Murine BAFF expression is up-regulated by estrogen and interferons: implications for sex bias in the development of autoimmunity
- PMID: 22784990
- PMCID: PMC3439561
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molimm.2012.06.013
Murine BAFF expression is up-regulated by estrogen and interferons: implications for sex bias in the development of autoimmunity
Abstract
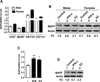
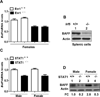
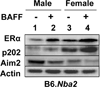
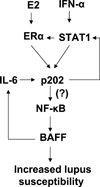
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in patients and certain mouse models exhibits a strong sex bias. Additionally, in most patients, increased serum levels of type I interferon (IFN-α) are associated with severity of the disease. Because increased levels of B cell activating factor (BAFF) in SLE patients and mouse models are associated with the development of SLE, we investigated whether the female sex hormone estrogen (E2) and/or IFNs (IFN-α or γ) could regulate the expression of murine BAFF. We found that steady-state levels of BAFF mRNA and protein were measurably higher in immune cells (CD11b(+), CD11c(+), and CD19(+)) isolated from C57BL/6 females than the age-matched male mice. Treatment of immune cells with IFN or E2 significantly increased levels of BAFF mRNA and protein and a deficiency of estrogen receptor-α, IRF5, or STAT1 expression in splenic cells decreased expression of BAFF. Moreover, treatment of RAW264.7 macrophage cells with IFN-α, IFN-γ, or E2 induced expression of BAFF. Interestingly, increased expression of p202, an IFN and estrogen-inducible protein, in RAW264.7 cells significantly increased the expression levels of BAFF and also stimulated the activity of the BAFF-luc-reporter. Accordingly, the increased expression of the p202 protein in lupus-prone B6.Nba2-ABC than non lupus-prone C57BL/6 and B6.Nba2-C female mice was associated with increased expression levels of BAFF. Together, our observations demonstrated that estrogen and IFN-induced increased levels of the p202 protein in immune cells contribute to sex bias in part through up-regulation of BAFF expression.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

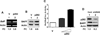

Similar articles
-
Expression of murine Unc93b1 is up-regulated by interferon and estrogen signaling: implications for sex bias in the development of autoimmunity.Int Immunol. 2013 Sep;25(9):521-9. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxt015. Epub 2013 Jun 1. Int Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23728775 Free PMC article.
-
Mutually positive regulatory feedback loop between interferons and estrogen receptor-alpha in mice: implications for sex bias in autoimmunity.PLoS One. 2010 May 28;5(5):e10868. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010868. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20526365 Free PMC article.
-
Female and male sex hormones differentially regulate expression of Ifi202, an interferon-inducible lupus susceptibility gene within the Nba2 interval.J Immunol. 2009 Dec 1;183(11):7031-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0802665. Epub 2009 Nov 4. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19890043 Free PMC article.
-
[BAFF: A regulatory cytokine of B lymphocytes involved in autoimmunity and lymphoid cancer].Rev Med Chil. 2006 Sep;134(9):1175-84. doi: 10.4067/s0034-98872006000900014. Epub 2006 Dec 12. Rev Med Chil. 2006. PMID: 17171221 Review. Spanish.
-
Targeting BAFF in autoimmunity.Curr Opin Immunol. 2010 Dec;22(6):732-9. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2010.09.010. Epub 2010 Oct 21. Curr Opin Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20970975 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulating the Polarization of Macrophages: A Promising Approach to Vascular Dermatosis.J Immunol Res. 2020 Jul 28;2020:8148272. doi: 10.1155/2020/8148272. eCollection 2020. J Immunol Res. 2020. PMID: 32775470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunopathological events surrounding IL-6 and IFN-α: A bridge for anti-lupus erythematosus drugs used to treat COVID-19.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Dec;101(Pt B):108254. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108254. Epub 2021 Oct 14. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34710657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of interferon-gamma genetic variants and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in onset and progression of generalized vitiligo.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2013 Nov;33(11):646-59. doi: 10.1089/jir.2012.0171. Epub 2013 Jun 18. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2013. PMID: 23777204 Free PMC article.
-
Sex Hormones in Acquired Immunity and Autoimmune Disease.Front Immunol. 2018 Oct 4;9:2279. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02279. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30337927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The BAFF/APRIL system in SLE pathogenesis.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014 Jun;10(6):365-73. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2014.33. Epub 2014 Mar 11. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 24614588 Review.
References
-
- Kotzin BL. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell. 1996;85(3):303–306. - PubMed
-
- Tsokos GC. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(22):2110–2121. - PubMed
-
- Whitacre CC. Sex differences in autoimmune disease. Nat Immunol. 2001;2(9):777–780. - PubMed
-
- Cohen-Solal JF, Jeganathan V, Hill L, Kawabata D, Rodriguez-Pinto D, Grimaldi C, et al. Hormonal regulation of B-cell function and systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2008;17(6):528–532. - PubMed
-
- Pennell LM, Galligan CL, Fish EN. Sex affects immunity. J Autoimmun. 2012;38(2–3):J282–J291. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

