Combination pharmacotherapy for the treatment of neuropathic pain in adults
- PMID: 22786518
- PMCID: PMC6481651
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008943.pub2
Combination pharmacotherapy for the treatment of neuropathic pain in adults
Abstract
Background: Pharmacotherapy remains an important modality for the treatment of neuropathic pain. However, as monotherapy current drugs are associated with limited efficacy and dose-related side effects. Combining two or more different drugs may improve analgesic efficacy and, in some situations, reduce overall side effects (e.g. if synergistic interactions allow for dose reductions of combined drugs).
Objectives: This review evaluated the efficacy, tolerability and safety of various drug combinations for the treatment of neuropathic pain.
Search methods: We identified randomised controlled trials (RCTs) of various drug combinations for neuropathic pain from CENTRAL, MEDLINE, EMBASE and handsearches of other reviews and trial registries. The most recent search was performed on 9 April 2012.
Selection criteria: Double-blind, randomised studies comparing combinations of two or more drugs (systemic or topical) to placebo and/or at least one other comparator for the treatment of neuropathic pain.
Data collection and analysis: Data extracted from each study included: proportion of participants a) reporting ≥ 30% pain reduction from baseline OR ≥ moderate pain relief OR ≥ moderate global improvement; b) dropping out of the trial due to treatment-emergent adverse effects; c) reporting each specific adverse effect (e.g. sedation, dizziness) of ≥ moderate severity. The primary comparison of interest was between study drug(s) and one or both single-agent comparators. We combined studies if they evaluated the same drug class combination at roughly similar doses and durations of treatment. We used RevMan 5 to analyse data for binary outcomes.
Main results: We identified 21 eligible studies: four (578 participants) evaluated the combination of an opioid with gabapentin or pregabalin; two (77 participants) evaluated an opioid with a tricyclic antidepressant; one (56 participants) of gabapentin and nortriptyline; one (120 participants) of gabapentin and alpha-lipoic acid, three (90 participants) of fluphenazine with a tricyclic antidepressant; three (90 participants) of an N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) blocker with an agent from a different drug class; five (604 participants) of various topical medications; one (313 participants) of tramadol with acetaminophen; and another one (44 participants) of a cholecystokinin blocker (L-365,260) with morphine. The majority of combinations evaluated to date involve drugs, each of which share some element of central nervous system (CNS) depression (e.g. sedation, cognitive dysfunction). This aspect of side effect overlap between the combined agents was often reflected in similar or higher dropout rates for the combination and may thus substantially limit the utility of such drug combinations. Meta-analysis was possible for only one comparison of only one combination, i.e. gabapentin + opioid versus gabapentin alone. This meta-analysis involving 386 participants from two studies demonstrated modest, yet statistically significant, superiority of a gabapentin + opioid combination over gabapentin alone. However, this combination also produced significantly more frequent side effect-related trial dropouts compared to gabapentin alone.
Authors' conclusions: Multiple, good-quality studies demonstrate superior efficacy of two-drug combinations. However, the number of available studies for any one specific combination, as well as other study factors (e.g. limited trial size and duration), preclude the recommendation of any one specific drug combination for neuropathic pain. Demonstration of combination benefits by several studies together with reports of widespread clinical polypharmacy for neuropathic pain surely provide a rationale for additional future rigorous evaluations. In order to properly identify specific drug combinations which provide superior efficacy and/or safety, we recommend that future neuropathic pain studies of two-drug combinations include comparisons with placebo and both single-agent components. Given the apparent adverse impact of combining agents with similar adverse effect profiles (e.g. CNS depression), the anticipated development and availability of non-sedating neuropathic pain agents could lead to the identification of more favourable analgesic drug combinations in which side effects are not compounded.
Conflict of interest statement
In the past five years, IG and RAM have consulted for various pharmaceutical companies. In the past five years, IG and RAM have received lecture fees from pharmaceutical companies that market analgesics and other healthcare interventions. IG and RAM have received research support from charities, government and industry sources at various times, but no such support was received for this work.
Two of the studies included in this review were authored by one of the review authors (IG).
LC has no conflicts to declare.
