Orbital radiotherapy for adult thyroid eye disease
- PMID: 22786503
- PMCID: PMC12152713
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007114.pub2
Orbital radiotherapy for adult thyroid eye disease
Abstract
Background: Thyroid eye disease is an autoimmune inflammatory condition of the orbital and periorbital tissues. Orbital radiotherapy is an anti-inflammatory treatment used in the treatment of active thyroid eye disease. It is administered as an outpatient procedure in 10 to 12 fractionated doses.
Objectives: To assess the effectiveness and adverse events of orbital radiotherapy in thyroid eye disease. The effectiveness was dependent on the level of 'success' of the intervention predefined in each randomised controlled trial (RCT).
Search methods: We searched CENTRAL (which contains the Cochrane Eyes and Vision Group Trials Register) (The Cochrane Library 2012, Issue 2), MEDLINE (January 1950 to March 2012), EMBASE (January 1980 to March 2012), Latin American and Caribbean Literature on Health Sciences (LILACS) (January 1982 to March 2012), the metaRegister of Controlled Trials (mRCT) (www.controlled-trials.com), ClinicalTrials.gov (www.clinicaltrials.gov) and the WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (ICTRP) (www.who.int/ictrp/search/en). We did not restrict the electronic searches for trials by date or language. We last searched the electronic databases on 12 March 2012. We screened reference lists of reports of included studies, other reviews and book chapters to find additional trials. We contacted trial investigators and experts in the field to identify additionally published studies.
Selection criteria: We included RCTs of orbital radiotherapy versus sham radiotherapy or other interventions enrolling adults, with a minimum of three months' follow-up and an endpoint of two years or less post treatment.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently assessed trial quality and extracted data. Trial authors were contacted for missing data. The risk ratio was used for our primary outcome. For our secondary outcomes, the odds ratio and mean difference were reported where possible.
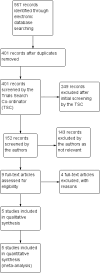
Main results: We obtained full-text copies of nine potential studies and included five trials with a total of 244 participants in this review. Orbital radiotherapy was compared to sham radiotherapy in two studies and to glucocorticoids in three studies, as a monotherapy or combination therapy. There was heterogeneity (as defined in our protocol) of trial outcome measures. Our primary outcome of a composite score was used in the two trials comparing radiotherapy versus sham radiotherapy and showed a risk ratio of success of 1.92 (95% confidence interval (CI) 1.27 to 2.91) in favour of orbital radiotherapy. The primary outcome was not used in the other three trials.
Authors' conclusions: This review found that orbital radiotherapy is more effective than sham radiotherapy for the treatment of mild-to-moderate thyroid eye disease. In a single trial no difference between radiotherapy and steroid monotherapy was found. A meta-analysis of our secondary outcome of disease severity was not possible but results from individual trials suggest a better outcome with combination treatment with steroids versus steroids alone. No significant changes in quality-of-life scores following treatment with radiotherapy versus alternative treatments were found. Short-term adverse events related to radiotherapy that were reported were local and mild but long-term data were lacking and development of retinal changes following radiotherapy was not reported on.
Conflict of interest statement
The three authors (RR, CB, RL) are investigators in an RCT of medical treatment for TED.
