Alprazolam for depression
- PMID: 22786504
- PMCID: PMC6769182
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007139.pub2
Alprazolam for depression
Abstract
Background: The 'off-label' effect of alprazolam on depression has not been systematically evaluated.
Objectives: To determine the antidepressant effect, including tolerability and acceptability, of alprazolam as monotherapy for major depression, when compared to placebo and conventional antidepressants in outpatients and patients in primary care.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials and the Cochrane Depression, Anxiety and Neurosis Group Register, which includes relevant randomised controlled trials from the following bibliographic databases: The Cochrane Library (all years to February 2012); EMBASE (1970 to February 2012); MEDLINE (1950 to February 2012) and PsycINFO (1960 to February 2012). Two review authors identified relevant trials by assessing the abstracts of all possible studies. We applied no language restrictions.
Selection criteria: We selected randomised controlled trials (RCTs) of alprazolam versus placebo or conventional antidepressants for depression in adults, excluding studies with inpatients only.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors performed the data extraction and 'Risk of bias' assessment independently with disagreements resolved through discussion with a third review author. Primary outcomes included the mean difference (MD) in reduction of depression on a continuous measure of depression symptoms, and the risk ratio (RR) of the clinical response based on a dichotomous measure, with 95% confidence intervals (CI).
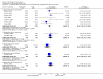
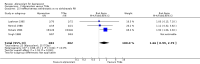
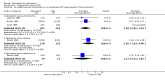
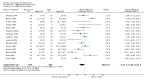
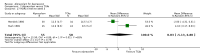
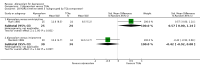
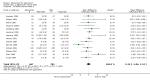
Main results: We identified 21 alprazolam studies (22 reports) with a total of 2693 participants. Seven studies used a placebo (n = 771) and 20 used cyclic antidepressants (n = 1765). The typical duration of the studies was four to six weeks. We considered six studies to have a high risk of bias.When alprazolam was compared with placebo for reduction in symptoms all estimates indicated a positive effect for alprazolam. Pooled estimates of efficacy data showed a moderately large continuous mean difference (MD) at the end of trial (-5.34, 95% CI -7.48 to -3.20; I(2) = 68%). The risk difference (RD) for the dichotomous measure of clinical response (50% improvement) was 0.32 in favour of alprazolam (95% CI 0.22 to 0.42; I(2) = 0%), with a number needed to treat to benefit (NNTB) of 3 (95% CI 2 to 5). The RD of all-cause withdrawals did not differ between alprazolam and placebo.When depression severity was measured as a continuum the effect of alprazolam did not differ statistically or clinically from the effects of any of the conventional antidepressants combined (MD 0.25, 95% CI -0.93 to 1.43; I(2) = 55%). However, for dichotomised depression severity, alprazolam had less effect than antidepressants (RR 0.86, 95% CI 0.75 to 0.99; I(2) = 37%; RD -0.11, 95% CI -0.24 to 0.01; I(2) = 58%; NNTB 9, 95% CI 4 to 100). The RD of all-cause withdrawals was -0.04 (95% CI -0.07 to 0.00; I(2) = 35%), in favour of alprazolam.
Authors' conclusions: Alprazolam appears to reduce depressive symptoms more effectively than placebo and as effectively as tricyclic antidepressants. However, the studies included in the review were heterogeneous, of poor quality and only addressed short-term effects, thus limiting our confidence in the findings. Whilst the rate of all-cause withdrawals did not appear to differ between alprazolam and placebo, and withdrawals were less frequent in the alprazolam group than in any of the conventional antidepressants combined group, these findings should be interpreted with caution, given the dependency properties of benzodiazepines.
Conflict of interest statement
Harm van Marwijk has not received any payments from relevant stakeholders, such as pharmaceutical industries, for this project. He is involved with research in mental health in primary care. The majority of his projects are sponsored by the Dutch government. He is a member of a Dutch working party on revision of national guidelines for anxiety and depression. GA, FW, AB and IR: none declared.