Figures

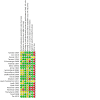
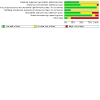




Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Agrawal 2009 {published data only}
-
- Agrawal RP, Goswami J, Jain S, Kochar DK. Management of diabetic neuropathy by sodium valproate and glyceryl trinitrate spray: a prospective double-blind randomised placebo-controlled study. Diabetes Research & Clinical Practice 2009;83(3):371-8. - PubMed
Amr 2010 {published data only}
-
- Amr YM. Multi-day low dose ketamine infusion as adjuvant to oral gabapentin in spinal cord injury related chronic pain: a prospective, randomised, double blind trial. Pain Physician 2010;13(3):245-9. - PubMed
Barton 2011 {published data only}
Caraceni 2004 {published data only}
-
- Caraceni A, Zecca E, Bonezzi C, Arcuri E, Yaya TR, Maltoni M, et al. Gabapentin for neuropathic cancer pain: a randomised controlled trial from the Gabapentin Cancer Pain Study Group. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2004;22(14):2909-17. - PubMed
Eichenberger 2008 {published data only}
-
- Eichenberger U, Neff F, Sveticic G, Bjorgo S, Petersen-Felix S, Arendt-Nielsen L, et al. Chronic phantom limb pain: the effects of calcitonin, ketamine, and their combination on pain and sensory thresholds. Anesthesia & Analgesia 2008;106(4):1265-73. - PubMed
Freeman 2007 {published data only}
-
- Freeman R, Raskin P, Hewitt DJ, Vorsanger GJ, Jordan DM, Xiang J, et al. Randomised study of tramadol/acetaminophen versus placebo in painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Current Medical Research & Opinion 2007;23(1):147-61. - PubMed
Gilron 2005b {published data only}
-
- Gilron I, Bailey JM, Tu D, Holden RR, Weaver DF, Houlden RL. Morphine, gabapentin, or their combination for neuropathic pain. New England Journal of Medicine 2005;352(13):1324-34. - PubMed
Gilron 2009 {published data only}
-
- Gilron I, Bailey JM, Tu D, Holden RR, Jackson AC, Houlden RL. Nortriptyline and gabapentin, alone and in combination for neuropathic pain: a double-blind, randomised controlled crossover trial. Lancet 2009;374(9697):1252-61. - PubMed
Gomez‐Perez 1985 {published data only}
-
- Gomez-Perez FJ, Rull JA, Dies H, Rodriquez-Rivera JG, Gonzalez-Barranco J, Lozano C. Nortriptyline and fluphenazine in the symptomatic treatment of diabetic neuropathy. A double-blind cross-over study. Pain 1985;23(4):395-400. - PubMed
Gomez‐Perez 1996 {published data only}
-
- Gomez-Perez FJ, Choza R, Rios JM, Reza A, Huerta E, Aguilar CA, Rull JA. Nortriptyline-fluphenazine vs. carbamazepine in the symptomatic treatment of diabetic neuropathy. Archives of Medical Research 1996;27(4):525-9. - PubMed
Graff‐Radford 2000 {published data only}
-
- Graff-Radford SB, Shaw LR, Naliboff BN. Amitriptyline and fluphenazine in the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia. Clinical Journal of Pain 2000;16(3):188-92. - PubMed
Hanna 2008 {published data only}
-
- Hanna M, O'Brien C, Wilson MC. Prolonged-release oxycodone enhances the effects of existing gabapentin therapy in painful diabetic neuropathy patients. European Journal of Pain 2008;12(6):804-13. - PubMed
Khoromi 2007 {published data only}
Lopez‐D'alessandro 2011 {published data only}
-
- Lopez-D'alessandro E, Escovich L. Combination of alpha lipoic acid and gabapentin, its efficacy in the treatment of Burning Mouth Syndrome: a randomised, double-blind, placebo controlled trial. Medicina Oral, Patologia Oral y Cirugia Bucal 2011;16(5):e635-40. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Lynch 2003 {published data only}
-
- Lynch ME, Clark AJ, Sawynok JA. A pilot study examining topical amitriptyline, ketamine, and a combination of both in the treatment of neuropathic pain. Clinical Journal of Pain 2003;19(5):323-8. - PubMed
Lynch 2005 {published data only}
-
- Lynch ME, Clark AJ, Sawynok J, Sullivan MJ. Topical 2% amitriptyline and 1% ketamine in neuropathic pain syndromes: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Anesthesiology 2005;103(1):140-6. - PubMed
McCleane 2000 {published data only}
McCleane 2003 {published data only}
-
- McCleane GJ. A randomised, double blind, placebo controlled crossover study of the cholecystokinin 2 antagonist L-365,260 as an adjunct to strong opioids in chronic human neuropathic pain. Neuroscience Letters 2003;338(2):151-4. - PubMed
Mercadante 2002 {published data only}
-
- Mercadante S, Arcuri E, Tirelli W, Villari P, Casuccio A. Amitriptyline in neuropathic cancer pain in patients on morphine therapy: a randomised placebo-controlled, double-blind crossover study. Tumori 2002;88(3):239-42. - PubMed
Tonet 2008 {published data only}
-
- Tonet C, Sakata RK, Issy AM, Garcia JBS, Marcelino ANM. Evaluation of oral ketamine for neuropathic pain [Avaliação da cetamina oral para dor neuropática]. Revista Brasileira de Medicina 2008;65(7):214-8.
