Eosinophilic ulcer of oral mucosa: a case report
- PMID: 22783449
- PMCID: PMC3392661
Eosinophilic ulcer of oral mucosa: a case report
Abstract
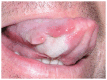
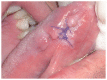
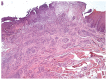
Eosinophilic Ulcer (EU) is a rare self-limiting chronic benign lesion of the oral mucosa with pathogenesis still unclear, however it may resemble malignancies, traumatic ulcerations and some infections such as deep fungal infections, tuberculosis and primary syphilis. This is a case report of a patient with EU in the lateral border of the tongue with no history of associated trauma and refractory to treatment with drugs. The ulcer rapidly healed after an incisional biopsy and the definite diagnosis was achieved only combining histologic findings and the clinical follow-up.
Keywords: eosinophilic ulcer; oral mucosa; ulcerative eosinophilic granuloma.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Eosinophilic ulcer of the tongue: a rare and confusing clinical entity.BMJ Case Rep. 2015 Apr 2;2015:bcr2015210107. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2015-210107. BMJ Case Rep. 2015. PMID: 25837658 Free PMC article.
-
Eosinophilic ulcer of the tongue masquerading as malignant ulcer: An unexplored distinct pathology.J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2017 May-Aug;21(2):321. doi: 10.4103/jomfp.JOMFP_93_16. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28932055 Free PMC article.
-
Traumatic ulcerative granuloma with stromal eosinophilia - clinical case report, literature review, and differential diagnosis.World J Surg Oncol. 2019 Nov 9;17(1):184. doi: 10.1186/s12957-019-1736-z. World J Surg Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31706333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eosinophilic ulcer of the oral mucosa: An update on clinicopathologic features, pathogenesis, and management.Int J Dermatol. 2022 Nov;61(11):1359-1363. doi: 10.1111/ijd.15986. Epub 2021 Nov 23. Int J Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 34812492 Review.
-
Traumatic ulcerative granuloma with stromal eosinophilia.Arch Iran Med. 2014 Jan;17(1):91-4. Arch Iran Med. 2014. PMID: 24444070
Cited by
-
Chronic idiopathic neutropenia: A periodontist's diagnosis.J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2020 Mar-Apr;24(2):173-177. doi: 10.4103/jisp.jisp_149_19. Epub 2020 Jan 27. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2020. PMID: 32189847 Free PMC article.
-
Eosinophilic ulcer of the tongue: a rare and confusing clinical entity.BMJ Case Rep. 2015 Apr 2;2015:bcr2015210107. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2015-210107. BMJ Case Rep. 2015. PMID: 25837658 Free PMC article.
-
Eosinophilic ulcer of the tongue in an 80-year-old Iranian woman after a psychologically stressful event.BMJ Case Rep. 2013 Feb 14;2013:bcr2012008487. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2012-008487. BMJ Case Rep. 2013. PMID: 23417388 Free PMC article.
-
Oral eosinophilic or traumatic ulcer: A case report and brief review.Natl J Maxillofac Surg. 2015 Jul-Dec;6(2):237-40. doi: 10.4103/0975-5950.183854. Natl J Maxillofac Surg. 2015. PMID: 27390505 Free PMC article.
-
Eosinophilic ulcer of the tongue--Case report.An Bras Dermatol. 2015 May-Jun;90(3 Suppl 1):88-90. doi: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20153600. An Bras Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 26312683 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Regezi JA, Zarbo RJ, Daniels TE, Greenspan JS. Oral traumatic granuloma. Characterization of the cellular infiltrate. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1993;75(6):723–727. - PubMed
-
- Lourenço SV, Silva MA, Nico MM. An ulcer on the lip. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2005;30(2):199–200. - PubMed
-
- Segura S, Romero D, Mascaró JM, Jr, Colomo L, Ferrando J, Estrach T. Eosinophilic ulcer of the oral mucosa: another histological simulator of CD30+ lymphoproliferative disorders. Br J Dermatol. 2006;155(2):460–463. - PubMed
-
- Hirshberg A, Amariglio N, Akrish S, Yahalom R, Rosenbaum H, Okon E, et al. Traumatic ulcerative granuloma with stromal eosinophilia: a reactive lesion of the oral mucosa. Am J Clin Pathol. 2006;126(4):522–529. - PubMed
-
- Segura S, Pujol RM. Eosinophilic ulcer of the oral mucosa: a distinct entity or a non-specific reactive pattern? Oral Dis. 2008;14(4):287–295. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
