AID targeting is dependent on RNA polymerase II pausing
- PMID: 22784681
- PMCID: PMC3630797
- DOI: 10.1016/j.smim.2012.06.001
AID targeting is dependent on RNA polymerase II pausing
Abstract
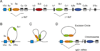
Activation induced deaminase (AID) is globally targeted to immunoglobulin loci, preferentially focused to switch (S) regions and variable (V) regions, and prone to attack hotspot motifs. Nevertheless, AID deamination is not exclusive to Ig loci and the rules regulating AID targeting remain unclear. Transcription is critically required for class switch recombination and somatic hypermutation. Here, I consider the unique features associated with S region transcription leading to RNA polymerase II pausing, that in turn promote the introduction of activating chromatin remodeling, histone modifications and recruitment of AID to targeted S regions. These findings allow for a better understanding of the interplay between transcription, AID targeting and mistargeting to Ig and non-Ig loci.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Muramatsu M, Kinoshita K, Fagarasan S, Yamada S, Shinkai Y, Honjo T. Class switch recombination and hypermutation require activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), a potential RNA editing enzyme. Cell. 2000;102:553–563. - PubMed
-
- Revy P, Muto T, Levy Y, Geissmann F, Plebani A, Sanal O, et al. Activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) deficiency causes the autosomal recessive form of the Hyper-IgM syndrome (HIGM2) Cell. 2000;102:565–575. - PubMed
-
- Peled JU, Kuang FL, Iglesias-Ussel MD, Roa S, Kalis SL, Goodman MF, et al. The biochemistry of somatic hypermutation. Annual Review of Immunology. 2008;26:481–511. - PubMed
-
- Neuberger MS, Di Noia JM, Beale RC, Williams GT, Yang Z, Rada C. Somatic hypermutation at A.T. pairs: polymerase error versus dUTP incorporation. Nature Reviews Immunology. 2005;5:171–178. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

