Effect of modifying quantum dot surface charge on airway epithelial cell uptake in vitro
- PMID: 22783847
- PMCID: PMC3737271
- DOI: 10.3109/17435390.2012.711862
Effect of modifying quantum dot surface charge on airway epithelial cell uptake in vitro
Abstract
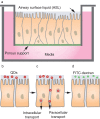
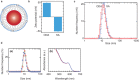
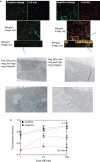
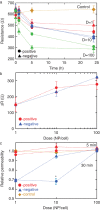
The respiratory system is one of the portals of entry into the body, and hence inhalation of engineered nanomaterials is an important route of exposure. The broad range of physicochemical properties that influence biological responses necessitate the systematic study to contribute to understanding occupational exposure. Here, we report on the influence of nanoparticle charge and dose on human airway epithelial cells, and show that this platform can be used to evaluate consequences of exposure to engineered nanomaterials.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Translocation of PEGylated quantum dots across rat alveolar epithelial cell monolayers.Int J Nanomedicine. 2011;6:2849-57. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S26051. Epub 2011 Nov 10. Int J Nanomedicine. 2011. PMID: 22131830 Free PMC article.
-
Selenium Redox Reactivity on Colloidal CdSe Quantum Dot Surfaces.J Am Chem Soc. 2016 Sep 7;138(35):11105-8. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b06548. Epub 2016 Aug 24. J Am Chem Soc. 2016. PMID: 27518320 Free PMC article.
-
Functionalization-dependent induction of cellular survival pathways by CdSe quantum dots in primary normal human bronchial epithelial cells.ACS Nano. 2013 Oct 22;7(10):8397-411. doi: 10.1021/nn305532k. Epub 2013 Sep 17. ACS Nano. 2013. PMID: 24007210
-
Cell type-dependent changes in CdSe/ZnS quantum dot uptake and toxic endpoints.Toxicol Sci. 2015 Apr;144(2):246-58. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfv002. Epub 2015 Jan 19. Toxicol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25601991 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Nanoparticle Surface Coating on Cell Toxicity and Mitochondria Uptake.J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2017 Feb;13(2):155-66. doi: 10.1166/jbn.2017.2337. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2017. PMID: 29377103 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Quantifying engineered nanomaterial toxicity: comparison of common cytotoxicity and gene expression measurements.J Nanobiotechnology. 2017 Nov 9;15(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s12951-017-0312-3. J Nanobiotechnology. 2017. PMID: 29121949 Free PMC article.
-
Acute exposure to silica nanoparticles aggravate airway inflammation: different effects according to surface characteristics.Exp Mol Med. 2015 Jul 17;47(7):e173. doi: 10.1038/emm.2015.50. Exp Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 26183169 Free PMC article.
-
Role of air pollutants in airway epithelial barrier dysfunction in asthma and COPD.Eur Respir Rev. 2022 Mar 23;31(163):210112. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0112-2021. Print 2022 Mar 31. Eur Respir Rev. 2022. PMID: 35321933 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anderson JM, Van Itallie CM. Tight junctions and the molecular basis for regulation of paracellular permeability. Am J Physiol. 1995;269(4 Pt 1):G467–G475. - PubMed
-
- Colegio OR, Van Itallie C, Rahner C, Anderson JM. Claudin extracellular domains determine paracellular charge selectivity and resistance but not tight junction fibril architecture. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2003;284(6):C1346–C1354. - PubMed
-
- Dausend J, Musyanovych A, Dass M, Walther P, Schrezenmeier H, Landfester K, et al. Uptake mechanism of oppositely charged fluorescent nanoparticles in HeLa cells. Macromol Biosci. 2008;8(12): 1135–1143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
