Irritable oppositional defiance and callous unemotional traits: is the association partially explained by peer victimization?
- PMID: 22783837
- PMCID: PMC3619049
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.2012.02579.x
Irritable oppositional defiance and callous unemotional traits: is the association partially explained by peer victimization?
Abstract
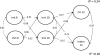
Background: Irritability is a subdimension of ODD, which predicts mainly to internalizing disorders, and to a lesser extent, conduct problems and callous-unemotional traits. Given that youth with similar dispositions as the irritable types - as well as youth high in callous-unemotional (CU) traits - have both been reported to experience high levels of victimization by peers, the authors examined an extension of the failure model (Patterson & Capaldi, 1990): that irritability increases peer victimization, which, in turn, predicts both CU and internalizing symptoms.
Sample: Using data from 5,923 mother-child pairs participating in The Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children, the authors tested the outcomes of internalizing difficulties and callous-unemotional traits (based on mother report at age 13) via the predictors (at ages 8 and 10) of irritability (mother report) and the experience of peer victimization (youth report).
Results: Irritability and peer victimization (age 10) directly predicted both CU and internalizing difficulties (age 13). Contrary to strict interpretation of the failure model, the significant indirect pathway described peer victimization (age 8) as increasing irritability (age 10), which, in turn, increased both CU and internalizing difficulties (age 13).
Conclusion: Results suggest that - for youth with irritable dispositions - co-occurring CU and internalizing difficulties can be acquired via adverse experiences in the social environment.
© 2012 The Authors. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry © 2012 Association for Child and Adolescent Mental Health.
Figures
References
-
- Angold A, Costello EJ, Erlanki A. Comorbidity. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry. 1999;40(1):57–87. - PubMed
-
- Barker ED, Oliver BR, Viding E, Salekin RT, Maughan B. The Impact of Prenatal Maternal Risk, Fearless Temperament and Early Parenting on Adolescent Callous-Unemotional Traits: A 14-year Longitudinal Investigation. Journal of Child Psychology & Psychiatry. 2011;52:878–888. - PubMed
-
- Beaver KM, Mancini C, DeLisi M, Vaughn MG. Resiliency to Victimization: The Role of Genetic Factors. Journal of Interpersonal Violence. 2011;26(5):874–898. - PubMed
-
- Beaver KM, Wright JP, DeLisi M, Daigle LE, Swatt ML, Gibson CL. Evidence of a Gene X Environment Interaction in the Creation of Victimization. International Journal of Offender Therapy and Comparative Criminology. 2007b;51(6):620–645. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