Zin 2010 {published data only}
-
- Zin CS, Nissen LM, O'Callaghan JP, Duffull SB, Smith MT, Moore BJ. A randomised, controlled trial of oxycodone versus placebo in patients with postherpetic neuralgia and painful diabetic neuropathy treated with pregabalin. Journal of Pain 2010;11(5):462-71. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Abbas 1997 {published data only}
-
- Abbas ZG, Swai AB. Evaluation of the efficacy of thiamine and pyridoxine in the treatment of symptomatic diabetic peripheral neuropathy. East African Medical Journal 1997;74(12):803-8. - PubMed
Achar 2010 {published data only}
-
- Achar A, Chatterjee G, Ray TG, Naskar B. Comparative study of clinical efficacy with amitriptyline, pregabalin, and amitriptyline plus pregabalin combination in postherpetic neuralgia. Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology & Leprology 2010;76(1):63-5. - PubMed
Aldrete 2006 {published data only}
-
- Aldrete JA, Guevara U, Arenoso HJ, Ceraso OL. Efficacy and tolerability of epidural steroids vs low doses of steroids plus metamizol plus propoxyphene administered paravertebrally for postaminectomy syndrome patients [Eficacia y tolerabilidad de esteroides epidurales vs. dosis bajas de esteroides mas metamizol mas D-propoxifeno administrados por vía paravertebral en pacientes con síndrome post-laminectomía]. Revista de la Sociedad Espanola del Dolor 2006;13(7):454-61.
Alvaro 1999 {published data only}
-
- Alvaro M, Kumar D, Julka IS. Transcutaneous electrostimulation: emerging treatment for diabetic neuropathic pain. Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics 1999;1(1):77-80. - PubMed
Amjad 2005 {published data only}
-
- Amjad M, Mashhood AA. The efficacy of local infiltration of triamcinolone acetonide with lignocaine compared with lignocaine alone in the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia. Journal of the College of Physicians & Surgeons - Pakistan 2005;15(11):683-5. - PubMed
Amr 2011 {published data only}
-
- Amr YM. Effect of addition of epidural ketamine to steroid in lumbar radiculitis: one-year follow-up. Pain Physician 2011;14(5):475-81. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Arai 2010 {published data only}
-
- Arai YC, Matsubara T, Shimo K, Suetomi K, Nishihara M, Ushida T, et al. Low-dose gabapentin as useful adjuvant to opioids for neuropathic cancer pain when combined with low-dose imipramine. Journal of Anesthesia 2010;24(3):407-10. - PubMed
Argoff 2004 {published data only}
-
- Argoff CE, Galer BS, Jensen MP, Oleka N, Gammaitoni AR. Effectiveness of the lidocaine patch 5% on pain qualities in three chronic pain states: assessment with the Neuropathic Pain Scale. Current Medical Research & Opinion 2004;20:Suppl 8. - PubMed
Atiyat 2000 {published data only}
-
- Atiyat B. Triple-target regimen for treatment of chronic pain following post herpic neuralgia (CPPHN): a prospective trial at Jordan University Hospital (JUH) pain unit. Bahrain Medical Bulletin 2000;22(4):167-9.
Autio 2004 {published data only}
-
- Autio RA, Karppinen J, Kurunlahti M, Haapea M, Vanharanta H, Tervonen O. Effect of periradicular methylprednisolone on spontaneous resorption of intervertebral disc herniations. Spine 2004;29(15):1601-7. - PubMed
Barbarisi 2010 {published data only}
-
- Barbarisi M, Pace MC, Passavanti MB, Maisto M, Mazzariello L, Pota V, et al. Pregabalin and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation for postherpetic neuralgia treatment. Clinical Journal of Pain 2010;26(7):567-72. - PubMed
Baron 2009b {published data only}
-
- Baron R, Mayoral V, Leijon G, Binder A, Steigerwald I, Serpell M. Efficacy and safety of combination therapy with 5% lidocaine medicated plaster and pregabalin in post-herpetic neuralgia and diabetic polyneuropathy. Current Medical Research & Opinion 2009;25(7):1677-87. - PubMed
Battla 1981 {published data only}
-
- Battla H, Silverblatt CW. Clinical trial of amitriptyline and fluphenazine in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Southern Medical Journal 1981;74(4):417-8. - PubMed
Bertolotto 2012 {published data only}
Bestard 2011 {published data only}
-
- Bestard JA, Toth CC. An open-label comparison of nabilone and gabapentin as adjuvant therapy or monotherapy in the management of neuropathic pain in patients with peripheral neuropathy. Pain Practice: the official journal of World Institute of Pain 2011;11(4):353-68. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Blonna 2004 {published data only}
-
- Blonna D, Calvi V, Collo G, Marmotti A, Castoldi F. Gabapentin in the conservative treatment of radiculopathy. Minerva Ortopedica e Traumatologica 2004;55(1):15-22.
Braun 1982 {published data only}
-
- Braun H, Huberty R. Therapy of lumbar sciatica. A comparative clinical study of a corticoid-free monosubstance and a corticoid-containing combination drug. Medizinische Welt 1982;33(13):490-1. - PubMed
Bush 1991 {published data only}
-
- Bush K, Hillier S. A controlled study of caudal epidural injections of triamcinolone plus procaine for the management of intractable sciatica. Spine 1991;16(5):572-5. - PubMed
Canovas 2009 {published data only}
-
- Canovas Martinez L, Gomez Gutierrez I, Castro Bande M, Peralta Espinosa E, Prieto Gutierrez JM, Segado Jimenez I. Analgesic efficacy of the association of duloxetine plus pregabalin in neuropathic pain: experience in 60 patients. Revista de la Sociedad Espanola del Dolor 2009;16(7):381-5.