Figures


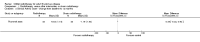
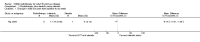

Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Bartalena 1983 {published data only}
-
- Bartalena L, Marcocci C, Chiovato L, Laddaga M, Lepri G, Andreani D, et al. Orbital cobalt irradiation combined with systemic corticosteroids for Graves' ophthalmopathy: comparison with systemic corticosteroids alone. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 1983;56(6):1139‐44. - PubMed
Mourits 2000 {published data only}
-
- Mourits MP, Kempen‐Hartveld ML, Garcia MB, Koppeschaar HP, Tick L, Terwee CB. Radiotherapy for Graves' orbitopathy: randomised placebo‐controlled study. Lancet 2000;355(9124):1505‐9. - PubMed
Ng 2005 {published data only}
-
- Ng CM, Yuen HK, Choi KL, Chan MK, Yuen KT, Ng YW, et al. Combined orbital irradiation and systemic steroids compared with systemic steroids alone in the management of moderate‐to‐severe Graves' ophthalmopathy: a preliminary study. Hong Kong Medical Journal 2005;11(5):322‐30. - PubMed
Prummel 1993 {published data only}
-
- Prummel MF, Mourits MP, Blank L, Berghout A, Koornneef L, Wiersinga WM. Randomized double‐blind trial of prednisone versus radiotherapy in Graves' ophthalmopathy. Lancet 1993;342(8877):949‐54. - PubMed
Prummel 2004 {published data only}
-
- Prummel MF, Terwee CB, Gerding MN, Baldeschi L, Mourits MP, Blank L, et al. A randomized controlled trial of orbital radiotherapy versus sham irradiation in patients with mild graves' ophthalmopathy. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2004;89(1):15‐20. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Antonelli 1992 {published data only}
-
- Antonelli A, Saracino A, Alberti B, Canapicchi R, Cartei F, Lepri A, et al. High‐dose intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in Graves' ophthalmopathy. Acta Endocrinologica 1992;126(1):13‐23. - PubMed
Gorman 2001 {published data only}
-
- Gorman CA, Garrity JA, Fatourechi V, Bahn, RS, Petersen IA, Stafford SL, et al. A prospective, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study of orbital radiotherapy for Graves' ophthalmopathy. Ophthalmology 2001;108(9):1523‐34. - PubMed
Li 2008 {published data only}
-
- Li LL, Wang F, Zhang Y, Sun R. Observation of curative effect of triamcinolone acetomide retrobular injection combined with orbital radiation on TAO. International Journal of Ophthalmology 2008;8(9):1860‐2.
Sterker 2009 {published data only}
-
- Sterker I, Tegetmeyer H, Papsdorf K, Fuhrer‐Sakel D. Effect of combined intravenous glucocorticoids and orbital radiotherapy in restoring driving competency in patients with Graves' orbitopathy. Hormone and Metabolic Research 2009;41(5):391‐6. - PubMed
Additional references
Bahn 1993
-
- Bahn RS, Heufelder AE. Pathogenesis of Graves' ophthalmopathy. New England Journal of Medicine 1993;329(20):1468‐75. - PubMed
Bahn 2010
Bartalena 2000
-
- Bartalena L, Pinchera A, Marcocci C. Management of Graves' ophthalmopathy: reality and perspectives. Endocrine Reviews 2000;21(2):168‐99. - PubMed
Bartalena 2004
-
- Bartalena L, Marcocci C, Pinchera A. Orbital radiotherapy for Graves' ophthalmopathy. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2004;89(1):13‐4. - PubMed
Behbehani 2004
-
- Behbehani R, Sergott RC, Savino PJ. Orbital radiotherapy for thyroid‐related orbitopathy. Current Opinion in Ophthalmology 2004;15(6):479‐82. - PubMed
Bradley 2008
-
- Bradley EA, Gower EW, Bradley DJ, Meyer DR, Cahill KV, Custer PL, et al. Orbital radiation for graves ophthalmopathy: a report by the American Academy of Ophthalmology. Ophthalmology 2008;115(2):398‐409. - PubMed
