Comparison of a high-resolution melting assay to next-generation sequencing for analysis of HIV diversity
- PMID: 22785188
- PMCID: PMC3421787
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01460-12
Comparison of a high-resolution melting assay to next-generation sequencing for analysis of HIV diversity
Abstract
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) has recently been used for analysis of HIV diversity, but this method is labor-intensive, costly, and requires complex protocols for data analysis. We compared diversity measures obtained using NGS data to those obtained using a diversity assay based on high-resolution melting (HRM) of DNA duplexes. The HRM diversity assay provides a single numeric score that reflects the level of diversity in the region analyzed. HIV gag and env from individuals in Rakai, Uganda, were analyzed in a previous study using NGS (n = 220 samples from 110 individuals). Three sequence-based diversity measures were calculated from the NGS sequence data (percent diversity, percent complexity, and Shannon entropy). The amplicon pools used for NGS were analyzed with the HRM diversity assay. HRM scores were significantly associated with sequence-based measures of HIV diversity for both gag and env (P < 0.001 for all measures). The level of diversity measured by the HRM diversity assay and NGS increased over time in both regions analyzed (P < 0.001 for all measures except for percent complexity in gag), and similar amounts of diversification were observed with both methods (P < 0.001 for all measures except for percent complexity in gag). Diversity measures obtained using the HRM diversity assay were significantly associated with those from NGS, and similar increases in diversity over time were detected by both methods. The HRM diversity assay is faster and less expensive than NGS, facilitating rapid analysis of large studies of HIV diversity and evolution.
Figures
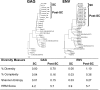
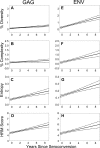
References
-
- Buzon MJ, et al. 2011. Deep molecular characterization of HIV-1 dynamics under suppressive HAART. PLoS Pathog. 7:e1002314 doi:10.1371/joural.ppat.1002314 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cousins MM, et al. 2011. Use of a high resolution melting (HRM) assay to compare gag, pol, and env diversity in adults with different stages of HIV infection. PLoS One 6:e27211 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0027211 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Reference deleted.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 AI051171/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1UO1AI075115-O1A1/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01-AI095068/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI075115/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI095068/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01AI068613/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068613/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068613/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U1AI51171/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5D43TW00010/TW/FIC NIH HHS/United States
- D43 TW000010/TW/FIC NIH HHS/United States
- UM1AI068613/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1-AI068617/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068617/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