De Benedittis 1992 {published data only}
-
- De Benedittis G, Besana F, Lorenzetti A. A new topical treatment for acute herpetic neuralgia and post-herpetic neuralgia: the aspirin/diethyl ether mixture. An open-label study plus a double-blind controlled clinical trial.. Pain 1992;48(3):383-90. - PubMed
Deshpande 2006 {published data only}
-
- Deshpande MA, Holden RR, Gilron I. The impact of therapy on quality of life and mood in neuropathic pain: what is the effect of pain reduction? Anesthesia & Analgesia 2006;102(5):1473-9. - PubMed
Devulder 1999 {published data only}
-
- Devulder J, Deene P, De LM, Van BM, Brusselmans G, Rolly G. Nerve root sleeve injections in patients with failed back surgery syndrome: a comparison of three solutions. Clinical Journal of Pain 1999;15(2):132-5. - PubMed
Dureja 2010 {published data only}
-
- Dureja GP, Usmani H, Khan M, Tahseen M, Jamal A. Efficacy of intrathecal midazolam with or without epidural methylprednisolone for management of post-herpetic neuralgia involving lumbosacral dermatomes. Pain Physician 2010;13(3):213-21. - PubMed
Eardley 2010 {published data only}
Eker 2012 {published data only}
-
- Eker HE, Cok OY, Aribogan A, Arslan G. Management of neuropathic pain with methylprednisolone at the site of nerve injury. Pain Medicine (Malden, Mass.) 2012;13(3):443-51. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Ertas 1998 {published data only}
-
- Ertas M, Sagduyu A, Arac N, Uludag B, Ertekin C. Use of levodopa to relieve pain from painful symmetrical diabetic polyneuropathy. Pain 1998;75(2-3):257-9. - PubMed
Fliege 1966 {published data only}
-
- Fliege K, Mistler O. Treatment of chronic painful conditions with a diazethylthiamine (fat-soluble vitamin B 1) combination preparation. [German]. Medizinische Klinik 1966;61(52):2080-2. - PubMed
Fromm 1984 {published data only}
-
- Fromm GH, Terrence CF, Chattha AS. Baclofen in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: double-blind study and long-term follow-up. Annals of Neurology 1984;15(3):240-4. - PubMed
Galer 2004 {published data only}
-
- Galer BS, Gammaitoni AR, Oleka N, Jensen MP, Argoff CE. Use of the lidocaine patch 5% in reducing intensity of various pain qualities reported by patients with low-back pain. Current Medical Research & Opinion 2004;20:Suppl 12. - PubMed
Galer 2005 {published data only}
-
- Galer BS, Lee D, Ma T, Nagle B, Schlagheck TG. MorphiDex (morphine sulfate/dextromethorphan hydrobromide combination) in the treatment of chronic pain: three multicenter, randomised, double-blind, controlled clinical trials fail to demonstrate enhanced opioid analgesia or reduction in tolerance. Pain 2005;115(3):284-95. - PubMed
Gatti 2009 {published data only}
-
- Gatti A, Sabato AF, Occhioni R, Colini Baldeschi G, Reale C. Controlled-release oxycodone and pregabalin in the treatment of neuropathic pain: results of a multicenter Italian study. European Neurology 2009;61(3):129-37. - PubMed
Gerson 1977 {published data only}
-
- Gerson GR, Jones RB, Luscombe DK. Studies on the concomitant use of carbamazepine and clomipramine for the relief of post-herpetic neuralgia. Postgraduate Medical Journal 1977;53:Suppl 9. - PubMed
Glantz 2004 {published data only}
-
- Glantz L, Godovic G, Lekar M, Kramer M, Eidelman LA. Efficacy of transdermal nitroglycerin combined with etodolac for the treatment of chronic post-thoracotomy pain: an open-label prospective clinical trial. Journal of Pain & Symptom Management 2004;27(3):277-81. - PubMed
Glynn 1996 {published data only}
-
- Glynn C, O'Sullivan K. A double-blind randomised comparison of the effects of epidural clonidine, lignocaine and the combination of clonidine and lignocaine in patients with chronic pain. Pain 1996;64(2):337-43. - PubMed
Gobel 1995 {published data only}
-
- Gobel H, Stadler T. Treatment of pain due to postherpetic neuralgia with tramadol - results of an open, parallel pilot study vs clomipramine with or without levomepromazine. Clinical Drug Investigation 1995;10(4):208-14.
Goebel 2003 {published data only}
Goldberg 2009 {published data only}
-
- Goldberg H, Scussel Jr, Cohen JC, Rzetelna H, Mezitis SGE, Nunes FP, et al. Neural compression-induced neuralgias: clinical evaluation of the effect of nucleotides associated with vitamin B12 [Neuralgias decorrentes de compressão neural: avaliação clínica da ação de nucleotídeos associados à vitamina B12]. Revista Brasileira de Medicina 2009;66(11):380-15.