Cawood 2004
Dickinson 2001
-
- Dickinson AJ, Perros P. Controversies in the clinical evaluation of active thyroid‐associated orbitopathy: use of a detailed protocol with comparative photographs for objective assessment. Clinical Endocrinology 2001;55(3):283‐303. - PubMed
Donaldson 1973
-
- Donaldson SS, Bagshaw MA, Kriss JP. Supervoltage orbital radiotherapy for Graves' ophthalmopathy. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 1973;37(2):276‐85. - PubMed
EUGOGO 2006a
-
- The European Group on Graves' Orbitopathy (EUGOGO), Wiersinga WM, Perros P, Kahaly GJ, Mourits MP, Baldeschi L, Boboridis K, et al. Clinical assessment of patients with Graves' orbitopathy: the European Group on Graves' Orbitopathy recommendations to generalists, specialists and clinical researchers. European Journal of Endocrinology 2006;155(3):387‐9. - PubMed
EUGOGO 2006b
-
- The European Group of Graves' Orbitopathy, Perros P, Baldeschi L, Boboridis K, Dickinson AJ, Hullo A, Kahaly GJ, et al. A questionnaire survey on the management of Graves' orbitopathy in Europe. European Journal of Endocrinology 2006;155(2):207‐11. - PubMed
Feldon 2001
-
- Feldon SE. Radiation therapy for Graves' ophthalmopathy: trick or treat?. Ophthalmology 2001;108(9):1521‐2. - PubMed
Glanville 2006
Gorman 2002
-
- Gorman CA, Garrity JA, Fatourechi V, Bahn RS, Petersen IA, Stafford SL, et al. The aftermath of orbital radiotherapy for graves' ophthalmopathy. Ophthalmology 2002;109(11):2100‐7. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC (editors). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Hildebrandt 1998
-
- Hildebrandt G, Seed MP, Freemantle CN, Aslam CAS, Colville‐Nash PR, Trott KR. Mechanisms of the anti‐inflammatory activity of low‐dose radiation therapy. International Journal of Radiation Biology 1998;74(3):367‐78. - PubMed
Kahaly 1988
-
- Kahaly G, Beyer J. Immunosuppressant therapy of thyroid eye disease. Klinische Wochenschrift 1988;66(21):1049‐59. - PubMed
Lehmann 2007
Marcocci 2001
-
- Marcocci C, Bartalena L, Tanda ML, Manetti L, Dell'Unto E, Rocchi R, et al. Comparison of the effectiveness and tolerability of intravenous or oral glucocorticoids associated with orbital radiotherapy in the management of severe Graves' ophthalmopathy: results of a prospective, single‐blind, randomized study. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2001;86(8):3562‐7. - PubMed
Marcocci 2003
-
- Marcocci C, Bartalena L, Rocchi R, Marino M, Menconi F, Morabito E, et al. Long‐term safety of orbital radiotherapy for Graves' ophthalmopathy. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2003;88(8):3561‐6. - PubMed
Marquez 2001
-
- Marquez SD, Lum BL, McDougall IR, Katkuri S, Levin PS, MacManus M, et al. Long‐term results of irradiation for patients with progressive Graves' ophthalmopathy. International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics 2001;51(3):766‐74. - PubMed
McNab 2002
-
- McNab AA. Does radiotherapy have a role in the management of thyroid orbitopathy?. British Journal of Ophthalmology 2002;86(1):106‐7. - PubMed
Mourits 1989
Mourits 1997
-
- Mourits MP, Prummel MF, Wiersinga WM, Koornneef L. Clinical activity score as a guide in the management of patients with Graves' ophthalmopathy. Clinical Endocrinology 1997;47(1):9‐14. - PubMed
Mourits 2002
-
- Mourits MP. Does radiotherapy have a role in the management of thyroid orbitopathy ‐ View 2. British Journal of Ophthalmology 2002;86(1):104‐6. - PubMed
NICE guidelines 2005
-
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Retrobulbar irradiation for thyroid eye disease. www.nice.org.uk/ip257overview 2005 (accessed March 2012).
