NRP1 and NRP2 cooperate to regulate gangliogenesis, axon guidance and target innervation in the sympathetic nervous system
- PMID: 22790009
- PMCID: PMC3430865
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.06.026
NRP1 and NRP2 cooperate to regulate gangliogenesis, axon guidance and target innervation in the sympathetic nervous system
Abstract
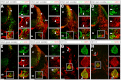
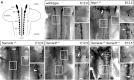
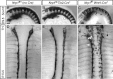
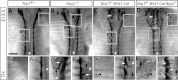
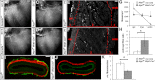
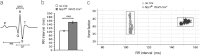
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) arises from neural crest (NC) cells during embryonic development and innervates the internal organs of vertebrates to modulate their stress response. NRP1 and NRP2 are receptors for guidance cues of the class 3 semaphorin (SEMA) family and are expressed in partially overlapping patterns in sympathetic NC cells and their progeny. By comparing the phenotypes of mice lacking NRP1 or its ligand SEMA3A with mice lacking NRP1 in the sympathetic versus vascular endothelial cell lineages, we demonstrate that SEMA3A signalling through NRP1 has multiple cell-autonomous roles in SNS development. These roles include neuronal cell body positioning, neuronal aggregation and axon guidance, first during sympathetic chain assembly and then to regulate the innervation of the heart and aorta. Loss of NRP2 or its ligand SEMA3F impaired sympathetic gangliogenesis more mildly than loss of SEMA3A/NRP1 signalling, but caused ectopic neurite extension along the embryonic aorta. The analysis of compound mutants lacking SEMA3A and SEMA3F or NRP1 and NRP2 in the SNS demonstrated that both signalling pathways cooperate to organise the SNS. We further show that abnormal sympathetic development in mice lacking NRP1 in the sympathetic lineage has functional consequences, as it causes sinus bradycardia, similar to mice lacking SEMA3A.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neuropilin-mediated neural crest cell guidance is essential to organise sensory neurons into segmented dorsal root ganglia.Development. 2009 Jun;136(11):1785-9. doi: 10.1242/dev.034322. Epub 2009 Apr 22. Development. 2009. PMID: 19386662 Free PMC article.
-
Defective gonadotropin-releasing hormone neuron migration in mice lacking SEMA3A signalling through NRP1 and NRP2: implications for the aetiology of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism.Hum Mol Genet. 2011 Jan 15;20(2):336-44. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddq468. Epub 2010 Nov 8. Hum Mol Genet. 2011. PMID: 21059704
-
Neuropilin receptors guide distinct phases of sensory and motor neuronal segmentation.Development. 2009 Jun;136(11):1879-88. doi: 10.1242/dev.032920. Epub 2009 Apr 29. Development. 2009. PMID: 19403658 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropilin regulation of angiogenesis, arteriogenesis, and vascular permeability.Microcirculation. 2014 May;21(4):315-23. doi: 10.1111/micc.12124. Microcirculation. 2014. PMID: 24521511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuropilin signalling in vessels, neurons and tumours.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2013 Mar;24(3):172-8. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2013.01.001. Epub 2013 Jan 11. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23319134 Review.
Cited by
-
Venous endothelin guides sympathetic innervation of the developing mouse heart.Nat Commun. 2014 May 29;5:3918. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4918. Nat Commun. 2014. PMID: 24875861 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Role of Semaphorin 3C in Modulating Systemic and Renal Hemodynamics.Nephron. 2023;147(7):434-440. doi: 10.1159/000528259. Epub 2022 Dec 29. Nephron. 2023. PMID: 36580904 Free PMC article.
-
The multi-lineage transcription factor ISL1 controls cardiomyocyte cell fate through interaction with NKX2.5.Stem Cell Reports. 2023 Nov 14;18(11):2138-2153. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2023.09.014. Epub 2023 Oct 19. Stem Cell Reports. 2023. PMID: 37863045 Free PMC article.
-
Autonomic cardiac innervation: development and adult plasticity.Organogenesis. 2013 Jul-Sep;9(3):176-93. doi: 10.4161/org.24892. Epub 2013 May 14. Organogenesis. 2013. PMID: 23872607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel computational model of gastrula morphogenesis to identify spatial discriminator genes by self-organizing map (SOM) clustering.Sci Rep. 2019 Aug 29;9(1):12597. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-49031-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31467377 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bronner-Fraser M. Analysis of the early stages of trunk neural crest migration in avian embryos using monoclonal antibody HNK-1. Dev. Biol. 1986;115:44–55. - PubMed
-
- Cariboni A., Davidson K., Rakic S., Maggi R., Parnavelas J.G., Ruhrberg C. Defective gonadotropin-releasing hormone neuron migration in mice lacking SEMA3A signalling through NRP1 and NRP2: implications for the aetiology of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Hum Mol. Genet. 2011;20:336–344. - PubMed
-
- Cau E., Gradwohl G., Fode C., Guillemot F. Mash1 activates a cascade of bHLH regulators in olfactory neuron progenitors. Development. 1997;124:1611–1621. - PubMed
-
- Chen H., He Z., Bagri A., Tessier-Lavigne M. Semaphorin-neuropilin interactions underlying sympathetic axon responses to class III semaphorins. Neuron. 1998;21:1283–1290. - PubMed
-
- Erickson C.A., Duong T.D., Tosney K.W. Descriptive and experimental analysis of the dispersion of neural crest cells along the dorsolateral path and their entry into ectoderm in the chick embryo. Dev. Biol. 1992;151:251–272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