Guo 2007 {published data only}
-
- Guo W-J, Xiao Z-Y, Yang Y-X. Effectiveness of transdermal fentanyl combined with clodine for pain control of acute herpes zoster [Chinese]. Journal of Dalian Medical University 2007;29(3):255-6.
Gustin 2010 {published data only}
-
- Gustin SM, Schwarz A, Birbaumer N, Sines N, Schmidt AC, Veit R, et al. NMDA-receptor antagonist and morphine decrease CRPS-pain and cerebral pain representation. Pain 2010;151(1):69-76. - PubMed
Irving 2012 {published data only}
-
- Irving GA, Backonja M, Rauck R, Webster LR, Tobias JK, Vanhove GF. NGX-4010, a capsaicin 8% dermal patch, administered alone or in combination with systemic neuropathic pain medications, reduces pain in patients with postherpetic neuralgia. Clinical Journal of Pain 2012;28(2):101-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Karppinen 2001 {published data only}
-
- Karppinen J, Malmivaara A, Kurunlahti M, Kyllönen E, Pienimäki T, Nieminen P, et al. Periradicular infiltration for sciatica: a randomised controlled trial. Spine 2001;26(9):1059-67. - PubMed
Keskinbora 2007 {published data only}
-
- Keskinbora K, Pekel AF, Aydinli I. Gabapentin and an opioid combination versus opioid alone for the management of neuropathic cancer pain: a randomised open trial. Journal of Pain & Symptom Management 2007;34(2):183-9. - PubMed
Ko 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ko SH, Kwon HS, Yu JM, Baik SH, Park IB, Lee JH, et al. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of tramadol/acetaminophen combination therapy and gabapentin in the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy. Diabetic Medicine 2010;27(9):1033-40. - PubMed
Kochar 1998 {published data only}
-
- Kochar DK, Agarwal RP, Joshi A, Kumawat BL. Herpes zoster and post-herpetic neuralgia--a clinical trial of aspirin in chloroform for anodyne. Journal of the Association of Physicians of India 1998;46(4):337-40. - PubMed
Kotani 2000 {published data only}
-
- Kotani N, Kushikata T, Hashimoto H, Kimura F, Muraoka M, Yodono M, et al. Intrathecal methylprednisolone for intractable postherpetic neuralgia. New England Journal of Medicine 2000;343(21):1514-9. - PubMed
Kottschade 2009 {published data only}
-
- Kottschade LA, Sloan JA, Mazurczak MA, Johnson DB, Murphy B, Rowland KM, et al. The use of vitamin E for prevention of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a phase III double-blind, placebo controlled study. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2009;Conference:9532.
Kukushkin 1996 {published data only}
-
- Kukushkin ML, Ivanova AF, Ovechkin AM, Gnezdilov AV, Reshetniak VK. Differential combined drug therapy of phantom pain syndrome after amputation of extremity [Russian]. Anesteziologiia i Reanimatologiia 1996;Jul-Aug(4):39-42. - PubMed
Lagalla 2002 {published data only}
-
- Lagalla G, Logullo F, Di Bella P, Provinciali L, Ceravolo MG. Influence of early high-dose steroid treatment on Bell's palsy evolution. Neurological Sciences 2002;23(3):107-12. - PubMed
Lampl 2010 {published data only}
-
- Lampl C, Schweiger C, Haider B, Lechner A. Pregabalin as mono- or add-on therapy for patients with refractory chronic neuropathic pain: a post-marketing prescription-event monitoring study. Journal of Neurology 2010;257(8):1265. - PubMed
Langohr 1982 {published data only}
-
- Langohr HD, Stöhr M, Petruch F. An open and double-blind cross-over study on the efficacy of clomipramine (Anafranil) in patients with painful mono- and polyneuropathies. European Neurology 1982;21(5):309-17. - PubMed
Lauretti 2002 {published data only}
-
- Lauretti GR, Rodrigues ADM, Gomes JMA, Dos Reis MP. Epidural ketamine versus epidural clonidine as therapeutic for refractory neuropathic chronic pain. Revista Brasileira de Anestesiologia 2002;52(1):34-40.