Figures
















































Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Ansseau 1984 {published data only}
-
- Ansseau M, Ansoms C, Beckers G, Bogaerts M, Botte L, Buck R, et al. Double‐blind clinical study comparing alprazolam and doxepin in primary unipolar depression. Journal of Affective Disorders 1984;7(3‐4):287‐96. - PubMed
Banerji 1989 {published data only}
-
- Banerji JR, Brantingham P, McEwan GD, Mason J, Munt DF, Renton RL, et al. A comparison of alprazolam with amitriptyline in the treatment of patients with neurotic or reactive depression. A report of a randomised, double blind study by a general practitioner working party. Irish Journal of Medical Science 1989;158(5):110‐3. - PubMed
Bassi 1990 {published data only}
-
- Bassi S, Albizzati MG, Sbacchi M, Corsini GU, Pancheri P, Romiti R, et al. Clinical evaluation of alprazolam versus mianserin in the treatment of patients with depressive neurosis [Valutazione clinica dell'alprazolam nei confronti della mianserina nel trattamento dei pazienti affetti da nevrosi depressiva]. Giornale di Neuropsicofarmacologia 1990;12(1):35‐8.
Borison 1989 {published data only}
-
- Borison RL, Sinha D, Albrecht W, Geber S, Diamond BI. Double‐blind comparison of 3‐ and 6‐mg fixed doses of alprazolam vs. placebo in outpatients with major depressive disorder. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1989;25(2):186‐9. - PubMed
Cropper 1987 {published data only}
-
- Cropper M, Garner A, McEwan GD, Munt FDF, Rushbrook LAW, Stevens V, et al. A double‐blind comparative study of alprazolam and dothiepin hydrochloride in the treatment of anxiety associated with depression. Pharmatherapeutica 1987;5(2):76‐82. - PubMed
di Perri 1990 {published data only}
-
- Perri R, Rosa AE, Morgante L, Rosa A, Sannino V. Alprazolam versus amitriptyline in the treatment of patients with nervous depression [Alprazolam versus amitriptilina nel trattamento di pazienti con nevrosi depressiva]. Rivista N.P.S. Neurologia Psichiatria Scienze Umane 1990;10:43‐53.
Draper 1983 {published data only}
-
- Draper RJ, Daly I. Alprazolam and amitriptyline: a double blind comparison of anxiolytic and anti‐depressant activity. Irish Medical Journal 1983;76(11):453‐6. - PubMed
Fabre 1980 {published data only}
-
- Fabre LF, McLendon DM. A double‐blind comparison of alprazolam, imipramine, and placebo in primary depression [conference abstract]. Clinical Research 1979;27(2):542A.
-
- Fabre LF, McLendon DM. A double‐blind study comparing the efficacy and safety of alprazolam with imipramine and placebo in primary depression. Current Therapeutic Research 1980;27(5):474‐82.
Feighner 1983a {published data only}
-
- Feighner JP, Meredith CH, Frost NR, Chammas S, Hendrickson G. A double‐blind comparison of alprazolam vs. imipramine and placebo in the treatment of major depressive disorder. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1983;68(4):223‐33. - PubMed
Goldberg 1986 {published data only}
-
- Goldberg SC, Ettigi P, Schulz PM, Hamer RM, Hayes PE, Friedel RO. Alprazolam versus imipramine in depressed out‐patients with neurovegetative signs. Journal of Affective Disorders 1986;11(2):139‐45. - PubMed
Imlah 1985 {published data only}
-
- Imlah NW. An evaluation of alprazolam in the treatment of reactive or neurotic (secondary) depression. British Journal of Psychiatry 1985;146:515‐9. - PubMed
Laakman 1995 {published data only}
-
- Laakman G, Faltermaier‐Temizel M, Bossert‐Zaudig S, Baghai T, Lorkowski G. Treatment of depressive outpatients with lorazepam, alprazolam, amitriptyline and placebo. Psychopharmacology 1995;120:109‐15. - PubMed
-
- Laakmann G, Faltermaier‐Temizel M, Bossert‐Zaudig S, Baghai T, Lorkowski G. Treatment of mild to moderate depressive syndrome. A placebo‐controlled double‐blind trial on therapy with benzodiazepines or antidepressants [German]. Munchener Medizinische Wochenschrift 1996;138(5):39‐44.
