Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids promote liver regeneration after 90% hepatectomy in rats
- PMID: 22783054
- PMCID: PMC3391767
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i25.3288
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids promote liver regeneration after 90% hepatectomy in rats
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the effectiveness of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid (ω-3 PUFA) administration on liver regeneration after 90% partial hepatectomy (PH) in rats.
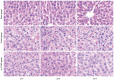
Methods: ω-3 PUFAs were intravenously injected in the ω-3 PUFA group before PH surgery. PH, sparing only the caudate lobe, was performed in both the control and the ω-3 PUFA group. Survival rates, liver weight/body weight ratios, liver weights, HE staining, transmission electron microscope imaging, nuclear-associated antigen Ki-67, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and signal transduction were evaluated to analyze liver regeneration.
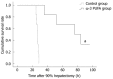
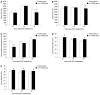
Results: All rats in the control group died within 30 h after hepatectomy. Survival rates in the ω-3 PUFA group were 20/20 at 30 h and 4/20 1 wk after PH. Liver weight/body weight ratios and liver weights increased significantly in the ω-3 PUFA group. The structure of sinusoidal endothelial cells and space of Disse was greatly restored in the ω-3 PUFA group compared to the control group after PH. In the ω-3 PUFA group, interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-10 levels were significantly increased whereas IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α levels were dramatically decreased. In addition, activation of protein kinase B (Akt) and of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling pathway were identified at an earlier time after PH in the ω-3 PUFA group.
Conclusion: Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids may prevent acute liver failure and promote liver regeneration after 90% hepatectomy in rats.
Keywords: Inflammatory cytokines; Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids; Signaling pathways; Survival rate.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids prevent progression of liver fibrosis and promote liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy in cirrhotic rats.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Nov;23(22):10151-10160. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201911_19585. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31799687
-
Effects of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on rat livers after partial hepatectomy via LKB1-AMPK signaling pathway.Transplant Proc. 2011 Dec;43(10):3604-12. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2011.10.045. Transplant Proc. 2011. PMID: 22172813
-
Magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate inhibits inflammatory response through STAT3 pathway to protect remnant liver function.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Nov 21;21(43):12370-80. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i43.12370. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26604644 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on liver function and inflammatory reaction in patients undergoing hepatectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized control trials.Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Apr;13(4):375-384. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2019.1578648. Epub 2019 Feb 22. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30791756
-
n-3 Polyunsaturated fatty acids for the management of alcoholic liver disease: A critical review.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(sup1):S116-S129. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1544542. Epub 2018 Dec 22. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30580553 Review.
Cited by
-
Rat hepatocytes weighted gene co-expression network analysis identifies specific modules and hub genes related to liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 17;9(4):e94868. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0094868. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24743545 Free PMC article.
-
Co-Enzyme Q10 and n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplementation Reverse Intermittent Hypoxia-Induced Growth Restriction and Improved Antioxidant Profiles in Neonatal Rats.Antioxidants (Basel). 2017 Dec 16;6(4):103. doi: 10.3390/antiox6040103. Antioxidants (Basel). 2017. PMID: 29258174 Free PMC article.
-
Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Intake to Regulate Helicobacter pylori-Associated Gastric Diseases as Nonantimicrobial Dietary Approach.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:712363. doi: 10.1155/2015/712363. Epub 2015 Aug 3. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26339635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Omega-3 fatty acid supplementation does not influence liver regeneration in rats after partial hepatectomy.Clin Exp Hepatol. 2018 Dec;4(4):253-259. doi: 10.5114/ceh.2018.80127. Epub 2018 Dec 3. Clin Exp Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 30603673 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schibler U. Circadian rhythms. Liver regeneration clocks on. Science. 2003;302:234–235. - PubMed
-
- Michalopoulos GK, DeFrances MC. Liver regeneration. Science. 1997;276:60–66. - PubMed
-
- Makino H, Togo S, Kubota T, Morioka D, Morita T, Kobayashi T, Tanaka K, Shimizu T, Matsuo K, Nagashima Y, et al. A good model of hepatic failure after excessive hepatectomy in mice. J Surg Res. 2005;127:171–176. - PubMed
-
- Myronovych A, Murata S, Chiba M, Matsuo R, Ikeda O, Watanabe M, Hisakura K, Nakano Y, Kohno K, Kawasaki T, et al. Role of platelets on liver regeneration after 90% hepatectomy in mice. J Hepatol. 2008;49:363–372. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

