Pain modality and spinal glia expression by streptozotocin induced diabetic peripheral neuropathy in rats
- PMID: 22787487
- PMCID: PMC3389837
- DOI: 10.5625/lar.2012.28.2.131
Pain modality and spinal glia expression by streptozotocin induced diabetic peripheral neuropathy in rats
Abstract
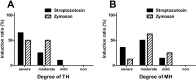
Pain symptoms are a common complication of diabetic peripheral neuropathy or an inflammatory condition. In the most experiments, only one or two evident pain modalities are observed at diabetic peripheral neuropathy according to experimental conditions. Following diabetic peripheral neuropathy or inflammation, spinal glial activation may be considered as an important mediator in the development of pain. For this reason, the present study was aimed to address the induction of pain modalities and spinal glial expression after streptozotocin injection as compared with that of zymosan inflammation in the rat. Evaluation of pain behavior by either thermal or mechanical stimuli was performed at 3 weeks or 5 hours after either intravenous streptozotocin or zymosan. Degrees of pain were divided into 4 groups: severe, moderate, mild, and non-pain induction. On the mechanical allodynia test, zymosan evoked predominantly a severe type of pain, whereas streptozotocin induced a weak degree of pain (severe+moderate: 57.1%). Although zymosan did not evoke cold allodynia, streptozotocin evoked stronger pain behavior, compared with zymosan (severe+moderate: 50.0%). On the other hand, the high incidence of thermal hyperalgesia (severe+moderate: 90.0%) and mechanical hyperalgesia (severe+moderate: 85.7%) by streptozotocin was observed, as similar to that of zymosan. In the spinal cord, the increase of microglia and astrocyte was evident by streptozotocin, only microglia was activated by zymosan. Therefore, it is recommended that the selection of mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia is suitable for the evaluation of streptozotocin induced diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Moreover, spinal glial activation may be considered an important factor.
Keywords: Diabetic peripheral neuropathy; allodynia; glia; hyperalgesia; inflammation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Acute peripheral inflammation induces moderate glial activation and spinal IL-1beta expression that correlates with pain behavior in the rat.Brain Res. 1999 May 22;829(1-2):209-21. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(99)01326-8. Brain Res. 1999. PMID: 10350552
-
Pharmacological characterization of different fractions of Calotropis procera (Asclepiadaceae) in streptozotocin induced experimental model of diabetic neuropathy.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Mar 14;152(2):349-57. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.01.020. Epub 2014 Jan 29. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24486599
-
Chronic Treatment With Hydrogen Sulfide Donor GYY4137 Mitigates Microglial and Astrocyte Activation in the Spinal Cord of Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2020 Dec 4;79(12):1320-1343. doi: 10.1093/jnen/nlaa127. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2020. PMID: 33271602
-
Role of hydrogen sulfide in the pain processing of non-diabetic and diabetic rats.Neuroscience. 2013 Oct 10;250:786-97. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.06.053. Epub 2013 Jul 2. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 23830907
-
Benefits of exercise intervention in reducing neuropathic pain.Front Cell Neurosci. 2014 Apr 4;8:102. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00102. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24772065 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of nefopam on streptozotocin-induced diabetic neuropathic pain in rats.Korean J Pain. 2014 Oct;27(4):326-33. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2014.27.4.326. Epub 2014 Oct 1. Korean J Pain. 2014. PMID: 25317281 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in the basal membrane of dorsal root ganglia Schwann cells explain the biphasic pattern of the peripheral neuropathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.J Mol Neurosci. 2014 Dec;54(4):704-13. doi: 10.1007/s12031-014-0424-2. Epub 2014 Sep 27. J Mol Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25260693
-
Nerve decompression for diabetic peripheral neuropathy with nerve entrapment: a narrative review.Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2024 Oct 14;17:17562864241265287. doi: 10.1177/17562864241265287. eCollection 2024. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2024. PMID: 39411723 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Morrow TJ. Animal models of painful diabetic neuropathy: the STZ rat model. Curr Protoc Neurosci. 2004;Chapter 9:Unit 9. 18. - PubMed