Lapierre 1994 {published data only}
-
- Lapierre YD, Browne M, Oyewumi K, Sarantidis D. Alprazolam and amitriptyline in the treatment of moderate depression. International Clinical Psychopharmacology 1994;9:41‐5. - PubMed
Mendels 1986 {published data only}
-
- Mendels J, Schless AP. Comparative efficacy of alprazolam, imipramine, and placebo administered once a day in treating depressed patients. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1986;47(7):357‐61. - PubMed
Murthy 1991 {published data only}
Overall 1987 {published data only}
-
- Overall JE, Biggs J, Jacobs M, Holden K. Comparison of alprazolam and imipramine for treatment of outpatient depression. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1987;48(1):15‐9. - PubMed
-
- Overall JE, Donachie ND, Faillace LA. Implications of restrictive diagnosis for compliance to antidepressant drug therapy: alprazolam versus imipramine. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1987;48(2):51‐4. - PubMed
Remick 1988 {published data only}
-
- Remick RA, Fleming JAE, Buchanan RA, Keller FD, Hamilton P, Loomer F, et al. A comparison of the safety and efficacy of alprazolam and desipramine in moderately severe depression. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry 1985;30(8):597‐601. - PubMed
-
- Remick RA, Keller D, Buchanan RA, Gibson RE, Fleming JAE. A comparison of the efficacy and safety of alprazolam and desipramine in depressed outpatients. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry 1988;33:590‐4. - PubMed
Rickels 1985 {published data only}
-
- Rickels K, Feighner JP, Smith WT. Alprazolam, amitriptyline, doxepin, and placebo in the treatment of depression. Archives of General Psychiatry 1985;42(2):134‐41. - PubMed
Rickels 1987 {published data only}
-
- Rickels K, Chung HR, Csanalosi IB, Hurowitz AM, London J, Wiseman K, et al. Alprazolam, diazepam, imipramine, and placebo in outpatients with major depression. Archives of General Psychiatry 1987;44(10):862‐6. - PubMed
Rush 1985 {published data only}
-
- Rush AJ, Erman MK, Schlesser MA, Roffwarg HP, Vasavada N, Khatami M, et al. Alprazolam vs amitriptyline in depression with reduced REM latencies. Archives of General Psychiatry 1985;42:1154‐9. - PubMed
Singh 1988 {published data only}
-
- Singh AN, Nair NPV, Suranyi‐Cadotte B, Schwartz G, Lizondo E. A double blind comparison of alprazolam and amitriptyline hydrochloride in the treatment of nonpsychotic depression. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry 1988;33(3):218‐22. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Aden 1983 {published data only}
-
- Aden GC. Alprazolam in clinically anxious patients with depressed mood. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1983;44(1):22‐4. - PubMed
Beutler 1987 {published data only}
-
- Beutler LE, Scogin F, Kirkish P, Schretlen D, Corbishley A, Hamblin D, et al. Group cognitive therapy and alprazolam in the treatment of depression in older patients. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1987;55(4):550‐6. - PubMed
Ceskova 1989 {published data only}
-
- Ceskova E, Svestka J, Nahunek K, Obrovska V. Double blind comparison of alprazolam with dosulepine in endogenous depression. Activitas Nervosa Superior 1989;31(4):290‐1. - PubMed
Eriksson 1987 {published data only}
-
- Eriksson B, Nagy A, Starmark J‐E, Thelander U. Alprazolam compared to amitriptyline in the treatment of major depression. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1987;75:656‐63. - PubMed
Ettigi 1988 {published data only}
-
- Ettigi PE, Goldberg SC, Schulz PM, Hamer RM, Blackard WG. Cortisol differentially predicts response to imipramine and alprazolam. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1988;24(1):206‐9. - PubMed
Fawcett 1987 {published data only}
-
- Fawcett J, Edwards JH, Kravitz HM, Jeffriess H. Alprazolam: an antidepressant? Alprazolam, desipramine, and an alprazolam‐desipramine combination in the treatment of adult depressed outpatients. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 1987;7(5):295‐310. - PubMed
Feighner 1983b {published data only}
-
- Feighner JP, Aden GC, Fabre LF, Rickels K, Smith WT. Comparison of alprazolam, imipramine, and placebo in the treatment of depression. JAMA 1983;249(22):3057‐64. - PubMed
Hubain 1990 {published data only}
-
- Hubain PP, Castro P, Mesters P, Maertelaer V, Mendlewicz J. Alprazolam and amitriptyline in the treatment of major depressive disorder: a double‐blind clinical and sleep EEG study. Journal of Affective Disorders 1990;18:67‐73. - PubMed
Keller 1993 {published data only}
-
- Keller MB, Lavori PW, Goldenberg IM, Baker LA, Pollack MH, Sachs GS, et al. Influence of depression on the treatment of panic disorder with imipramine, alprazolam and placebo. Journal of Affective Disorders 1993;28:27‐38. - PubMed
Kravitz 1990 {published data only}
-
- Kravitz HM, Fogg L, Fawcett J, Edwards J. Antidepressant or antianxiety? A study of the efficacy of antidepressant medication. Psychiatry Research 1990;32:141‐9. - PubMed
Lenox 1984 {published data only}
-
- Lenox RH, Shipley JE, Peyser JM, Williams JM, Weaver LA. Double‐blind comparison of alprazolam versus imipramine in the inpatient treatment of major depressive illness. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1984;20(1):79‐82. - PubMed
Pitts 1983 {published data only}
-
- Pitts WM, Fann WE, Sajadi C, Snyder S. Alprazolam in older depressed patients. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1983;44:213‐5. - PubMed
Pollack 1994 {published data only}
-
- Pollack MH, Otto MW, Sachs GS, Leon A, Shear MK, Deltito JA, et al. Anxiety psychopathology predictive of outcome in patients with panic disorder and depression treated with imipramine, alprazolam and placebo. Journal of Affective Disorders 1994;30(4):273‐81. - PubMed
Rickels 1982 {published data only}
-
- Rickels K, Cohen D, Csanalosi I, Harris H, Koepke H, Werblowsky J. Alprazolam and imipramine in depressed outpatients: a controlled study. Current Therapeutic Research 1982;32(6):157‐64.
