The combination of inhibitors of FGF/MEK/Erk and GSK3β signaling increases the number of OCT3/4- and NANOG-positive cells in the human inner cell mass, but does not improve stem cell derivation
- PMID: 22784186
- PMCID: PMC3545355
- DOI: 10.1089/scd.2012.0256
The combination of inhibitors of FGF/MEK/Erk and GSK3β signaling increases the number of OCT3/4- and NANOG-positive cells in the human inner cell mass, but does not improve stem cell derivation
Abstract
In embryonic stem cell culture, small molecules can be used to alter key signaling pathways to promote self-renewal and inhibit differentiation. In mice, small-molecule inhibition of both the FGF/MEK/Erk and the GSK3β pathways during preimplantation development suppresses hypoblast formation, and this results in more pluripotent cells of the inner cell mass (ICM). In this study, we evaluated the effects of different small-molecule inhibitors of the FGF/MEK/Erk and GSK3β pathway on embryo preimplantation development, early lineage segregation, and subsequent embryonic stem cell derivation in the humans. We did not observe any effect on blastocyst formation, but small-molecule inhibition did affect the number of OCT3/4- and NANOG-positive cells in the human ICM. We found that combined inhibition of the FGF/MEK/Erk and GSK3β pathways by PD0325901 and CHIR99021, respectively, resulted in ICMs containing significantly more OCT3/4-positive cells. Inhibition of FGF/MEK/Erk alone as well as in combination with inhibition of GSK3β significantly increased the number of NANOG-positive cells in blastocysts possessing good-quality ICMs. Secondly, we verified the influence of this increased pluripotency after 2i culture on the efficiency of stem cell derivation. Similar human embryonic stem cell (hESC) derivation rates were observed after 2i compared to control conditions, resulting in 2 control hESC lines and 1 hESC line from an embryo cultured in 2i conditions. In conclusion, we demonstrated that FGF/MEK/Erk and GSK3β signaling increases the number of OCT3/4- and NANOG-positive cells in the human ICM, but does not improve stem cell derivation.
Figures
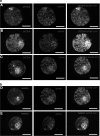

Similar articles
-
WNT signalling supported by MEK/ERK inhibition is essential to maintain pluripotency in bovine preimplantation embryo.Dev Biol. 2020 Jul 1;463(1):63-76. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2020.04.004. Epub 2020 Apr 28. Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32360193
-
The effect of dual inhibition of Ras-MEK-ERK and GSK3β pathways on development of in vitro cultured rabbit embryos.Zygote. 2020 Jun;28(3):183-190. doi: 10.1017/S0967199419000753. Epub 2020 Mar 20. Zygote. 2020. PMID: 32192548
-
The roles of FGF and MAP kinase signaling in the segregation of the epiblast and hypoblast cell lineages in bovine and human embryos.Development. 2012 Mar;139(5):871-82. doi: 10.1242/dev.071688. Epub 2012 Jan 25. Development. 2012. PMID: 22278923 Free PMC article.
-
[OCT4 and NANOG are the key genes in the system of pluripotency maintenance in mammalian cells].Genetika. 2008 Dec;44(12):1589-608. Genetika. 2008. PMID: 19178078 Review. Russian.
-
Accessing naïve human pluripotency.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2012 Jun;22(3):272-82. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2012.03.001. Epub 2012 Mar 29. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2012. PMID: 22463982 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A mRNA landscape of bovine embryos after standard and MAPK-inhibited culture conditions: a comparative analysis.BMC Genomics. 2015 Apr 10;16(1):277. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1448-x. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25888366 Free PMC article.
-
GATA6 levels modulate primitive endoderm cell fate choice and timing in the mouse blastocyst.Dev Cell. 2014 May 27;29(4):454-67. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2014.04.011. Epub 2014 May 15. Dev Cell. 2014. PMID: 24835466 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic and epigenetic dysfunctions underlie the arrest of in vitro fertilized human embryos in a senescent-like state.PLoS Biol. 2022 Jun 30;20(6):e3001682. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001682. eCollection 2022 Jun. PLoS Biol. 2022. PMID: 35771762 Free PMC article.
-
Learning Towards Maturation of Defined Feeder-free Pluripotency Culture Systems: Lessons from Conventional Feeder-based Systems.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2024 Feb;20(2):484-494. doi: 10.1007/s12015-023-10662-7. Epub 2023 Dec 11. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2024. PMID: 38079087 Review.
-
Inhibition of transforming growth factor β signaling promotes epiblast formation in mouse embryos.Stem Cells Dev. 2015 Feb 15;24(4):497-506. doi: 10.1089/scd.2014.0206. Epub 2014 Oct 29. Stem Cells Dev. 2015. PMID: 25245024 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chazaud C. Yamanaka T. Pawson T. Rossant J. Early lineage segregation between epiblast and primitive endoderm in mouse blastocysts through the Grb2- MAPK pathway. Dev Cell. 2006;10:615–624. - PubMed
-
- Strumpf D. Mao CA. Yamanaka Y. Ralston A. Chawengsaksophak K. Beck F. Rossant J. Cdx2 is required for correct cell fate specification and differentiation of trophectoderm in the mouse blastocyst. Development. 2005;132:2093–2102. - PubMed
-
- Dietrich JE. Hiiragi T. Stochastic patterning in the mouse pre-implantation embryo. Development. 2007;134:4219–4231. - PubMed
-
- Niwa H. Toyooka Y. Shimosato D. Strumpf D. Takahashi K. Yagi R. Rossant J. Interaction between Oct3/4 and Cdx2 determines trophectoderm differentiation. Cell. 2005;123:917–929. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

