The initiative on hip fractures of the Veneto Region
- PMID: 22783336
- PMCID: PMC3392679
The initiative on hip fractures of the Veneto Region
Abstract
Objective: to assess the prevalence of the most relevant environmental and individual risk factors in subjects with a recent hip fracture was the aim of this observational study promoted by the Health Authorities of the Regione Veneto (Italy).
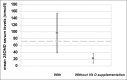
Methods: patients aged > 60 years of both genders with a recent hip fracture not associated with malignancies, were administered questionnaires on dietary habits, sun exposure, disability score. A complete family, pharmacological and pathology history was collected together with previous falls, details of the fracture index, anthropometric data. In a subgroup of patients blood was taken for the measurements of serum 25 hydroxy-vitamin D (25OHD).
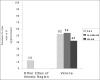
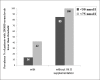
Results: the study includes 704 patients (573 women and 131 men). Mean age was 81±8 years (range 60-102). Severe pre-fracture disability was a common feature (58%) associated with multiple co-morbidities (84%), more frequently cardiovascular and neurological diseases, and specific medications. In a large proportion (86%) of the patients environmental or individual risk factors for falling were found. Vitamin D insufficiency was quite common, particularly in the regional Health Districts were strategies for preventing vitamin D deficiency were not implemented. Only a small proportion (17%) of the study population had been evaluate and treated for osteoporosis.
Conclusions: in senile patients with a recent hip fracture pre-existing disability, multiple co-morbidities, high risk of falling and inadequate intake of calcium and vitamin D was quite common. Community and case-finding interventions are highly warranted.
Keywords: co-morbidities; disability; fall; hip fracture; vitamin D.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Risk factors for hip fracture in elderly persons].Reumatismo. 2010 Oct-Dec;62(4):273-82. doi: 10.4081/reumatismo.2010.273. Reumatismo. 2010. PMID: 21253621 Italian.
-
Effect of oral vitamin D2 yearly bolus on hip fracture risk in elderly women: a community primary prevention study.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2004 Dec;16(6):432-6. doi: 10.1007/BF03327397. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2004. PMID: 15739592 Clinical Trial.
-
Prevention of hip fractures by correcting calcium and vitamin D insufficiencies in elderly people.Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 1996;103:75-8; discussion 79-80. doi: 10.3109/03009749609103753. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 1996. PMID: 8966494 Clinical Trial.
-
Calcium and vitamin D nutrition and bone disease of the elderly.Public Health Nutr. 2001 Apr;4(2B):547-59. doi: 10.1079/phn2001140. Public Health Nutr. 2001. PMID: 11683549 Review.
-
[Vitamin D in geriatric patients].Internist (Berl). 2020 Jun;61(6):535-540. doi: 10.1007/s00108-020-00803-2. Internist (Berl). 2020. PMID: 32458373 Review. German.
References
-
- International Osteoporosis Foundation. IOF; 2002. Osteoporosis in the European Community: a call for action.
-
- Johnell O. The socioeconomic burden of fractures: today and in the 21st century. Am J Med. 1997;103:20S–25S. discussion 25S–26S. - PubMed
-
- Rossini M, Piscitelli P, Fitto F, Camboa P, Angeli A, Guida G, Adami S. Incidenza e costi delle fratture di femore in Italia. Reumatismo. 2005;57:97–102. - PubMed
-
- Piscitelli P, Gimigliano F, Gatto S, Marinelli A, Gimigliano A, Marinelli P, et al. Hip fractures in Italy: 2000–2005 extension study. Osteoporos Int. 2010;21:1323–30. - PubMed
-
- Piscitelli P, Iolascon G, Gimigliano F, Muratore M, Camboa P, Borgia O, et al. Incidence and costs of hip fractures compared to acute myocardial infarction in the Italian population: a 4-year survey. Osteoporos Int. 2007;18:211–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources