Effects of Astragalus polysaccharides on P-glycoprotein efflux pump function and protein expression in H22 hepatoma cells in vitro
- PMID: 22784390
- PMCID: PMC3493361
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6882-12-94
Effects of Astragalus polysaccharides on P-glycoprotein efflux pump function and protein expression in H22 hepatoma cells in vitro
Abstract
Background: Astragalus polysaccharides (APS) are active constituents of Astragalus membranaceus. They have been widely studied, especially with respect to their immunopotentiating properties, their ability to counteract the side effects of chemotherapeutic drugs, and their anticancer properties. However, the mechanism by which APS inhibit cancer and the issue of whether that mechanism involves the reversal of multidrug resistance (MDR) is not completely clear. The present paper describes an investigation of the effects of APS on P-glycoprotein function and expression in H22 hepatoma cell lines resistant to Adriamycin (H22/ADM).
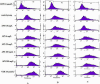
Methods: H22/ADM cell lines were treated with different concentrations of APS and/or the most common chemotherapy drugs, such as Cyclophosphamid, Adriamycin, 5-Fluorouracil, Cisplatin, Etoposide, and Vincristine. Chemotherapeutic drug sensitivity, P-glycoprotein function and expression, and MDR1 mRNA expression were detected using MTT assay, flow cytometry, Western blotting, and quantitative RT-PCR.
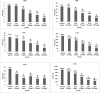
Results: When used alone, APS had no anti-tumor activity in H22/ADM cells in vitro. However, it can increase the cytotoxicity of certain chemotherapy drugs, such as Cyclophosphamid, Adriamycin, 5-Fluorouracil, Cisplatin, Etoposide, and Vincristine, in H22/ADM cells. It acts in a dose-dependent manner. Compared to a blank control group, APS increased intracellular Rhodamine-123 retention and decreased P-glycoprotein efflux function in a dose-dependent manner. These factors were assessed 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h after administration. APS down regulated P-glycoprotein and MDR1 mRNA expression in a concentration-dependent manner within a final range of 0.8-500 mg/L and in a time-dependent manner from 24-72 h.
Conclusion: APS can enhance the chemosensitivity of H22/ADM cells. This may involve the downregulation of MDR1 mRNA expression, inhibition of P-GP efflux pump function, or both, which would decrease the expression of the MDR1 protein.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Astragalus polysaccharides can regulate cytokine and P-glycoprotein expression in H22 tumor-bearing mice.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Dec 21;18(47):7079-86. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i47.7079. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 23323011 Free PMC article.
-
Reversal of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance of human hepatic cancer cells by Astragaloside II.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2012 Dec;64(12):1741-50. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.2012.01549.x. Epub 2012 Jun 8. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 23146037
-
Development and characterization of multidrug resistant human hepatocarcinoma cell line in nude mice.World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Nov 7;12(41):6614-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i41.6614. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 17075973 Free PMC article.
-
p53 and P-glycoprotein influence chemoresistance in hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2018 Jun 1;10(3):461-468. doi: 10.2741/E833. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2018. PMID: 29772519 Review.
-
A critical review of Astragalus polysaccharides: From therapeutic mechanisms to pharmaceutics.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Mar;147:112654. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112654. Epub 2022 Jan 25. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 35086031
Cited by
-
Astragalus polysaccharides inhibit avian infectious bronchitis virus infection by regulating viral replication.Microb Pathog. 2018 Jan;114:124-128. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2017.11.026. Epub 2017 Nov 21. Microb Pathog. 2018. PMID: 29170045 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of drug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma.Biol Proced Online. 2025 May 28;27(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s12575-025-00281-6. Biol Proced Online. 2025. PMID: 40437363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A network pharmacology approach for investigating the multi-target mechanisms of Huangqi in the treatment of colorectal cancer.Transl Cancer Res. 2021 Feb;10(2):681-693. doi: 10.21037/tcr-20-2596. Transl Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 35116401 Free PMC article.
-
Astragalus Polysaccharides Inhibits Tumorigenesis and Lipid Metabolism Through miR-138-5p/SIRT1/SREBP1 Pathway in Prostate Cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2020 May 5;11:598. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00598. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32431616 Free PMC article.
-
Towards novel anti-tumor strategies for hepatic cancer: ɛ-viniferin in combination with vincristine displays pharmacodynamic synergy at lower doses in HepG2 cells.OMICS. 2014 May;18(5):324-34. doi: 10.1089/omi.2013.0045. Epub 2013 Dec 17. OMICS. 2014. PMID: 24341688 Free PMC article.
References
-
- The World Health Report 2008 – primary health care: Now more than ever. http://www.who.int/whr/2008/whr08_en.pdf.
-
- Kellof GJ. Perspective on cancer chemoprevention research and drug development. Adv Cancer Res. 2000;78:199–334. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