Lemos 2008 {published data only}
-
- Lemos L, Flores S, Oliveira P, Almeida A. Gabapentin supplemented with ropivacain block of trigger points improves pain control and quality of life in trigeminal neuralgia patients when compared with gabapentin alone. Clinical Journal of Pain 2008;24(1):64-75. - PubMed
Levin 2009 {published data only}
-
- Levin OS, Moseĭkin IA. Vitamin B complex (milgamma) in the treatment of vertebrogenic lumbosacral radiculopathy [Russian]. Zhurnal Nevrologii i Psikhiatrii Imeni S.S.Korsakova 2009;109(10):30-5. - PubMed
Martinez 1990 {published data only}
-
- Martinez GC, Abarca B, Alvarado CL, Almonte C, Acevedo M, Leyton R, et al. Bell's palsy: evaluation of steroidal treatment: peripheral streptomycin/lidocaine injections versus lidocaine alone in the treatment of idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia. A double blind controlled trial. Journal of Craniomaxillofacial Surgery 1990;18:243-6. - PubMed
McCleane 1998 {published data only}
-
- McCleane GJ, McLaughlin M. The addition of GTN to capsaicin cream reduces the discomfort associated with application of capsaicin alone. A volunteer study. Pain 1998;78(2):149-51. - PubMed
Mendel 1986 {published data only}
-
- Mendel CM, Klein RF, Chappell DA, Dere WH, Gertz BJ, Karam JH, et al. A trial of amitriptyline and fluphenazine in the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy. JAMA 1986;255(5):637-9. - PubMed
Mercadante 1998 {published data only}
-
- Mercadante S, Casuccio A, Genovese G. Ineffectiveness of dextromethorphan in cancer pain. Journal of Pain & Symptom Management 1998;16(5):317-22. - PubMed
Mercadante 2000 {published data only}
-
- Mercadante S, Arcuri E, Tirelli W, Casuccio A. Analgesic effect of intravenous ketamine in cancer patients on morphine therapy: a randomised, controlled, double-blind, crossover, double-dose study. Journal of Pain & Symptom Management 2000;20(4):246-52. - PubMed
Minotti 1998 {published data only}
-
- Minotti V, De Angelis V, Righetti E, Celani MG, Rossetti R, Lupatelli M, et al. Double-blind evaluation of short-term analgesic efficacy of orally administered diclofenac, diclofenac plus codeine, and diclofenac plus imipramine in chronic cancer pain. Pain 1998;74(2-3):133-7. - PubMed
Palangio 2000 {published data only}
-
- Palangio M, Damask MJ, Morris E, Doyle RT Jr, Jiang JG, Landau CJ, et al. Combination hydrocodone and ibuprofen versus combination codeine and acetaminophen for the treatment of chronic pain. Clinical Therapeutics 2000;22(7):879-92. - PubMed
Patarica‐Huber 2011 {published data only}
-
- Patarica-Huber E, Boskov N, Pjevic M. Multimodal approach to therapy-related neuropathic pain in breast cancer. Journal of B.U.ON: official journal of the Balkan Union of Oncology 2011;16(1):40-5. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Pieri 2007 {published data only}
-
- Pieri M. Treatment of post-herpetic neuralgia with a combination of tramadol, paracetamol, gabapentin and local anaesthetic: clinical trial on 26 patients [Italian]. Trends in Medicine 2007;7(3):181-8.
Pirbudak 2003 {published data only}
-
- Pirbudak L, Karakurum G, Oner U, Gulec A, Karadasli H. Epidural corticosteroid injection and amitriptyline for the treatment of chronic low back pain associated with radiculopathy. Pain Clinic 2003;15(3):247-53.
Rabben 1999 {published data only}
-
- Rabben T, Skjelbred P, Oye I. Prolonged analgesic effect of ketamine, an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor inhibitor, in patients with chronic pain. Journal of Pharmacology & Experimental Therapeutics 1999;289(2):1060-6. - PubMed
Rehm 2010 {published data only}
-
- Rehm S, Binder A, Baron R. Post-herpetic neuralgia: 5% lidocaine medicated plaster, pregabalin, or a combination of both? A randomised, open, clinical effectiveness study. Current Medical Research & Opinion 2010;26(7):1607-19. - PubMed
Rodriguez 1999 {published data only}
-
- Rodriguez Hernandez R, Flores Lopez D. Assessment of pain intensity in patients with diabetic polineuropathy treated with peridural 2% lidocaine methylprednisolone acetate vs peridural 2% lidocaine. Anestesia en Mexico 1999;11(2):65-9.