Rimon 1991 {published data only}
-
- Rimon R, Kultalahti ER, Kalli A, Koskinen T, Lepola U, Naarala M, et al. Alprazolam and oxazepam in the treatment of anxious out‐patients with depressive symptoms: a double‐blind multicenter study. Pharmacopsychiatry 1991;24(3):81‐4. - PubMed
Rothblum 1982 {published data only}
-
- Rothblum ED, Sholomskas AJ, Berry C, Prusoff BA. Issues in clinical trials with depressed elderly. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 1982;30(11):694‐9. - PubMed
Weissman 1985 {published data only}
-
- Weissman MM, Prusoff BA, Kleber HD, Sholomskas AJ, Rounsaville BJ. Alprazolam (Xanax) in the treatment of major depression. Clinical and Pharmacological Studies in Psychiatric Disorders. John Libbey, 1985:52‐8.
Weissman 1992 {published data only}
-
- Weissman MM, Prushoff B, Sholomskas AJ, Greenwald S. A double‐blind clinical trial of alprazolam, imipramine, or placebo in the depressed elderly. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 1992;12(3):175‐82. - PubMed
Zung 1983 {published data only}
-
- Zung WWK, King RE. Identification and treatment of masked depression in a general medical practice. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1983;44(10):365‐8. - PubMed
Additional references
APA 1980
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 3rd Edition. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association, 1980.
APA 1994
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM‐IV). 4th Edition. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association, 1994.
APA 2000
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th Edition, Text Revision (DSM‐IV‐TR). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association, 2000.
Bandelow 2008
-
- Bandelow B, Zohar J, Hollander E, Kasper S, Moller HJ, WFSB task force on treatment guidelines for anxiety obsessive‐compulsive post‐traumatic stress disorders. World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry (WFSBP) guidelines for the pharmacological treatment of anxiety, obsessive‐compulsive and post‐traumatic stress disorders ‐ first revision. World Journal of Biological Psychiatry 2008;9(4):248‐312. - PubMed
Barbone 1998
-
- Barbone F, McMahon AD, Davey PG, Morris AD, Reid IC, McDevitt DG, et al. Association of road‐traffic accidents with benzodiazepine use. Lancet 1998;352(9137):1331‐6. - PubMed
Birkenhager 1995
-
- Birkenhager TK, Moleman P, Nolen WA. Benzodiazepines for depression? A review of the literature. International Clinical Psychopharmacology 1995;10:181‐93. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Committee 1980
Covi 1976
-
- Lipman RS, Covi L. Outpatient treatment of neurotic depression: medication and group psychotherapy. In: Spitzer RL, Klein DF editor(s). Evaluation of Psychological Therapies. Baltimore, MD: Baltimore University Press, 1976:178‐218. - PubMed
DerSimonian 1986
-
- DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta‐analysis in clinical trials. Controlled Clinical Trials 1986;7(3):177‐88. - PubMed
Feighner 1972
-
- Feighner JP, Robins E, Guze SB, Woodruff RA Jr, Winokur G, Munoz R. Diagnostic criteria for use in psychiatric research. Archives of General Psychiatry 1972;26(1):57‐63. - PubMed
Fournier 2010
Furukawa 2001
-
- Furukawa TA, Streiner D, Young LT, Kinoshita Y. Antidepressants plus benzodiazepines for major depression. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2001, Issue 3. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001026] - DOI
Furukawa 2006
-
- Furukawa TA, Barbui C, Cipriani A, Brambilla P, Watanabe N. Imputing missing standard deviations in meta‐analyses can provide accurate results. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2006;59:7‐10. - PubMed
Hamilton 1960
Hansen 2004
-
- Hansen DG, Vach W, Rosholm JU, Sondergaard J, Gram LF, Kragstrup J. Early discontinuation of antidepressants in general practice: association with patient and prescriber characteristics. Family Practice 2004;21:623‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Higgins 2009
