Immunoregulatory function of IL-27 and TGF-β1 in cardiac allograft transplantation
- PMID: 22790384
- PMCID: PMC3442234
- DOI: 10.1097/TP.0b013e31825b0c38
Immunoregulatory function of IL-27 and TGF-β1 in cardiac allograft transplantation
Abstract
Background: Deciphering the mechanisms of tolerance represents a crucial aim of research in transplantation. We previously identified by DNA chip interleukin (IL)-27 p28 and transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 as overexpressed in a model of rat cardiac allograft tolerance mediated by regulatory CD4CD25 T cells. The role of these two molecules on the control of the inflammatory response remains controversial. However, both are involved in the regulation of the T helper 17/Treg axis, suggesting their involvement in tolerance.
Methods: We analyzed regulation of IL-27 and TGF-β1 expression in allograft response and their role in tolerance by using blocking anti-TGF-β antibody and by generating an adeno-associated virus encoding IL-27.
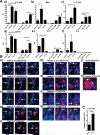
Results: Here, we confirmed the overexpression of IL-27 and TGF-β1 in tolerated cardiac allografts in two different rodent models. We observed that their expression correlates with inhibition of T helper 17 differentiation and with expansion of regulatory CD4CD25 T cells. We showed in a rat model that anti-TGF-β treatment abrogates infectious tolerance mediated by the transfer of regulatory CD4CD25 T cells. Moreover, overexpression of IL-27 by adeno-associated virus administration in combination with a short-term immunosuppression allows prolongation of cardiac allograft survival and one tolerant recipient. We found that IL-27 overexpression did not induce Foxp3CD4CD25 T-cell expansion but rather IL-10-expressing CD4 T cells in the tolerant recipient.
Conclusions: Taken together, these data suggest that both TGF-β1 and IL-27 play a role in the mechanisms of tolerance. However, in contrast to TGF-β1, IL-27 seems not to be involved in regulatory CD4CD25 T-cell expansion but rather in their mode of action.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Dendritic cells with TGF-β1 and IL-2 differentiate naive CD4+ T cells into alloantigen-specific and allograft protective Foxp3+ regulatory T cells.Transplantation. 2012 Mar 27;93(6):580-8. doi: 10.1097/TP.0b013e318244dd67. Transplantation. 2012. PMID: 22270834 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-17 accelerates allograft rejection by suppressing regulatory T cell expansion.Circulation. 2011 Sep 13;124(11 Suppl):S187-96. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.014852. Circulation. 2011. PMID: 21911812
-
Transforming growth factor-beta1 gene transfer is associated with the development of regulatory cells.Am J Transplant. 2005 Oct;5(10):2378-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2005.01042.x. Am J Transplant. 2005. PMID: 16162185
-
CD4+CD25+ T Regulatory Cells in Transplantation Tolerance: 25 Years On.Transplantation. 2016 Dec;100(12):2533-2547. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000001436. Transplantation. 2016. PMID: 27861285 Review.
-
Modulation of autoimmune diseases by interleukin (IL)-17 producing regulatory T helper (Th17) cells.Indian J Med Res. 2013 Nov;138(5):591-4. Indian J Med Res. 2013. PMID: 24434314 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transplant Tolerance, Not Only Clonal Deletion.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 21;13:810798. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.810798. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35529847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tolerogenic Dendritic Cells: The Pearl of Immunotherapy in Organ Transplantation.Front Immunol. 2020 Oct 6;11:552988. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.552988. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33123131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-34 is a Treg-specific cytokine and mediates transplant tolerance.J Clin Invest. 2015 Oct 1;125(10):3952-64. doi: 10.1172/JCI81227. Epub 2015 Sep 21. J Clin Invest. 2015. PMID: 26389674 Free PMC article.
-
Transplanted terminally differentiated induced pluripotent stem cells are accepted by immune mechanisms similar to self-tolerance.Nat Commun. 2014 May 30;5:3903. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4903. Nat Commun. 2014. PMID: 24875164 Free PMC article.
-
Regulator Versus Effector Paradigm: Interleukin-10 as Indicator of the Switching Response.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016 Feb;50(1):97-113. doi: 10.1007/s12016-015-8514-7. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26450621 Review.
References
-
- Kastelein RA, Hunter CA, Cua DJ. Discovery and Biology of IL-23 and IL-27: Related but Functionally Distinct Regulators of Inflammation. Annual Review of Immunology. 2007;25(1):221. - PubMed
-
- Goldberg R, Zohar Y, Wildbaum G, Geron Y, Maor G, Karin N. Suppression of ongoing experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by neutralizing the function of the p28 subunit of IL-27. J Immunol. 2004;173(10):6465. - PubMed
-
- Kido MTS, Sugiyama N, Esaki H, Nakashima H, Yoshida H, Furue M. T cell-specific overexpression of interleukin-27 receptor α subunit (WSX-1) prevents spontaneous skin inflammation in MRL/lpr mice. Br J Dermatol. 2011;164(6):1214. - PubMed
-
- Chen Q, Ghilardi N, Wang H, et al. Development of Th1-type immune responses requires the type I cytokine receptor TCCR. Nature. 2000;407(6806):916. - PubMed
-
- Pflanz S, Timans JC, Cheung J, et al. IL-27, a heterodimeric cytokine composed of EBI3 and p28 protein, induces proliferation of naive CD4(+) T cells. Immunity. 2002;16(6):779. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