Romano 2009 {published data only}
Russo 2006 {published data only}
-
- Russo E, Guy GW. A tale of two cannabinoids: the therapeutic rationale for combining tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol. Medical Hypotheses 2006;66(2):234-46. - PubMed
Ruts 2007 {published data only}
Schechtmann 2010 {published data only}
-
- Schechtmann G, Lind G, Winter J, Meyerson BA, Linderoth B. Intrathecal clonidine and baclofen enhance the pain-relieving effect of spinal cord stimulation: a comparative placebo-controlled, randomised trial. Neurosurgery 2010;67(1):173-81. - PubMed
Shaibani 2012 {published data only}
-
- Shaibani AI, Pope LE, Thisted R, Hepner A. Efficacy and safety of dextromethorphan/quinidine at two dosage levels for diabetic neuropathic pain: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter study. Pain Medicine (Malden, Mass.) 2012;13(2):243-54. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Shlay 1998 {published data only}
-
- Shlay JC, Chaloner K, Max MB, Flaws B, Reichelderfer P, Wentworth D, et al. Acupuncture and amitriptyline for pain due to HIV-related peripheral neuropathy: a randomised controlled trial. Terry Beirn Community Programs for Clinical Research on AIDS. JAMA 1998;280(18):1590-5. - PubMed
Siddall 2000 {published data only}
-
- Siddall PJ, Molloy AR, Walker S, Mather LE, Rutkowski SB, Cousins MJ. The efficacy of intrathecal morphine and clonidine in the treatment of pain after spinal cord injury. Anesthesia & Analgesia 2000;91(6):1493-8. - PubMed
Silver 2007 {published data only}
-
- Silver M, Blum D, Grainger J, Hammer AE, Quessy S. Double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of lamotrigine in combination with other medications for neuropathic pain. Journal of Pain & Symptom Management 2007;34(4):446-54. - PubMed
Simpson 2001 {published data only}
-
- Simpson DA. Gabapentin and venlafaxine for the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy. Journal of Clinical Neuromuscular Disease 2001;3(2):53-62. - PubMed
Stajcic 1990 {published data only}
-
- Stajcic Z, Juniper RP, Todorovic L. Peripheral streptomycin/lidocaine injections versus lidocaine alone in the treatment of idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia. A double blind controlled trial. Journal of Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surgery 1990;18(6):243-6. - PubMed
Sullivan 2009 {published data only}
-
- Sullivan FM, Swan IR, Donnan PT, Morrison JM, Smith BH, McKinstry B, et al. A randomised controlled trial of the use of aciclovir and/or prednisolone for the early treatment of Bell's palsy: the BELLS study. Health Technology Assessment (Winchester, England) 2009;13(47):iii-v. - PubMed
Takahashi 2010 {published data only}
-
- Takahashi H, Shimoyama N. A prospective open-label trial of gabapentin as an adjuvant analgesic with opioids for Japanese patients with neuropathic cancer pain. International Journal of Clinical Oncology 2010;15(1):46-51. - PubMed
Tanenberg 2011 {published data only}
-
- Tanenberg RJ, Irving GA, Risser RC, Ahl J, Robinson MJ, Skljarevski V, et al. Duloxetine, pregabalin, and duloxetine plus gabapentin for diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain management in patients with inadequate pain response to gabapentin: an open-label, randomised, noninferiority comparison. Mayo Clinic Proceedings 2011;86(7):615-26. [PMID: ] - PMC - PubMed
Tian 2005 {published data only}
-
- Tian Z-W, Song X-F, Li W-L, Feng J. Chinese medicine plus mecobalamin for postherpetic neuralgia in patients with refractory herpes zoster. Zhongguo Linchuang Kangfu 2005;9(17):24-5.
Venancio‐Ramirez 2004 {published data only}
-
- Venancio-Ramirez L, Hernandez-Santos JR, Tenopala-Villegas S, Torres-Huerta JC, Rivera-Leon G, Canseco-Aguilar C. Comparison of oxcarbazepine and gabapentin at standard dose in treatment of pain for postherpetic neuropathy [Comparacion de oxcarbazepina y gabapentina a dosis estandar en el tratamiento del dolor por neuropatia postherpetica]. Revista Mexicana de Anestesiologia 2004;27(3):129-33.
Wang 2007 {published data only}
-
- Wang XP, Mok MS, Li YI, Cai JY. Combined therapy of Super Lizer and Durogesic patch in elderly patients with herpes zoster and diabetes mellitus. Journal of Clinical Rehabilitative Tissue Engineering Research 2007;11(13):2589-92.
Ward 1981 {published data only}
-
- Ward J, Armstrong W, Preston E. Pain in the diabetic leg: a trial of aspirin and dipyridamole in diabetic neuropathy. Pharmatherapeutica 1981;2(10):642.
Winkler 1999 {published data only}
-
- Winkler G, Pál B, Nagybéganyi E, Ory I, Porochnavec M, Kempler P. Effectiveness of different benfotiamine dosage regimens in the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy. Arzneimittel-Forschung 1999;49(3):220-4. - PubMed
Additional references
Attal 2010
-
- Attal N, Cruccu G, Baron R, Haanpää M, Hansson P, Jensen TS, et al. European Federation of Neurological Societies. EFNS guidelines on the pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain: 2010 revision. European Journal of Neurology 2010;17(9):1113-e88. - PubMed
Baron 2009a
-
- Baron R. Neuropathic pain: a clinical perspective. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology 2009;194:3-30. - PubMed
Bennett 2011
-
