Hypoglycemic effects of brassinosteroid in diet-induced obese mice
- PMID: 22785239
- PMCID: PMC3774328
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00024.2012
Hypoglycemic effects of brassinosteroid in diet-induced obese mice
Abstract
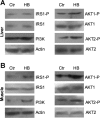
The prevalence of obesity is increasing globally, and obesity is a major risk factor for metabolic diseases such as type 2 diabetes. Previously, we reported that oral administration of homobrassinolide (HB) to healthy rats triggered a selective anabolic response that was associated with lower blood glucose. Therefore, the aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of HB administration on glucose metabolism, insulin sensitivity, body composition, and gluconeogenic gene expression profiles in liver of C57BL/6J high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Acute oral administration of 50-300 mg/kg HB to obese mice resulted in a dose-dependent decrease in fasting blood glucose within 3 h of treatment. Daily chronic administration of HB (50 mg/kg for 8 wk) ameliorated hyperglycemia and improved oral glucose tolerance associated with obesity without significantly affecting body weight or body composition. These changes were accompanied by lower expression of two key gluconeogenic enzymes, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) and glucose-6-phosphatase (G-6-Pase), and increased phosphorylation of AMP-activated protein kinase in the liver and muscle tissue. In vitro, HB treatment (1-15 μM) inhibited cyclic AMP-stimulated but not dexamethasone-stimulated upregulation of PEPCK and G-6-Pase mRNA levels in H4IIE rat hepatoma cells. Among a series of brassinosteroid analogs related to HB, only homocastasterone decreased glucose production in cell culture significantly. These results indicate the antidiabetic effects of brassinosteroids and begin to elucidate their putative cellular targets both in vitro and in vivo.
Figures


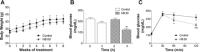



References
-
- Argaud D, Zhang Q, Pan W, Maitra S, Pilkis SJ, Lange AJ. Regulation of rat liver glucose-6-phosphatase gene expression in different nutritional and hormonal states: gene structure and 5′-flanking sequence. Diabetes 45: 1563– 1571, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Bajguz A, Tretyn A. The chemical characteristic and distribution of brassinosteroids in plants. Phytochemistry 62: 1027– 1046, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Baron DL, Luo W, Janzen L, Pharis RP, Back TG. Structure-activity studies of brassinolide b-ring analogues. Phytochemistry 49: 1849– 1858, 1998
-
- Bathori M, Toth N, Hunyadi A, Marki A, Zador E. Phytoecdysteroids and anabolic-androgenic steroids—structure and effects on humans. Curr Med Chem 15: 75– 91, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Berasi SP, Huard C, Li D, Shih HH, Sun Y, Zhong W, Paulsen JE, Brown EL, Gimeno RE, Martinez RV. Inhibition of gluconeogenesis through transcriptional activation of EGR1 and DUSP4 by AMP-activated kinase. J Biol Chem 281: 27167– 27177, 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

