Chronic ethanol feeding enhances miR-21 induction during liver regeneration while inhibiting proliferation in rats
- PMID: 22790595
- PMCID: PMC3468539
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00019.2012
Chronic ethanol feeding enhances miR-21 induction during liver regeneration while inhibiting proliferation in rats
Abstract
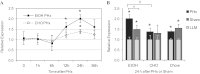
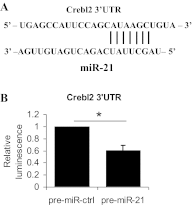
Liver regeneration is an important repair response to liver injury. Chronic ethanol consumption inhibits and delays liver regeneration in experimental animals. We studied the effects of chronic ethanol treatment on messenger RNA (mRNA) and microRNA (miRNA) expression profiles during the first 24 h after two-thirds partial hepatectomy (PHx) and found an increase in hepatic miR-21 expression in both ethanol-fed and pair-fed control rats after PHx. We demonstrate that the increase of miR-21 expression during liver regeneration is more robust in ethanol-fed rats. Peak miR-21 expression occurs at 24 h after PHx in both ethanol-fed and control rats, corresponding to the peak of hepatocyte S phase in control rats, but not in ethanol-exposed livers in which cell cycle is delayed. The induction of miR-21 24 h after PHx in control rats is not greater than the increase in expression of miR-21 due to sham surgery. However, in the ethanol-fed rat, miR-21 is induced to a greater extent by PHx than by sham surgery. To elucidate the implications of increased miR-21 expression during liver regeneration, we employed unbiased global target analysis using gene expression data compiled by our group. Our analyses suggest that miR-21 may play a greater role in regulating gene expression during regeneration in the ethanol-fed rat than in the control rat. Our analysis of potential targets of miR-21 suggests that miR-21 affects a broad range of target processes and may have a widespread regulatory role under conditions of suppressed liver regeneration in ethanol-treated animals.
Figures


References
-
- Albrecht JH, Hu MY, Cerra FB. Distinct patterns of cyclin D1 regulation in models of liver regeneration and human liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 209: 648–655, 1995 - PubMed
-
- Betel D, Wilson M, Gabow A, Marks DS, Sander C. The microRNA.org resource: targets and expression. Nucleic Acids Res 36 (Database issue): D149–D153, 2008 - PMC - PubMed
-
- DeCarli LM, Lieber CS. Fatty liver in the rat after prolonged intake of ethanol with a nutritionally adequate new liquid diet. J Nutr 91: 331–336, 1967 - PubMed
-
- Diehl AM, Thorgeirsson SS, Steer CJ. Ethanol inhibits liver regeneration in rats without reducing transcripts of key protooncogenes. Gastroenterology 99: 1105–1112, 1990 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

