LPS-induced nuclear translocation of RhoA is dependent on NF-κB in the human lung cancer cell line A549
- PMID: 22783434
- PMCID: PMC3392595
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2012.667
LPS-induced nuclear translocation of RhoA is dependent on NF-κB in the human lung cancer cell line A549
Abstract
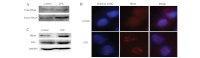
RhoA, an extensively studied member of the Rho GTPase family, has been identified as a mediator of pro-inflammatory responses and aggressive carcinogenesis. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is known to be a potent stimulator of inflammatory cytokine production. LPS is able to alter the activity of RhoA and the subcellular distribution of RhoA is altered according to its activity. In this study, we investigated a possible link between RhoA and the LPS/nuclear factor (NF)-κB signaling pathway. In the present study, western blotting and pull-down and immunofluorescence assays were performed to investigate the activity of RhoA in A549 cells following LPS stimulation. The results showed that LPS was able to activate RhoA. Furthermore, western blotting and an immunofluorescence assay were carried out to investigate the nuclear expression of RhoA in A549 cells following LPS stimulation. The results indicated that LPS triggers the nuclear translocation of RhoA. Furthermore, western blotting, NF-κB small interfering RNA (siRNA) transfection and an immunofluorescence assay were performed to investigate the role of NF-κB in LPS-induced RhoA nuclear translocation in A549 cells. The results showed that LPS-induced RhoA nuclear translocation was inhibited by NF-κB depletion in A549 cells. RhoA and NF-κB siRNA transfection, western blotting and ELISA were carried out to investigate the role of RhoA in the LPS-induced secretion of interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-8 in A549 cells. The depletion of RhoA using RhoA siRNA decreased the LPS-induced secretion of IL-6 and IL-8, similar to the effect of NF-κB depletion. These results demonstrate that LPS is able to activate RhoA and trigger its nuclear translocation, which is dependent on NF-κB, and that RhoA plays a significant role in the LPS/NF-κB signaling pathway.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Involvement of nuclear factor-kB activation through RhoA/Rho-kinase pathway in LPS-induced IL-8 production in human cervical stromal cells.Mol Hum Reprod. 2007 Mar;13(3):181-7. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gal113. Epub 2007 Jan 16. Mol Hum Reprod. 2007. PMID: 17227815
-
GEF-H1-RhoA signaling pathway mediates LPS-induced NF-κB transactivation and IL-8 synthesis in endothelial cells.Mol Immunol. 2012 Feb;50(1-2):98-107. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2011.12.009. Epub 2012 Jan 4. Mol Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22226472
-
1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 Ameliorates Seawater Aspiration-Induced Lung Injury By Inhibiting The Translocation Of NF-κB and RhoA.Inflammation. 2017 Jun;40(3):832-839. doi: 10.1007/s10753-017-0527-3. Inflammation. 2017. PMID: 28161733 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of p300 alleviates LPS-induced inflammatory injuries through regulation of RhoA/ROCK/NF-κB pathways in A549 cells.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Jan;97:369-374. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.10.104. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29091886
-
Rho-kinase inhibitor Y-27632 downregulates LPS-induced IL-6 and IL-8 production via blocking p38 MAPK and NF-κB pathways in human gingival fibroblasts.J Periodontol. 2018 Jul;89(7):883-893. doi: 10.1002/JPER.17-0571. J Periodontol. 2018. PMID: 29630729
Cited by
-
Oncogenic K-Ras and loss of Smad4 mediate invasion by activating an EGFR/NF-κB Axis that induces expression of MMP9 and uPA in human pancreas progenitor cells.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 5;8(12):e82282. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082282. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24340014 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of Boric Acid Taken in Different Ways on Experimental Ovarian İschemia and Reperfusion.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2024 Jun;202(6):2730-2743. doi: 10.1007/s12011-023-03871-1. Epub 2023 Sep 25. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2024. PMID: 37743417
-
Post-Translational Modification and Subcellular Distribution of Rac1: An Update.Cells. 2018 Dec 11;7(12):263. doi: 10.3390/cells7120263. Cells. 2018. PMID: 30544910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angelica polysaccharide promotes proliferation and osteoblast differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by regulation of long non-coding RNA H19: An animal study.Bone Joint Res. 2019 Aug 2;8(7):323-332. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.87.BJR-2018-0223.R2. eCollection 2019 Jul. Bone Joint Res. 2019. PMID: 31463041 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview of Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: Review on Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Response.Eurasian J Med. 2022 Dec;54(Suppl1):62-65. doi: 10.5152/eurasianjmed.2022.22293. Eurasian J Med. 2022. PMID: 36655447 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Price LS, Collard JG. Regulation of the cytoskeleton by Rho-family GTPases: implications for tumour cell invasion. Semin Cancer Biol. 2001;11:167–173. - PubMed
-
- Sotiropoulos A, Gineitis D, Copeland J, Treisman R. Signal-regulated activation of serum response factor is mediated by changes in actin dynamics. Cell. 1999;98:159–169. - PubMed
-
- Kjoller L, Hall A. Signaling to Rho GTPases. Exp Cell Res. 1999;253:166–179. - PubMed
-
- Narumiya S. The small GTPase Rho: cellular functions and signal transduction. J Biochem. 1996;120:215–228. - PubMed
-
- Hall A. The cellular functions of small GTP-binding proteins. Science. 1990;249:635–640. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