Nygaard 1998
-
- Nygaard B, Specht L. Transitory blindness after retrobulbar irradiation of Graves ophthalmopathy. Lancet 1998;351(9104):725‐6. - PubMed
Perros 1993
-
- Perros P, Crombie AL, Matthews JN, Kendall‐Taylor P. Age and gender influence the severity of thyroid‐associated ophthalmopathy: a study of 101 patients attending a combined thyroid‐eye clinic. Clinical Endocrinology 1993;38(4):367‐72. - PubMed
Prummel 1989
-
- Prummel MF, Mourits MP, Berghout A, Krenning EP, Gaag R, Koornneef L, et al. Prednisone and cyclosporine in the treatment of severe Graves' ophthalmopathy. New England Journal of Medicine 1989;321(20):1353‐9. - PubMed
Rajendram 2008
Review Manager 2011 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.1. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.
Robertson 2003
-
- Robertson DM, Buettner H, Gorman CA, Garrity JA, Fatourechi V, Bahn RS, et al. Retinal microvascular abnormalities in patients treated with external radiation for graves ophthalmopathy. Archives of Ophthalmology 2003;121(5):652‐7. - PubMed
Rundle 1945
-
- Rundle F, Wilson C. Development and course of exophthalmos and ophthalmoplegia in Graves' disease with special reference to the effect of thyroidectomy. Clinical Science 1945;5:177‐94. - PubMed
Schaefer 2002
-
- Schaefer U, Hesselmann S, Micke O, Schueller P, Bruns F, Palma C, et al. A long‐term follow‐up study after retro‐orbital irradiation for Graves' ophthalmopathy. International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics 2002;52(1):192‐7. - PubMed
Smith 2003
-
- Smith TJ. The putative role of fibroblasts in the pathogenesis of Graves' disease: evidence for the involvement of the insulin‐like growth factor‐1 receptor in fibroblast activation. Autoimmunity 2003;36:409‐15. - PubMed
Smith 2004
-
- Smith TJ, Hoa N. Immunoglobulins from patients with Graves' disease induce hyaluronan synthesis in their orbital fibroblasts through the self‐antigen, insulin‐like growth factor‐I receptor. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2004;89(10):5076‐80. - PubMed
Stan 2010
Stiebel‐Kalish 2009
-
- Stiebel‐Kalish H, Robenshtok E, Hasanreisoglu M, Ezrachi D, Shimon I, Leibovici L. Treatment modalities for Graves' ophthalmopathy: systematic review and metaanalysis. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2009;94(8):2708‐16. - PubMed
Terwee 2001
-
- Terwee CB, Dekker FW, Mourits MP, Gerding MN, Baldeschi L, Kalmann R, et al. Interpretation and validity of changes in scores on the Graves' ophthalmopathy quality of life questionnaire (GO‐QOL) after different treatments. Clinical Endocrinology 2001;54(3):391‐8. - PubMed
Terwee 2002
-
- Terwee C, Wakelkamp I, Tan S, Dekker F, Prummel MF, Wiersinga W. Long‐term effects of Graves' ophthalmopathy on health‐related quality of life. European Journal of Endocrinology 2002;146(6):751‐7. - PubMed
Van Steensel 2010
-
- Steensel L, Dik WA. The orbital fibroblast: a key player and target for therapy in Graves' ophthalmopathy. Orbit 2010;29(4):202‐6. - PubMed
Wakelkamp 2004
-
- Wakelkamp IM, Tan H, Saeed P, Schlingemann RO, Verbraak FD, Blank LE, et al. Orbital irradiation for Graves' ophthalmopathy: is it safe? A long‐term follow‐up. Ophthalmology 2004;111(8):1557‐62. - PubMed
Wei 2008
-
- Wei RL, Cheng JW, Cai JP. The use of orbital radiotherapy for Graves' ophthalmopathy: quantitative review of the evidence. Ophthalmologica 2008;222(1):27‐31. - PubMed
Werner 1977
-
- Werner SC. Modification of the classification of the eye changes of Graves' disease: recommendations of the Ad Hoc Committee of the American Thyroid Association. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 1977;44(1):203‐4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

