Low oxygen concentrations for embryo culture in assisted reproductive technologies
- PMID: 22786519
- PMCID: PMC11683526
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008950.pub2
Low oxygen concentrations for embryo culture in assisted reproductive technologies
Abstract
Background: During in vitro fertilisation (IVF) procedures, human preimplantation embryos are cultured in the laboratory. While some laboratories culture in an atmospheric oxygen concentration (˜ 20%), others use a lower concentration (˜ 5%) as this is more comparable to the oxygen concentration observed in the oviduct and the uterus. Animal studies have shown that high oxygen concentration could have a negative impact on embryo quality via reactive oxygen species causing oxidative stress. In humans, it is currently unknown which oxygen concentration provides the best success rates of IVF procedures, eventually resulting in the hightest birth rate of healthy newborns.
Objectives: To determine whether embryo culture at low oxygen concentrations improves treatment outcome (better embryo development and more pregnancies and live births) in IVF and intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) as compared to embryo culture at atmospheric oxygen concentrations.
Search methods: The Menstrual Disorders and Subfertility Group Trials Register, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE, EMBASE and PsycINFO electronic databases were searched (up to 4th November 2011) for randomised controlled trials on the effect of low oxygen concentrations for human embryo culture. Furthermore, reference lists of all obtained studies were checked and conference abstracts handsearched.
Selection criteria: Only truly randomised controlled trials comparing embryo culture at low oxygen concentrations (˜ 5%) with embryo culture at atmospheric oxygen concentrations (˜ 20%) were included in this systematic review and meta-analysis.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors selected the trials for inclusion according to the above criteria. After that two authors independently extracted the data for subsequent analysis, and one author functioned as a referee in case of ambiguities. The statistical analysis was performed in accordance with the guidelines developed by The Cochrane Collaboration.
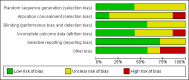
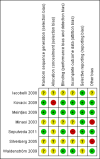
Main results: Seven studies with a total of 2422 participants were included in this systematic review. Meta-analysis could be performed with the data of four included studies, with a total of 1382 participants. The methodological quality of the included trials was relatively low. Evidence of a beneficial effect of culturing in low oxygen concentration was found for live birth rate (OR 1.39; 95% CI 1.11 to 1.76; P = 0.005; I(2) = 0%); this would mean that a typical clinic could improve a 30% live birth rate using atmospheric oxygen concentration to somewhere between 32% and 43% by using a low oxygen concentration. The results were very similar for ongoing and clinical pregnancy rates. There was no evidence that culturing embryos under low oxygen concentrations resulted in higher numbers of adverse events such as multiple pregnancies, miscarriages or congenital abnormalities.
Authors' conclusions: The results of this systematic review and meta-analysis suggest that culturing embryos under conditions with low oxygen concentrations improves the success rates of IVF and ICSI, resulting in the birth of more healthy newborns.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this systematic review have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures













Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Iacobelli 2008 {published data only}
-
- Iacobelli M, Nagy ZP, Minasi MG, Casciani V, Albricci L, Ferrero S, et al. The effect of reduced oxygen concentration on ICSI outcomes in two different culture media systems. Abstracts of the 24th annual meeting of the ESHRE 2008.
Kovacic 2009 {published data only}
-
- Kovacic B, Sajko MS, Vlaisavljevic V. A prospective, randomized trial on the effect of atmospheric versus reduced oxygen concentration on the outcome of intracytoplasmic sperm injection cycles. Fertility and Sterility 2009;94:511‐9. - PubMed
Meintjes 2009 {published data only}
-
- Meintjes M, Chantilis SJ, Douglas JD, Rodriquez AJ, Guerami AR, Bookout DM, et al. A controlled randomized trial evaluating the effect of the lowered incubator oxygen tension on live births in a predominantly blastocyst transfer program. Human Reproduction 2009;24:300‐7. - PubMed
Minasi 2003 {published data only}
-
- Minasi MG, Rienzi L, Ubaldi F, Romano S, Iacobelli M, Ferrero S, et al. Effect of oxygen concentration on the culture of human embryos: a prospective, randomized study. Abstracts of the 19th annual meeting of the ESHRE 2003.
Sepulveda 2011 {published data only}
-
- Sepulveda S, Steurer I, Gazzo E, Escudero E, Noriega L. Effect of oxygen conditions on the results of an oocyte donation program: A prospective randomized trial [Efeito das condicoes de oxigenio no resultado de um programa de ovo‐doacao: Estudo prospectivo e randomizado]. Jornal Brasileiro de Reproducao Assistida May‐June 2011;15(3):32‐3.
Silverberg 2005 {published data only}
-
- Silverberg KM, Turner T, Minter T, Schuster C, Fields R, Vaughn TC. Choosing the optimal incubator environment for day 3 culture: triple gas vs. 5% CO2 in air, a prospective, randomized trial. Fertility and Sterility 2005;84 Suppl 1:88.
Waldenström 2009 {published data only}
-
- Waldenström U, Engström AB, Hellberg D, Nilsson S. Low‐oxygen compared with high‐oxygen atmosphere in blastocyst culture, a prospective randomized study. Fertility and Sterility 2009;91:2461‐5. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Bahceci 2005 {published data only}
-
- Bahceci M, Ciray HN, Karagenc L, Ulug U, Bener F. Effect of oxygen concentration during the incubation of embryos of women undergoing ICSI and embryo transfer: A prospective randomized study. Reproductive Biomedicine Online 2005 Oct;11(4):438‐43. - PubMed
Cieslak Janzen 2008 {published data only}
-
- Cieslak Janzen JM, Graff D, Anderson S, Matt DW. Comparison of atmospheric oxygen versus low oxygen on human sibling embryo development. Fertility and Sterility 2008;90 Suppl 1:431‐2.
Ciray 2008 {published data only}
-
- Ciray HN, Aksoy T, Yaramanci K, Ulug U, Bahceci M. Reduced O2 concentration in first 3 days of culture yields more blastocysts with better quality: A prospective randomized study on sibling oocytes. Human Reproduction 2008;23 Suppl 1:i160.
Ciray 2009 {published data only}
-
- Ciray HN, Aksoy T, Yaramanci K, Karayaka I, Bahceci M. In vitro culture under physiologic oxygen concentration improves blastocyst yield and quality: a prospective randomized survey on sibling oocytes. Fertility and Sterility 2009;91 Suppl(4):1459‐61. - PubMed
Curnelle 2010 {published data only}
-
- Curnelle S, Nogueira D, Guitard V, Bonald F, Guillen N, Montagut J. The effect of culture under low oxygen tension on developmental competence of post‐thawed human embryos. Abstracts of the annual meeting of the ESHRE 2010.
Dasig 2006 {published data only}
-
- Dasig D, Dangcil M, Telles T, Farah L, D’Amico J, Shen W. The use of low oxygen culture conditions yields similar pregnancy rates with day 2 vs day 3 embryo transfer. Fertility and Sterility 2006;86 Suppl 2:241‐2.
Dumoulin 1995 {published data only}
-
- Dumoulin JC, Vanvuchelen RC, Land JA, Pieters MH, Geraedts JP, Evers JL. Effect of oxygen concentration on in vitro fertilization and embryo culture in the human and the mouse. Fertility and Sterility 1995;63(1):115‐9. - PubMed
Dumoulin 1999 {published data only}
-
- Dumoulin JC, Meijers CJ, Bras M, Coonen E, Geraedts JP, Evers JL. Effect of oxygen concentration on human in‐vitro fertilization and embryo culture. Human Reproduction 1999;14(2):465‐9. - PubMed
Fujiwara 2007 {published data only}
-
- Fujiwara M, Takahashi K, Izuno M, Duan YR, Kazono M, Kimura F, Noda Y. Effect of micro‐environment maintenance on embryo culture after in‐vitro fertilization: Comparison of top‐load mini incubator and conventional front‐load incubator. Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics 2007;24(1):5‐9. - PMC - PubMed
Gamiz Izquierdo 2010 {published data only}
-
- Gamiz Izquierdo P, Santos JM, Tejera A, Pellicer A, Romero JL, Galan A, et al. Culture embryos under low oxygen conditions improves clinical results. Abstract of the annual meeting of the ESHRE 2010.
Graham 2010 {published data only}
-
- Graham J, Richter K, Siques J, Vermilyea M, Widra E, Tucker M. Improved preimplantation development and higher pregnancy rates associated with 6% versus ambient oxygen concentration during in vitro embryo culture. Human Reproduction 2010;25 Suppl 1:i59.
Gvakharia 2008 {published data only}
-
- Gvakharia M, Lee SC, Palao L, Cubukcu A, Milette BJ, Adamson GD. Effects on low oxygen culture on embryo development and IVF outcome. Fertility and Sterility 2008;90 Suppl 1:434.
Higdon 2008 {published data only}
-
- Higdon HL, Blackhurst DW, Boone WR. Incubator management in an assisted reproductive technology laboratory. Fertility and Sterility 2008;89(3):703‐10. - PubMed
Hoff 2008 {published data only}
-
- Hoff A, Khabani A, Khabani C, Hickok L, Marshall L. Reduced oxygen tension helps increase the quality of blastocyst available on D5. Fertility and Sterility 2008;90 Suppl 1:350.
Kasterstein 2008 {published data only}
-
- Kasterstein E, Strassburger D, Komarovsky D, Bern O, Komsky A, Maslansky B, et al. Improved embryo development after incubation in reduced oxygen concentration. Abstracts of the 24th annual meeting of the ESHRE. 2008.
Kea 2005 {published data only}
-
- Kea B, Gebhardt J, Westphal L, Lathi R, Watt J, Behr B. Effects of reduced oxygen concentrations on IVF outcome. Fertility and Sterility 2005;83 Suppl 2:19. - PubMed
Kea 2007 {published data only}
-
- Kea B, Gebhardt J, Watt J, Westphal LM, Lathi RB, Milki AA, Behr B. Effect of reduced oxygen concentrations on the outcome of in vitro fertilization. Fertility and Sterility 2007;87(1):213‐6. - PubMed
Khabani 2008 {published data only}
-
- Khabani C, Marshall L, Woodford D, Khabani A, Hickok L. Improving embryo culture conditions by reducing oxygen tension may help increase the implantation potential of an embryo in the donor recipient population. Fertility and Sterility 2008;89 Suppl 2:14.
Kim 2005 {published data only}
-
- Kim SB, Kwon H, Kim EK, Kim JM, Choi DH, Cha KY. The comparison of embryo developments and pregnancy rates in human in vitro culture conditions at different oxygen gas phase. Fertility and Sterility 2005;84 Suppl 1:16.
Kim 2007 {published data only}
-
- Kim EA, Kim EK, Kang KY, Choi MA, Kwon H, Choi DH. Effect of oxygen concentrations on IVM, IVF and embryo development of immature oocytes from stimulated cycles of human IVF‐ET program. Fertility & Sterility 2007;88(Suppl 1):S319.
Kovacic 2008 {published data only}
-
- Kovacic B, Vlaisavljevic V. Influence of atmospheric versus reduced oxygen concentration on development of human blastocysts in vitro: a prospective study on sibling oocytes. Reproductive Biomedicine Online 2008;17(2):229‐36. - PubMed
Loutradi 2009 {published data only}
-
- Loutradi K, Kolibianakis EM, Mitsoli A, Venetis CA, Tzamtzoglou A, Tarlatzis BC. The effect of oxygen concentration on human embryo culture: A prospective randomized controlled trial. Fertility and Sterility 2009;92 Suppl(3):230.
Madashi 2010 {published data only}
-
- Madaschi C, Guilherme P, Izzo CPM, Yamakami LY, Fassolas G, Izzo CR. Evaluation the effect of lowered incubator oxygen tension on embryo quality. Fertility and Sterility. Annual Meeting of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine, ASRM 2010.
Mancebo 2009 {published data only}
-
- Mancebo ABA, Souza MDCB, Henriques CA, Souza MM, Cardoso FFO, Santos HCN. Prospective randomized study to compare the effects of embryo culture performed in an incubator Class 100 with High Efficiency Particulate Air filter (HEPA) plus Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC) filter on outcome measures of ICSI cycles. Jornal Brasileiro de Reproducao Assistida April‐June 2009;13 (2), 2009:9‐12.
Meijers 1998 {published data only}
-
- Meijers C, Dumoulin JCM, Bras M, Bergers Jansen JM, Ignoul Vanvuchelen RCM. Comparison between ambient (20%) or reduced (5%) oxygen concentration for human in‐vitro fertilization using a system of culture medium droplets under oil. Human Reproduction 1998;13:111.
Meintjes 2000 {published data only}
-
- Meintjes M, Hill K, Johnston S, Waugh T, Rodriguez A, Madden J. The effect of lowered incubator oxygen tension on implantation, pregnancy and cryopreservation rates in a predominantly Day‐5 embryo transfer program. Fertility and Sterility 2000;74 Suppl 1(3):256.
Mitsoli 2011 {published data only}
-
- Mitsoli A, Kolibianakis EM, Loutradi K, Venetis CA, Triantafilidis S, Makedos A, et al. Low oxygen embryo culture is associated with improved day 3 embryo quality: A prospective randomized controlled trial. Human Reproduction. Conference: 27th Annual Meeting of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology, ESHRE 2011 Stockholm Sweden 2011;26:i2.
Nanassy 2010 {published data only}
-
- Nanassy L, Peterson CA, Wilcox AL, Peterson CM, Hammoud A, Carrell DT. Comparison of 5% and ambient oxygen during days 3–5 of in vitro culture of human embryos. Fertility and Sterility 2010;93(2):579‐85. - PubMed
Oliveira 2011 {published data only}
-
- Oliveira JBA, Petersen CG, Mauri AL, Massoro FC, Silva LFI, Ricci J, et al. IVF/ICSI outcomes after human embryo development on low oxygen tension: A meta‐analysis. Human Reproduction. Conference: 27th Annual Meeting of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology, ESHRE 2011 Stockholm Sweden 2011;26:i199‐i200.
Park 2001 {published data only}
-
- Park SJ, Son WY, Yoon SH, Lee SW, Lim JH. Effect of low oxygen tension on human IVM/F‐ET program. http://www.liyabiotech.com/upfiles/house/1134436097.pdf 2001.
Petersen 2005 {published data only}
-
- Petersen A, Mikkelsen AL, Lindenberg S. The impact of oxygen tension on developmental competence of post‐thaw human embryos. Acta Obstetrica Gynecologica Scandinavica 2005;84:1181‐4. - PubMed
Portmann 2008 {published data only}
-
- Portmann MP, Morrison LS, Carney SM, Boylan CF, Feinberg RF, Kovalevsky G. Is triple gas culture effective? Practical?. Fertility and Sterility 2008;90(Suppl):S351.
Prados 2010 {published data only}
-
- Prados N, Ruiz M, Garca‐Ortega J, Vime P, Hernez MJ, Crespo M, et al. Improved human embryo quality in days 3 and 5 with a low oxygen closed culture system. Human Reproduction. Conference: 26th Annual Meeting of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology, ESHRE Rome Italy. June 2010:25 (pp i190).
Reeka 2004 {published data only}
-
- Reeka N, Jelinkova L, Brucker C, Gagsteiger F. Lower oxygen concentration is beneficial for the early human embryo development. Abstracts of the 20th annual meeting of the ESHRE 2004.
Ryu 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ryu H, Park CY, Min SH, Choi SK, Park C, Lee SH, et al. Effect of low‐oxygen compared with high‐oxygen atmosphere on the outcomes of in vitro fertilization, a prospective randomized study. Abstracts of the annual meeting of the ESHRE 2010.
Sjoblom 2008 {published data only}
-
- Sjoblom C, Chamberlain S, Devlin L, Priddle H. Reduced oxygen during embryo culture increase fertilisation and subsequent pregnancy rates in IVF. Abstracts of the 24th annual meeting of the ESHRE 2008.
Sobrinho 2011 {published data only}
Tejera 2010 {published data only}
-
- Tejera A, Gmiz P, Romero JL, Santos JM, Grau N, Santos MJ. Culture under low oxygen tension improves embryo quality in egg donation cycles. Molecular Human Reproduction. 25th Annual Meeting of the European Society of Human Reproduction Embryology, ESHRE Amsterdam Netherlands.
Additional references
Catt 2000
-
- Catt JW, Henman M. Toxic effects of oxygen on human embryo development. Human Reproduction 2000;15 Suppl 2:199‐206. - PubMed
Dumoulin 2010
-
- Dumoulin JC, Land JA, Montfoort AP, Nelissen EC, Coonen E, Derhaag JG, et al. Effect of in vitro culture of human embryos on birthweight of newborns. Human Reproduction 2010;25(3):605‐12. - PubMed
Feil 2006
Fischer 1993
-
- Fischer B, Bavister BD. Oxygen tension in the oviduct and uterus of rhesus monkeys, hamsters and rabbits. Journal of Reproduction and Fertility 1993;99(2):673‐9. - PubMed
Harvey 2007
-
- Harvey AJ. The role of oxygen in ruminant preimplantation embryo development and metabolism. Animal Reproduction Science 2007;98(1‐2):113‐28. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Karagenc 2004
-
- Karagenc L, Sertkaya Z, Ciray N, Ulug U, Bahceci M. Impact of oxygen concentration on embryonic development of mouse zygotes. Reproductive Biomedicine Online 2004;9(4):409‐17. - PubMed
Lim 2011
Mastenbroek 2005
-
- Mastenbroek S, Bossuyt PMM, Heineman MJ, Repping S, Veen F. Comment 1 on. Design and analysis of a randomized controlled trial studying preimplantation genetic screening. Human Reproduction August 2005;20(8):2362‐3. - PubMed
Vail 2003
-
- Vail A, Gardener E. Common statistical errors in the design and analysis of subfertility trials. Human Reproduction 2003;18(5):1000‐4. - PubMed
Yedwab 1976
-
- Yedwab GA, Paz G, Homonnai TZ, David MP, Kraicer PF. The temperature, pH, and partial pressure of oxygen in the cervix and uterus of women and uterus of rats during the cycle. Fertility and Sterility 1976;27(3):304‐9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

