Social skills groups for people aged 6 to 21 with autism spectrum disorders (ASD)
- PMID: 22786515
- PMCID: PMC11975264
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008511.pub2
Social skills groups for people aged 6 to 21 with autism spectrum disorders (ASD)
Abstract
Background: Since autism was first described, major difficulties in social interaction have been a defining feature of individuals with autism spectrum disorders (ASD). Social skills groups are a common intervention for individuals with ASD. Although a frequently recommended practice, the few studies that have addressed the efficacy of social skills groups have shown mixed results.
Objectives: To determine the effectiveness of social skills groups for improving social competence, social communication, and quality of life for people with ASD who are six to 21 years of age.
Search methods: We searched the following databases in December 2011: CENTRAL (2011 Issue 4), MEDLINE (1948 to November Week 3, 2011), EMBASE (1980 to Week 50, 2011), PsycINFO (1887 to December Week 2, 2011), CINAHL (1937 to current), ERIC (1966 to current), Sociological Abstracts (1952 to current), OCLC WorldCat (12 December 2011), Social Science Citation Index (1970 to 16 December 2011), and the metaRegister of Controlled Trials (20 December 2011). We also searched the reference lists of published papers.
Selection criteria: Randomized control trials (RCTs) comparing treatment (social skills groups) with a control group who were not receiving the treatment for participants aged six to 21 years with ASD. The control group could be no intervention, wait list, or treatment as usual. Outcomes sought were standardized measures of social competence, social communication, quality of life, emotion recognition, and any other specific behaviors.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently selected and appraised studies for inclusion and assessed the risk of bias in each included study. All outcome data were continuous and standardized mean difference effect sizes (ES) with small sample correction were calculated. We conducted random-effects meta-analysis where possible.
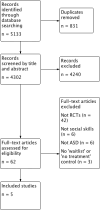
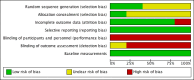
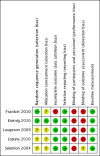
Main results: We included five RCTs evaluating the effects of social skills groups in 196 participants with ASD aged 6 to 21 years old. The results show there is some evidence that social skills groups improve overall social competence (ES = 0.47, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.16 to 0.78, P = 0.003) and friendship quality (ES = 0.41, 95% CI 0.02 to 0.81, P = 0.04) for this population. No differences were found between treatment and control groups in relation to emotional recognition (ES = 0.34, 95% CI -0.20 to 0.88, P = 0.21) assessed in two studies or social communication as related to the understanding of idioms (ES = 0.05, 95% CI -0.63 to 0.72, P = 0.89), which was assessed in only one study. Two additional quality of life outcomes were evaluated, with results of single studies suggesting decreases in loneliness (ES = -0.66, 95% CI -1.15 to -0.17) but no effect on child or parental depression. No adverse events were reported.Given the nature of the intervention and the selected outcome measures, the risk of performance and detection bias are high. There is limited generalizability from the studies as they were all conducted in the US; they focused mainly on children aged 7 to 12, and the participants were all of average or above average intelligence.
Authors' conclusions: There is some evidence that social skills groups can improve social competence for some children and adolescents with ASD. More research is needed to draw more robust conclusions, especially with respect to improvements in quality of life.
Conflict of interest statement
Brian Reichow ‐ receives royalties from book publication, honoraria from lectures on autism spectrum disorders, and has received funding from the US Department of Education, none of which supported or influenced my work on this review. Amanda M Steiner ‐ receives honoraria from lectures on autism spectrum disorders, and has received funding from the US National Institutes of Health, none of which supported or influenced my work on this review. Fred Volkmar ‐ receives royalties from book publication, honoraria from lectures on autism spectrum disorders, and has received funding from the US National Institutes of Health, none of which supported or influenced my work on this review.
