Surgical protocol in patients at risk for bisphosphonate osteonecrosis of the jaws: clinical use of serum telopetide CTX in preventive monitoring of surgical risk
- PMID: 22783453
- PMCID: PMC3392664
Surgical protocol in patients at risk for bisphosphonate osteonecrosis of the jaws: clinical use of serum telopetide CTX in preventive monitoring of surgical risk
Abstract
Aim: This study investigates the association between cross linked C-terminal telopetide test (CTX) and individual surgical risk of osteonecrosis in patients taking oral bisphosphonates.
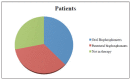
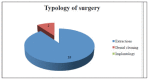
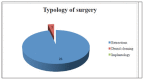
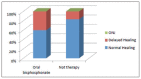
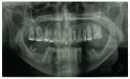
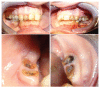
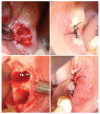
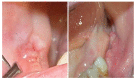
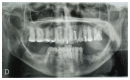
Materials and methods: 32 patients receiving bisphosphonate were treated surgically. Patients were divided into three groups according to type of drug administrated and were subjected to a treatment of oral surgery, such as simple tooth extractions and extraction of all residual teeth of the oral cavity, upon evaluation of CTX values and antibiotic prophylaxis.
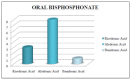
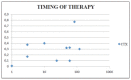
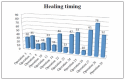
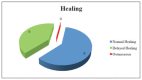
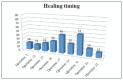
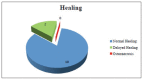
Results: Within the sample of 32 patients, 12 patients had been treated with bisphosphonates for several years and none developed osteonecrosis of the jaw upon surgery. As for CTX, patients treated with oral bisphosphonates showed a mean value of serum Ctelopetides of 0.2869 ng/ml. The mean value of CTX did not differ significantly between patients taking oral bisphosphonates and healthy patients not treated with bisphosphonates.
Conclusion: None of the patients subjected to preoperative antibiotic prophylaxis developed osteonecrosis of the jaw after surgery. The pharmacological and surgical protocol tested appeared valid in the prevention of osteonecrosis associated to bisphosphonates.
Keywords: bisphosphonate; osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ); serum C-terminal C-telopeptide (CTX).
Figures
References
-
- Rutkowsi JL, Johnson DA, Smith DM. Clinical concerns of alendronate use. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007;65:363– 364. - PubMed
-
- Marx RE, Stern DS. Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology: A Rationale for Diagnosis and Treatment. Chicago: Quintessence; 2002.
-
- Marx RE. Reconstruction of defects caused by Bisphosphonate- Induced Osteonecrosis of jaws. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009;67:107–119. - PubMed
-
- Marx RE, Sawatari Y, Fortin M, Broumand V. Biphosphonate induced exposed bone (osteonecrosis/osteopetrosis) of the jaws: Risk factors, recognition, prevenction and treatment. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005;63:1567–1575. - PubMed
-
- Marx RE, Cillo JE, Ulloa JJ. Oral Bisphosphonate induced osteonecrosis: Risk Factors, prediction of risk using serum CTX testing, prevention and treatment. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007;65:2397–2410. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
