Gynecomastia: physiopathology, evaluation and treatment
- PMID: 22790552
- PMCID: PMC10876201
- DOI: 10.1590/s1516-31802012000300009
Gynecomastia: physiopathology, evaluation and treatment
Abstract
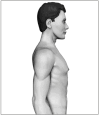
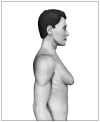
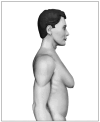
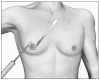
Gynecomastia (GM) is characterized by enlargement of the male breast, caused by glandular proliferation and fat deposition. GM is common and occurs in adolescents, adults and in old age. The aim of this review is to discuss the pathophysiology, etiology, evaluation and therapy of GM. A hormonal imbalance between estrogens and androgens is the key hallmark of GM generation. The etiology of GM is attributable to physiological factors, endocrine tumors or dysfunctions, non-endocrine diseases, drug use or idiopathic causes. Clinical evaluation must address diagnostic confirmation, search for an etiological factor and classify GM into severity grades to guide the treatment. A proposal for tailored therapy is presented. Weight loss, reassurance, pharmacotherapy with tamoxifen and surgical correction are the therapeutic options. For long-standing GM, the best results are generally achieved through surgery, combining liposuction and mammary adenectomy.
A ginecomastia (GM) é caracterizada pelo aumento do volume mamário em homens, provocada por proliferação glandular e depósito de gordura. É comum e pode ocorrer em adolescentes, adultos e idosos. O objetivo desta revisão é discutir a fisiopatologia, etiologia, avaliação clínica e terapia da GM. Um desequilíbrio entre estrogênios e androgênios é reconhecido como a condição fundamental para a determinação do quadro, podendo ser atribuído a fatores fisiológicos, tumores ou distúrbios endócrinos, doenças não-endócrinas, uso de drogas ou ser de causa idiopática. A avaliação clínica deve enfocar a confirmação diagnóstica, a procura de uma causa específica e a classificação em graus de gravidade para orientar o tratamento. Um roteiro de conduta individualizada é apresentado, variando entre perda de peso e explicações verbais, tratamento com tamoxifeno e correção cirúrgica. Para casos de GM persistente, os melhores resultados são obtidos em geral mediante abordagem cirúrgica, combinando lipoaspiração e adenectomia mamária.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



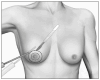
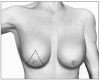
References
-
- Georgiadis E, Papandreou L, Evangelopoulou C, et al. Incidence of gynaecomastia in 954 young males and its relationship to somatometric parameters. Ann Hum Biol. 1994;21(6):579–587. - PubMed
-
- Nuttall FQ. Gynecomastia as a physical finding in normal men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979;48(2):338–340. - PubMed
-
- Nydick M, Bustos J, Dale JH, Jr, Rawson RW. Gynecomastia in adolescent boys. JAMA. 1961;178:449–454. - PubMed
-
- Niewoehner CB, Nuttall FQ. Gynecomastia in a hospitalized male population. Am J Med. 1984;77(4):633–638. - PubMed
-
- Bannayan GA, Hajdu SI. Gynecomastia: clinicopathologic study of 351 cases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1972;57(4):431–437. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

