces degradation of bacterial DNA, and inhibits bacterial and viral infection.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 2;9(9):e106543. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106543. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25180858 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boman HG. Antimicrobial peptides. Chairman’s opening remarks. Ciba Found Symp. 1994;186:1–4. - PubMed
-
- Wang Q, Wang Y, Xu P, Liu Z. NK-lysin of channel catfish: Gene triplication, sequence variation, and expression analysis. Mol Immunol. 2006;43:1676–1686. - PubMed
-
- Gansert JL, et al. Human NKT cells express granulysin and exhibit antimycobacterial activity. J Immunol. 2003;170:3154–3161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

