The association of statins plus LDL receptor-targeted liposome-encapsulated doxorubicin increases in vitro drug delivery across blood-brain barrier cells
- PMID: 22788770
- PMCID: PMC3514758
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.02103.x
The association of statins plus LDL receptor-targeted liposome-encapsulated doxorubicin increases in vitro drug delivery across blood-brain barrier cells
Abstract
Background and purpose: The passage of drugs across the blood-brain barrier (BBB) limits the efficacy of chemotherapy in brain tumours. For instance, the anticancer drug doxorubicin, which is effective against glioblastoma in vitro, has poor efficacy in vivo, because it is extruded by P-glycoprotein (Pgp/ABCB1), multidrug resistance-related proteins and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2) in BBB cells. The aim of this study was to convert poorly permeant drugs like doxorubicin into drugs able to cross the BBB.
Experimental approach: Experiments were performed on primary human cerebral microvascular endothelial hCMEC/D3 cells, alone and co-cultured with human brain and epithelial tumour cells.
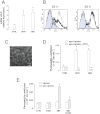
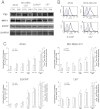
Key results: Statins reduced the efflux activity of Pgp/ABCB1 and BCRP/ABCG2 in hCMEC/D3 cells by increasing the synthesis of NO, which elicits the nitration of critical tyrosine residues on these transporters. Statins also increased the number of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptors exposed on the surface of BBB cells, as well as on tumour cells like human glioblastoma. We showed that the association of statins plus drug-loaded nanoparticles engineered as LDLs was effective as a vehicle for non-permeant drugs like doxorubicin to cross the BBB, allowing its delivery into primary and metastatic brain tumour cells and to achieve significant anti-tumour cytotoxicity.
Conclusions and implications: We suggest that our 'Trojan horse' approach, based on the administration of statins plus a LDL receptor-targeted liposomal drug, might have potential applications in the pharmacological therapy of different brain diseases for which the BBB represents an obstacle.
© 2012 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2012 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Statins revert doxorubicin resistance via nitric oxide in malignant mesothelioma.Int J Cancer. 2006 Jul 1;119(1):17-27. doi: 10.1002/ijc.21832. Int J Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16450390
-
The cross-talk between canonical and non-canonical Wnt-dependent pathways regulates P-glycoprotein expression in human blood-brain barrier cells.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2014 Aug;34(8):1258-69. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2014.100. Epub 2014 Jun 4. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2014. PMID: 24896565 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of Thiosemicarbazone Compounds as P-Glycoprotein Inhibitors in Human Primary Brain-Blood Barrier and Glioblastoma Stem Cells.Mol Pharm. 2019 Aug 5;16(8):3361-3373. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.9b00018. Epub 2019 Jul 2. Mol Pharm. 2019. PMID: 31265310
-
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Similarities and differences.Clin Pharmacokinet. 1997 May;32(5):403-25. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199732050-00005. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1997. PMID: 9160173 Review.
-
Drug transport across the blood-brain barrier and the impact of breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2).Curr Top Med Chem. 2009;9(2):130-47. doi: 10.2174/156802609787521580. Curr Top Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19200001 Review.
Cited by
-
The hCMEC/D3 cell line as a model of the human blood brain barrier.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2013 Mar 26;10(1):16. doi: 10.1186/2045-8118-10-16. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2013. PMID: 23531482 Free PMC article.
-
Low-density lipoprotein encapsulated thiosemicarbazone metal complexes is active targeting vehicle for breast, lung, and prostate cancers.Drug Deliv. 2022 Dec;29(1):2206-2216. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2096713. Drug Deliv. 2022. PMID: 35815732 Free PMC article.
-
SLC and ABC Transporters: Expression, Localization, and Species Differences at the Blood-Brain and the Blood-Cerebrospinal Fluid Barriers.AAPS J. 2017 Sep;19(5):1317-1331. doi: 10.1208/s12248-017-0110-8. Epub 2017 Jun 29. AAPS J. 2017. PMID: 28664465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nose to brain strategy coupled to nano vesicular system for natural products delivery: Focus on synaptic plasticity in Alzheimer's disease.J Pharm Anal. 2024 Dec;14(12):101057. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2024.101057. Epub 2024 Aug 5. J Pharm Anal. 2024. PMID: 39802402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nature vs. Manmade: Comparing Exosomes and Liposomes for Traumatic Brain Injury.AAPS J. 2023 Aug 23;25(5):83. doi: 10.1208/s12248-023-00849-8. AAPS J. 2023. PMID: 37610471 Review.
References
-
- Ahn KS, Sethi G, Chaturvedi MM, Aggarwal BB. Simvastatin, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitor, suppresses osteoclastogenesis induced by receptor activator of nuclear factor-kB ligand through modulation of NF-kB pathway. Int J Cancer. 2008;123:1733–1740. - PubMed
-
- Ambruosi A, Khalansky AS, Yamamoto H, Gelperina SE, Begley DJ, Kreuter J. Biodistribution of polysorbate 80-coated doxorubicin-loaded [14C]-poly(butyl cyanoacrylate) nanoparticles after intravenous administration to glioblastoma-bearing rats. J Drug Target. 2006;14:97–105. - PubMed
-
- Ananda S, Nowak AK, Cher L, Dowling A, Brown C, Simes J, et al. Phase 2 trial of temozolomide and pegylated liposomal doxorubicin in the treatment of patients with glioblastoma multiforme following concurrent radiotherapy and chemotherapy. J Clin Neurosci. 2011;18:1444–1448. - PubMed
-
- Bababeygy SR, Polevaya NV, Youssef S, Sun A, Xiong A, Prugpichailers T, et al. HMG-CoA reductase inhibition causes increased necrosis and apoptosis in an in vivo mouse glioblastoma multiforme model. Anticancer Res. 2009;29:4901–4908. - PubMed
-
- Bauer B, Hartz AMS, Miller DS. Tumor necrosis factor α and endothelin-1 increase P-glycoprotein expression and transport activity at the blood-brain barrier. Mol Pharmacol. 2007;71:667–675. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