Figures


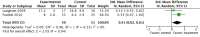

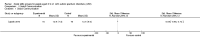

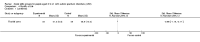

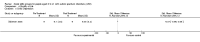
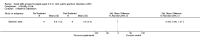
Comment in
-
Review: social skills groups may improve social competence in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder.Evid Based Ment Health. 2013 Feb;16(1):11. doi: 10.1136/eb-2012-100985. Epub 2012 Oct 23. Evid Based Ment Health. 2013. PMID: 23093693 No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
Frankel 2010 {published data only}
Koenig 2010 {published data only}
-
- Koenig K, White SW, Pachler M, Lau M, Lewis M, Klin A, et al. Promoting social skill development in children with pervasive developmental disorders: a feasibility and efficacy study. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 2010;40(10):1209‐18. - PubMed
Laugeson 2009 {published data only}
-
- Laugeson EA, Frankel F, Mogil C, Dillon AR. Parent‐assisted social skills training to improve friendships in teens with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 2009;39(4):596‐606. - PubMed
Lopata 2010 {published data only}
-
- Lopata C, Thomeer ML, Volker MA, Toomey JA, Nida RE, Lee GK, et al. RCT of a manualized social treatment for high‐functioning autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 2010;40(11):1297‐310. - PubMed
Solomon 2004 {published data only}
-
- Solomon M, Goodlin‐Jones BL, Anders TF. A social adjustment enhancement intervention for high functioning autism, Asperger's syndrome and pervasive developmental disorder NOS. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 2004;34(6):649‐68. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Baghdadli 2010 {published data only}
-
- Baghdadli A, Brisot‐Dubois J, Picot MC, Michelon C. Comparison of the effect of two prosocial interventions about the evolution of recognition of facial expression abilities and social cognition of children with Asperger syndrome or high functioning autism [Comparaison de leffet de deux interventions prosociales sur lévolution des capacités didentification des expressions faciales et du raisonnement social denfants avec un syndrome dAsperger ou autisme de haut niveau]. Neuropsychiatrie de l'Enfrance et de l'Adolescence 2010;58(8):456‐62.
Barry 2003 {published data only}
-
- Barry TD, Klinger LG, Lee JM, Palardy N, Gilmore T, Bodin SD. Examining the effectiveness of an outpatient clinic‐based social skills group for high‐functioning children with autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 2003;33(6):685‐701. - PubMed
Beaumont 2008 {published data only}
-
- Beaumont R, Sofronoff K. A multi‐component social skills intervention for children with Asperger syndrome: The junior Detective program. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry 2008;49(7):743‐53. - PubMed
Domitrovich 2007 {published data only}
-
- Domitrovich CE, Cortes RC, Greenberg MT. Improving young children's social and emotional competence: A randomized trial of the preschool "PATHS" curriculum. The Journal of Primary Prevention 2007;28(2):67‐91. - PubMed
Godfrey 2005 {published data only}
-
- Godfrey J, Pring T, Gascoigne M. Developing children's conversational kills in mainstream schools: An evaluation of group therapy. Child Language Teaching and Therapy 2005;21(3):251‐62.
Golan 2006 {published data only}
-
- Golan O, Baron‐Cohen S. Systematizing empathy: Teaching adults with Asperger syndrome or high‐functioning autism to recognize complex emotions using interactive multimedia. Develompent and Psychopathology 2006;18:591‐617. - PubMed
Kroeger 2007 {published data only}
-
- Kroeger KA, Schultz JR, Newsom C. A comparison of two group‐delivered social skills programs for young children with autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 2007;37(5):808‐17. - PubMed
Mesibov 1984 {published data only}
-
- Mesibov GB. Social skills training with verbal autistic adolescents and adults: a program model. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 1984;14(4):395‐404. - PubMed
Ozonoff 1995 {published data only}
-
- Ozonoff S, Miller JN. Teaching theory of mind: a new approach to social skills training for individuals with autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 1995;25(4):514‐33. - PubMed
Additional references
APA 2000
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th Edition. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association, 2000.
Asher 1984
-
- Asher SR, Hymel S, Renshaw PD. Loneliness in children. Child Development 1984;55(4):1456‐64.
Bukowski 1994
-
- Bukowski WM, Hoza B, Boivin M. Measuring friendship quality during pre‐and early adolescence: the development and psychometric properties of the Friendship Qualities Scale. Journal of Social and Personal Relationships 1994;11(3):471‐84.
Burlingame 2003
-
- Burlingame GM, Fuhriman A, Mosier J. The differential effectiveness of group psychotherapy: A meta‐analytic perspective. Group Dynamics: Theory, Research, and Practice 2003;7(1):3‐12.
Cappadocia 2011
-
- Cappadocia MC, Weiss JA. Review of social skills training groups for youth with Asperger syndrome and high functioning autism. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders 2011;5(1):70‐8.
Carrow‐Woolfolk 1999
-
- Carrow‐Woolfolk E. Comprehensive Assessment of Spoken Language. Circle Pines, MN: American Guidance Services, 1999.
Carter 2005
-
- Carter AS, Davis NO, Klin A, Volkmar FR. Social development in autism. In: Volkmar FR, Paul R, Klin A, Cohen DJ editor(s). Handbook of Autism and Pervasive Developmental Disorders. 3rd Edition. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2005:312‐34.
Constantino 2005
-
- Constantino JH, Gruber CP. Social Responsiveness Scale. Los Angeles, CA: Western Psychological Services, 2005.
Cotugno 2009
-
- Cotugno AJ. Group Interventions with Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. London: Jessica Kingsley, 2009.
Dawson 2011
-
- Dawson G, Burner K. Behavioral interventions in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder: A review of recent findings. Current Opinion in Pediatrics 2011;23(6):616‐20. - PubMed
Dunn 2006
-
- Dunn MA. S.O.S.: Social Skills in our Schools: A Social Skills Program for Children with Pervasive Developmental Disorders, including High‐Functioning Autism and Asperger Syndrome, and their Typical Peers. Shawnee Mission, KS: Autism Asperger Publishing Company, 2006.
Elbourne 2002
-
- Elbourne DR, Altman DG, Higgins JPT, Curtin F, Worthington HV, Vail A. Meta‐analyses involving cross‐over trials: methodological issues. International Journal of Epidemiology 2002;31(1):140‐9. - PubMed
Frankel 2003
-
- Frankel F, Myatt R. Children's Friendship Training. New York: Brunner‐Routledge, 2003.
Goin‐Kochel 2007
-
- Goin‐Kochel RP, Myers BJ, Mackintosh VH. Parental reports on the use of treatments and therapies for children with autism spectrum disorder. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders 2007;1(3):195‐209.
Goldstein 2000
-
- Goldstein AP, McGinnis E. Skill Streaming the Adolescent: New Strategies and Perspectives for Teaching Prosocial Skills. Champaign, IL: Research Press, 2000.
GRADEpro 2012 [Computer program]
-
- GRADEpro. Version 3.2 for Windows. Jan Brozek, Andrew Oxman, Holger Schünemann, 2008.
Green 2006
-
- Green VA, Pituch KA, Itchon J, Choi A, O'Reilly M, Sigafoos J. Internet survey of treatments used by parents of children with autism. Research in Developmental Disabilities 2006;27(1):70‐84. - PubMed
Gresham 1990
-
- Gresham FM, Elliot SN. Social Skills Rating System. Circle Pines, MN: American Guidance Service, 1990.
Gupta 2007
-
- Gupta AR, State MW. Recent advances in the genetics of autism. Biological Psychiatry 2007;61(4):429‐37. - PubMed
Hedges 1985
-
- Hedges L, Olkin I. Statistical Models for Meta‐Analysis. New York: Academic Press, 1985.
Higgins 2002
-
- Higgins JPT, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta‐analysis. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21:1539‐58. - PubMed
Higgins 2008
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, 2008.
Hoag 1997
-
- Hoag MJ, Burlingame GM. Evaluating the effectiveness of child and adolescent group treatment: A meta‐analytic review. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology 1997;26(3):234‐46. - PubMed
Howlin 2005
-
- Howlin P. Outcomes in autism spectrum disorders. In: Volkmar FR, Paul R, Klin A, Cohen DJ editor(s). Handbook of Autism and Pervasive Developmental Disorders. Third Edition. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2005:201‐22.
Kanner 1943
-
- Kanner L. Autistic disturbances of affective contact. Nervous Child 1943;2:217‐50. - PubMed
Klin 2002a
-
- Klin A, Jones W, Schultz R, Volkmar FR, Cohen D. Defining and quantifying the social phenotype in autism. American Journal of Psychiatry 2002;159(6):895‐908. - PubMed
Klin 2002b
-
- Klin A, Jones W, Schultz R, Volkmar FR, Cohen D. Visual fixation patterns during viewing of naturalistic social situations as predictors of social competence in individuals with autism. Archives of General Psychiatry 2002;59(9):809‐16. - PubMed
Klin 2003
Klin 2005
-
- Klin A, Pauls D, Schultz R. Three diagnostic approaches to Asperger syndrome: implications for research. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 2005;35(2):221‐34. - PubMed
Laugeson 2010
-
- Laugeson EA, Frankel F. Social Skills for Teenagers With Developmental and Autism Spectrum Disorders: The PEERS Treatment Manual. New York: Routledge, 2010. - PubMed
McGinnis 1997
-
- McGinnis E, Goldstien AP. Skillstreaming the Elementary School Child: New Strategies and Perspectives for Teaching Prosocial Skills. Revised. Champaign, IL: Research Press, 1997.
