Early reconstruction of orbital roof fractures: clinical features and treatment outcomes
- PMID: 22783488
- PMCID: PMC3385302
- DOI: 10.5999/aps.2012.39.1.31
Early reconstruction of orbital roof fractures: clinical features and treatment outcomes
Abstract
Background: Orbital roof fractures are frequently associated with a high energy impact to the craniofacial region, and displaced orbital roof fractures can cause ophthalmic and neurologic complications and occasionally require open surgical intervention. The purpose of this article was to investigate the clinical features and treatment outcomes of orbital root fractures combined with neurologic injuries after early reconstruction.
Methods: Between January 2006 and December 2008, 45 patients with orbital roof fractures were admitted; among them, 37 patients were treated conservatively and 8 patients underwent early surgical intervention for orbital roof fractures. The type of injuries that caused the fractures, patient characteristics, associated fractures, ocular and neurological injuries, patient management, and treatment outcomes were investigated.
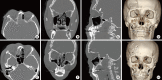
Results: The patients underwent frontal craniotomy and free bone fragment removal, their orbital roofs were reconstructed with titanium micromesh, and associated fractures were repaired. The mean follow up period was 11 months. There were no postoperative neurologic sequelae. Postoperative computed tomography scans showed anatomically reconstructed orbital roofs. Two of the five patients with traumatic optic neuropathy achieved full visual acuity recovery, one patient showed decreased visual acuity, and the other two patients completely lost their vision due to traumatic optic neuropathy. Preoperative ophthalmic symptoms, such as proptosis, diplopia, upper eyelid ptosis, and enophthalmos were corrected.
Conclusions: Early recognition and treatment of orbital roof fractures can reduce intracranial and ocular complications. A coronal flap with frontal craniotomy and orbital roof reconstruction using titanium mesh provides a versatile method and provides good functional and cosmetic results.
Keywords: Optic nerve; Orbital fracture; Postoperative complication.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Early Surgical Management of Displaced Orbital Roof Fractures: Prospective Observational Study.Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2023 Dec;75(4):3770-3777. doi: 10.1007/s12070-023-04056-x. Epub 2023 Jul 22. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2023. PMID: 37974754 Free PMC article.
-
Displaced orbital roof fractures: presentation and treatment.Plast Reconstr Surg. 1991 Apr;87(4):657-61. doi: 10.1097/00006534-199104000-00008. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1991. PMID: 2008463
-
Surgical Treatment and Visual Outcomes of Adult Orbital Roof Fractures.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2021 Jan 1;147(1):82e-93e. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000007436. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2021. PMID: 33370060
-
Demographics and treatment options for orbital roof fractures.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002 Mar;93(3):238-46. doi: 10.1067/moe.2002.120975. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002. PMID: 11925530 Review.
-
Orbital Roof Fractures: An Evidence-Based Approach.Facial Plast Surg Aesthet Med. 2020 Nov/Dec;22(6):471-480. doi: 10.1089/fpsam.2020.0029. Epub 2020 Aug 10. Facial Plast Surg Aesthet Med. 2020. PMID: 32779938
Cited by
-
Orbital Roof Fractures: A Clinically Based Classification and Treatment Algorithm.Craniomaxillofac Trauma Reconstr. 2015 Sep;8(3):198-204. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1393728. Epub 2014 Dec 17. Craniomaxillofac Trauma Reconstr. 2015. PMID: 26269727 Free PMC article.
-
Recovery of ocular motility after surgical intervention in orbital roof fracture-induced cranial nerve injuries.Surg Neurol Int. 2025 Jul 18;16:296. doi: 10.25259/SNI_271_2025. eCollection 2025. Surg Neurol Int. 2025. PMID: 40837291 Free PMC article.
-
Early Surgical Management of Displaced Orbital Roof Fractures: Prospective Observational Study.Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2023 Dec;75(4):3770-3777. doi: 10.1007/s12070-023-04056-x. Epub 2023 Jul 22. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2023. PMID: 37974754 Free PMC article.
-
An Unusual Transorbital Penetrating Injury by House-key (lock): A Case Report with a Small Review of Literature.J Clin Diagn Res. 2015 Sep;9(9):PD08-9. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2015/14257.6434. Epub 2015 Sep 1. J Clin Diagn Res. 2015. PMID: 26500948 Free PMC article.
-
Does Training Background Influence Outcomes after Coronal Scalp Incision for Treating Craniomaxillofacial Injuries?: A German Pilot Study.J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2023 Jun;22(2):442-452. doi: 10.1007/s12663-023-01860-4. Epub 2023 Feb 2. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2023. PMID: 37122780 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bolling JP, Wesley RE. Conservative treatment of orbital roof blow-in fracture. Ann Ophthalmol. 1987;19:75–76. - PubMed
-
- Sullivan WG. Displaced orbital roof fractures: presentation and treatment. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1991;87:657–661. - PubMed
-
- Piotrowski WP, Beck-Mannagetta J. Surgical techniques in orbital roof fractures: early treatment and results. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 1995;23:6–11. - PubMed
-
- Converse JM, Hogan VM. Open-sky approach for reduction of naso-orbital fractures: case report. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1970;46:396–398. - PubMed
-
- Haug RH, Nuveen E, Bredbenner T. An evaluation of the support provided by common internal orbital reconstruction materials. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1999;57:564–570. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