- Bennett MI. Effectiveness of antiepileptic or antidepressant drugs when added to opioids for cancer pain: systematic review. Palliative Medicine 2011;25(5):553-9. - PubMed
Bhandari 2005
-
- Bhandari M, Haynes RB. How to appraise the effectiveness of treatment. World Journal of Surgery 2005;29(5):570-5. - PubMed
Bouhassira 2008
-
- Bouhassira D, Lantéri-Minet M, Attal N, Laurent B, Touboul C. Prevalence of chronic pain with neuropathic characteristics in the general population. Pain 2008;136(3):380-7. - PubMed
Dworkin 2005
-
- Dworkin RH, Turk DC, Farrar JT, Haythornthwaite JA, Jensen MP, Katz NP, et al. Core outcome measures for chronic pain clinical trials: IMMPACT recommendations. Pain 2005;113(1-2):9-19. - PubMed
Dworkin 2010
-
- Dworkin RH, Turk DC, Peirce-Sandner S, Baron R, Bellamy N, Burke LB, et al. Research design considerations for confirmatory chronic pain clinical trials: IMMPACT recommendations. Pain 2010;149(2):177-93. - PubMed
Farrar 2001
-
- Farrar JT, Young JP Jr, LaMoreaux L, Werth JL, Poole RM. Clinical importance of changes in chronic pain intensity measured on an 11-point numerical pain rating scale. Pain 2001;94(2):149-58. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Finnerup 2010
-
- Finnerup NB, Sindrup SH, Jensen TS. The evidence for pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain. Pain 2010;150(3):573-81. - PubMed
Furlan 2010
Gilron 2005a
-
- Gilron I, Max MB. Combination pharmacotherapy for neuropathic pain: current evidence and future directions. Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics 2005;5(6):823-30. - PubMed
Gilron 2006
Greenhalgh 2005
Higgins 2011
Jensen 2011
-
- Jensen TS, Baron R, Haanpää M, Kalso E, Loeser JD, Rice AS, et al. A new definition of neuropathic pain. Pain 2011;152(10):2204-5. - PubMed
L'Abbé 1987
-
- L’Abbé KA, Detsky AS, O’Rourke K. Meta-analysis in clinical research. Annals of Internal Medicine 1987;107:224–33. - PubMed
Maier 2010
-
- Maier C, Baron R, Tölle TR, Binder A, Birbaumer N, Birklein F, et al. Quantitative sensory testing in the German Research Network on Neuropathic Pain (DFNS): somatosensory abnormalities in 1236 patients with different neuropathic pain syndromes. Pain 2010;150(3):439-50. - PubMed
Manchikanti 2010
-
- Manchikanti L, Datta S, Gupta S, Munglani R, Bryce DA, Ward SP, et al. A critical review of the American Pain Society clinical practice guidelines for interventional techniques: part 2. Therapeutic interventions. Pain Physician 2010;13(4):E215-64. - PubMed
Max 1991
-
- Max MB, Laska EM. Single dose analgesic comparisons. In: Max MB, Portenoy RK, Laska EM, editors(s). The Design of Analgesic Clinical Trials. 1 edition. Vol. 18. New York: Raven Press, 1991:55-95.
Moore 1998
-
- Moore RA, Gavaghan D, Tramèr MR, Collins SL, McQuay HJ. Size is everything--large amounts of information are needed to overcome random effects in estimating direction and magnitude of treatment effects. Pain 1998;78(3):209-16. - PubMed
Moore 2008
-
- Moore RA, Barden J, Derry S, McQuay HJ. Managing potential publication bias. In: McQuay HJ, Kalso E, Moore RA, editors(s). Systematic Reviews in Pain Research: Methodology Refined. 1 edition. Seattle: IASP Press, 2008:15-23.
Moore 2010a
-
- Moore RA, Moore OA, Derry S, Peloso PM, Gammaitoni AR, Wang H. Responder analysis for pain relief and numbers needed to treat in a meta-analysis of etoricoxib osteoarthritis trials: bridging a gap between clinical trials and clinical practice. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2010;69(2):374-9. - PMC - PubMed
Moore 2010b
-
- Moore RA, Eccleston C, Derry S, Wiffen P, Bell RF, Straube S, et al. "Evidence" in chronic pain - establishing best practice in the reporting of systematic reviews. Pain 2010;150(3):386-9. - PubMed
Moore 2011
Moore 2012a
-
- Moore RA, Derry CJ, Derry S, Straube S, McQuay HJ. A conservative method of testing whether combination analgesics produce additive or synergistic effects using evidence from acute pain and migraine. European Journal of Pain 2012;16(4):585-91. - PubMed
Moore 2012b
-
- Moore RA, Straube S, Eccleston C, Derry S, Aldington D, Wiffen P, et al. Estimate at your peril: imputation methods for patient withdrawal can bias efficacy outcomes in chronic pain trials using responder analyses. Pain 2012;153(2):265-8. - PubMed
Nuesch 2010
Patel 2009
-
- Patel VB, Manchikanti L, Singh V, Schultz DM, Hayek SM, Smith HS. Systematic review of intrathecal infusion systems for long-term management of chronic non-cancer pain. Pain Physician 2009;12(2):345-60. - PubMed
RevMan 2011 [Computer program]
-
- Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.1. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.
Tarride 2006
-
- Tarride JE, Collet JP, Choiniere M, Rousseau C, Gordon A. The economic burden of neuropathic pain in Canada. Journal of Medical Economics 2006;9(1-4):55-68.
Torrance 2006
-
- Torrance N, Smith BH, Bennett MI, Lee AJ. The epidemiology of chronic pain of predominantly neuropathic origin. Results from a general population survey. Journal of Pain 2006;7(4):281-9. - PubMed
Vorobeychik 2011
-
- Vorobeychik Y, Gordin V, Mao J, Chen L. Combination therapy for neuropathic pain: a review of current evidence. CNS Drugs 2011;25(12):1023-34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