Minshew 2005
-
- Minshew NJ, Sweeney JA, Bauman ML, Webb SJ. Neurologic aspects of autism. In: Volkmar FR, Paul R, Klin A, Cohen DJ editor(s). Handbook of Autism and Pervasive Developmental Disorders. Third Edition. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2005.
National Research Council 2001
-
- National Research Council. Educating Children With Autism. Washington, DC: National Academies Press, 2001.
Nowicki 1997
-
- Nowicki S. Instructional Manual for the Receptive Tests of the Diagnostic Analysis of Nonverbal Accuracy 2. Atlanta, GA: Peachtree, 1997.
Painter 2006
-
- Painter KK. Social Skills Groups for Children and Adolescents with Asperger's Syndrome: A Step By Step Program. London: Jessica Kingsley Publishers, 2006.
Paul 2003
-
- Paul R. Promoting social communication in high functioning individuals with autistic spectrum disorders. Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics of North America 2003;12:87‐106. - PubMed
Piers 1984
-
- Piers EV. Piers‐Harris Children's Self‐Concept Scale: Revised Manual. Los Angeles: Western Psychological Services, 1984.
Rao 2008
-
- Rao PA, Beidel PC, Murray MJ. Social skills interventions for children with Aspergers syndrome or high‐functioning autism: a review and recommendations. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 2008;38(2):353‐61. - PubMed
Reichow 2010
-
- Reichow B, Volkmar FR. Social skills interventions for individuals with autism: evaluation for evidence‐based practices within a best evidence synthesis framework. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 2010;40(2):149‐66. - PubMed
Reichow 2011
-
- Reichow B, Doehring P, Cicchetti DV, Volkmar FR. Evidence‐Based Practices and Treatments for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. New York, NY: Springer, 2011.
Rydell 1997
-
- Rydell A, Hadekull B, Bohlin G. Measurement of two social competence aspects in middle childhood. Developmental Psychology 1997;33(5):824‐33. - PubMed
Schultz 2000
-
- Schultz RT, Gauthier I, Klin A, Fulbright R, Anderson A, Volkmar FR, et al. Abnormal ventral temporal cortical activity during face discrimination among individuals with autism and Asperger syndrome. Archives of General Psychiatry 2000;57(4):331‐40. - PubMed
Shea 2005
-
- Shea V, Mesibov GB. Adolescents and adults with autism. In: Volkmar FR, Paul R, Klin A, Cohen DJ editor(s). Handbook of Autism and Pervasive Developmental Disorders. Third Edition. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2005:288‐311.
Siegel 1989
-
- Siegel B, Vukicevic J, Elliot GR, Kraemer HC. The use of signal detection theory to assess DSM‐III‐R criteria for autistic disorder. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 1989;28(4):542‐8. - PubMed
Sparrow 1984
-
- Sparrow SS, Balla DA, Cicchetti DV. Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scales. Circle Pines, MN: American Guidance Service, 1984.
Sparrow 2005
-
- Sparrow SS, Cicchetti DV, Balla DA. Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scales. 2nd Edition. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson, 2005.
Towbin 2005
-
- Towbin KE, Pradella A, Gorrindo T, Pine DS, Leibenluft E. Autism spectrum traits in children with mood and anxiety disorders. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology 2005;15(3):452‐64. - PubMed
Volkmar 2005a
-
- Volkmar FR, Klin A. Issues in the classification of autism and related conditions. In: Volkmar FR, Paul R, Klin A, Cohen DJ editor(s). Handbook of Autism and Pervasive Developmental Disorders. 3rd Edition. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2005.
Volkmar 2005b
-
- Volkmar FR. International perspectives. In: Volkmar FR, Paul R, Klin A, Cohen DJ editor(s). Handbook of Autism and Pervasive Developmental Disorders. 3rd Edition. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2005:1193‐252.
Volkmar 2009
-
- Volkmar F, Wiesner L. A Practical Guide to Autism: What Every Parent, Family Member, and Teacher Needs to Know. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2009.
White 2007
-
- White SW, Keonig K, Schaill L. Social skills development in children with autism spectrum disorders: a review of the intervention research. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 2007;37(10):1858‐68. - PubMed
WHO 1994
-
- World Health Organization. Diagnostic Criteria for Research: International Classification of Disease. 10th Edition. Geneva: World Health Organization, 1994.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

