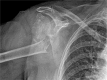
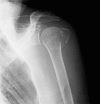
Indices of risk assessment of fracture of the proximal humerus
- PMID: 22783334
- PMCID: PMC3392680
Indices of risk assessment of fracture of the proximal humerus
Abstract
Osteoporotic fractures are now a social problem for incidence and costs. Fractures of the proximal humerus events are frequent and constantly increasing. It is estimated that they are 20% of all osteoporotic fractures. Bone densitometry in most cases underestimates the real humeral bone density.There is little information about osteoporotic changes in the proximal humerus and their association with the cortical thickness of the humeral shaft. The ratio between the thickness of the cortical and the total diameter of the humeral diaphysis is the cortical index. Fracture risk limit value is 0.231. Convinced of the need to quantify in a reproducible way the real local humerus bone density, we performed a comparative evaluation of bone density of the humerus and femur in patients admitted to our clinic for fractures of the humerus and femur.We evaluated 28 women treated surgically for a fragility fracture of the proximal humerus or femur neck in 2010. All cortical index obtained were lower than the limit for fracture risk set at 0.231, so the IC was more predictive of neck medial fractures of the femur than had DEXA and the U.S. The information about the cortical index may provide a simple way of determining the bone quality of the proximal humerus and of facilitating decision-making in the surgical treatment of patients with fractures of the humerus. So we want to emphasize the importance of therapy for osteoporosis even in patients with fractures of the proximal humerus, which often have not critical densitometric values of femur or column, but they are at risk of new fractures.
Keywords: cortical humerus index; osteoporosis; prediction.
Figures
References
-
- Dalle Carbonare L, Giannini S. Bone microarchitecture as an important determinant of bone strength. J Endocrinol Invest. 2004 Jan;27(1):99–105. - PubMed
-
- Calvo E, de Miguel I, de la Cruz JJ, Lopez-Martin N. Percutaneous fixation of displaced proximal humeral fractures: indications based on the correlation between clinical and radiographic results. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007;16(6):774–781. - PubMed
-
- Biggi F, Carnielli F, D’Antimo C. Il trattamento delle fratture prossimali di omero con inchiodamento endomidollare. G.I.O.T. 2007;33:192–19.
-
- Krappinger D, Roth T, Gschwentner M, Suckert A, Blauth M, Hengg C, Kralinger F. Preoperative assessment of the cancellous bone mineral density of the proximal humerus using CT data. Skeletal Radiol. 2011 Apr 21; - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources