An effector-reduced anti-β-amyloid (Aβ) antibody with unique aβ binding properties promotes neuroprotection and glial engulfment of Aβ
- PMID: 22787053
- PMCID: PMC6622286
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4742-11.2012
An effector-reduced anti-β-amyloid (Aβ) antibody with unique aβ binding properties promotes neuroprotection and glial engulfment of Aβ
Abstract
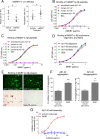
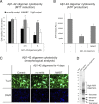
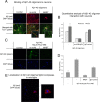
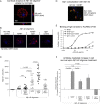
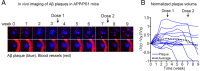
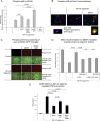
Passive immunization against β-amyloid (Aβ) has become an increasingly desirable strategy as a therapeutic treatment for Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, traditional passive immunization approaches carry the risk of Fcγ receptor-mediated overactivation of microglial cells, which may contribute to an inappropriate proinflammatory response leading to vasogenic edema and cerebral microhemorrhage. Here, we describe the generation of a humanized anti-Aβ monoclonal antibody of an IgG4 isotype, known as MABT5102A (MABT). An IgG4 subclass was selected to reduce the risk of Fcγ receptor-mediated overactivation of microglia. MABT bound with high affinity to multiple forms of Aβ, protected against Aβ1-42 oligomer-induced cytotoxicity, and increased uptake of neurotoxic Aβ oligomers by microglia. Furthermore, MABT-mediated amyloid plaque removal was demonstrated using in vivo live imaging in hAPP((V717I))/PS1 transgenic mice. When compared with a human IgG1 wild-type subclass, containing the same antigen-binding variable domains and with equal binding to Aβ, MABT showed reduced activation of stress-activated p38MAPK (p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase) in microglia and induced less release of the proinflammatory cytokine TNFα. We propose that a humanized IgG4 anti-Aβ antibody that takes advantage of a unique Aβ binding profile, while also possessing reduced effector function, may provide a safer therapeutic alternative for passive immunotherapy for AD. Data from a phase I clinical trial testing MABT is consistent with this hypothesis, showing no signs of vasogenic edema, even in ApoE4 carriers.
Figures

References
-
- Bandyopadhyay S, Hartley DM, Cahill CM, Lahiri DK, Chattopadhyay N, Rogers JT. Interleukin-1alpha stimulates non-amyloidogenic pathway by alpha-secretase (ADAM-10 and ADAM-17) cleavage of APP in human astrocytic cells involving p38 MAP kinase. J Neurosci Res. 2006;84:106–118. - PubMed
-
- Carlson C, Estergard W, Oh J, Suhy J, Jack CR, Jr, Siemers E, Barakos J. Prevalence of asymptomatic vasogenic edema in pretreatment Alzheimer's disease study cohorts from phase 3 trials of semagacestat and solanezumab. Alzheimers Dement. 2011;7:396–401. - PubMed
-
- Carty NC, Wilcock DM, Rosenthal A, Grimm J, Pons J, Ronan V, Gottschall PE, Gordon MN, Morgan D. Intracranial administration of deglycosylated C-terminal-specific anti-Abeta antibody efficiently clears amyloid plaques without activating microglia in amyloid-depositing transgenic mice. J Neuroinflamm. 2006;3:11. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