-
- Higgins JPT, Greene S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions 5.0.2 [Updated September 2009]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2009. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Jonas 1993
-
- Jonas JM, Cohon MS. A comparison of the safety and efficacy of alprazolam versus other agents in the treatment of anxiety, panic and depression: a review of the literature. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1993;54:S25‐45. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kirsch 2008
Lawrenson 2000
-
- Lawrenson RA, Tyrer F, Newson RB, Farmer RD. The treatment of depression in UK general practice: selective serotonin inhibitors and tricyclic antidepressants compared. Journal of Affective Disorders 2000;59:149‐57. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Moncrieff 2004
Montgomery 1979
-
- Montgomery SA, Asberg M. A new depression scale designed to be sensitive to change. British Journal of Psychiatry 1979;134:382‐9. - PubMed
Neutel 1996
-
- Neutel CI, Hirdes JP, Maxwell CJ, Patten SB. New evidence on benzodiazepine use and falls: the time factor. Age and Ageing 1996;25(4):273‐8. - PubMed
NICE 2009
-
- National Institute for Clinical Excellence (NICE). Depression. The Treatment and Management of Depression in Adults [CG90]. London: National Institute for Clinical Excellence, 2009.
Petty 1995
-
- Petty F, Trivedi MH, Fulton M, Rush AJ. Benzodiazepines as antidepressants: does GABA play a role in depression?. Biological Psychiatry 1995;38(9):578‐91. - PubMed
Raskin 1970
-
- Raskin A, Schulterbrandt JG, Reatig N, Chase C, McKeen JJ. Differential response to chlorpromazine, imipramine and placebo. Archives of General Psychiatry 1970;23:164‐73. - PubMed
RevMan 2011 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.1. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.
Rickels 1990
-
- Rickels K, Schweizer E, Case WG, Greenblatt DJ. Long‐term therapeutic use of benzodiazepines. I. Effects of abrupt discontinuation. Archives of General Psychiatry 1990;47(10):899‐907. - PubMed
Rijswijk 2007
-
- Rijswijk E, Borghuis M, Lisdonk E, Zitman F, Weel C. Treatment of mental health problems in general practice: a survey of psychotropics prescribed and other treatments provided. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2007;45(1):23‐9. - PubMed
Schweizer 1990
-
- Schweizer E, Rickels K, Case WG, Greenblatt DJ. Long‐term therapeutic use of benzodiazepines. II. Effects of gradual taper. Archives of General Psychiatry 1990;47(10):908‐15. - PubMed
Schweizer 1998
-
- Schweizer E, Rickels K. Benzodiazepine dependence and withdrawal: a review of the syndrome and its clinical management. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, Supplementum 1998;393:95‐101. - PubMed
Sethy 1982
-
- Sethy VH, Hodges DH Jr. Alprazolam in a biochemical model of depression. Biochemical Pharmacology 1982;31(19):3155‐7. - PubMed
Srisurapanont 1997
-
- Srisurapanont M, Boonyanaruthee V. Alprazolam and standard antidepressants in the treatment of depression: a meta‐analysis of antidepressant effect. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand 1997;80(3):183‐8. - PubMed
Van Marwijk 2003
-
- Marwijk HW, Grundmeijer HGLM, Bijl D, Gelderen MG, Haan M, Weel‐Baumgarten EM, et al. Dutch College of General Practitioners Guideline Depression, first revision. Huisarts en Wetenschap 2003;46:614‐23.
Van Marwijk 2006
-
- Marwijk H. "A catalogue of biases": the need for a European perspective on antidepressants' evidence in general practice. European Journal of General Practice 2006;12(3):98‐9. - PubMed
WHO 2003
-
- World Health Organization. International Classification of Diseases (ICD‐10). Geneva: World Health Organization, 2003.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

