Druggability analysis and structural classification of bromodomain acetyl-lysine binding sites
- PMID: 22788793
- PMCID: PMC3441041
- DOI: 10.1021/jm300346w
Druggability analysis and structural classification of bromodomain acetyl-lysine binding sites
Abstract
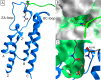
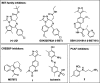
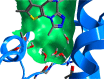
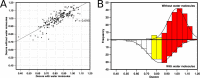
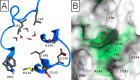
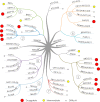
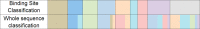
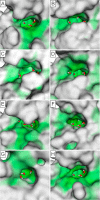
Bromodomains are readers of the epigenetic code that specifically bind acetyl-lysine containing recognition sites on proteins. Recently the BET family of bromodomains has been demonstrated to be druggable through the discovery of potent inhibitors, sparking an interest in protein-protein interaction inhibitors that directly target gene transcription. Here, we assess the druggability of diverse members of the bromodomain family using SiteMap and show that there are significant differences in predicted druggability. Furthermore, we trace these differences in druggability back to unique amino acid signatures in the bromodomain acetyl-lysine binding sites. These signatures were then used to generate a new classification of the bromodomain family, visualized as a classification tree. This represents the first analysis of this type for the bromodomain family and can prove useful in the discovery of inhibitors, particularly for anticipating screening hit rates, identifying inhibitors that can be explored for lead hopping approaches, and selecting proteins for selectivity screening.
Figures

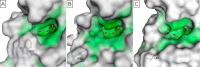
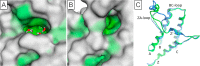
Comment in
-
Scaling the druggability landscape of human bromodomains, a new class of drug targets.J Med Chem. 2012 Sep 13;55(17):7342-5. doi: 10.1021/jm3011977. Epub 2012 Aug 28. J Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22928775 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kouzarides T. Chromatin Modifications and Their Function. Cell 2007, 128, 693–705. - PubMed
-
- Jenuwein T.; Allis C. D. Translating the Histone Code. Science 2001, 293, 1074–1080. - PubMed
-
- Zeng L.; Zhou M. M. Bromodomain: An acetyl-lysine binding domain. FEBS Lett. 2002, 513, 124–128. - PubMed
-
- Filippakopoulos P.; Picaud S.; Mangos M.; Keates T.; Lambert J.-P.; Barsyte-Lovejoy D.; Felletar I.; Volkmer R.; Müller S.; Gingras A.-C.; Pawson T.; Arrowsmith C.; Knapp S. Histone Recognition and Large-Scale Structural Analysis of the Human Bromodomain Family. Cell 2012, 149, 214–231. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mutjaba S.; Zeng L.; Zhou M. M. Structure and acetyl-lysine recognition of the bromodomain. Oncogene 2007, 26, 5521–5527. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

