Organismal regulation of XBP-1-mediated unfolded protein response during development and immune activation
- PMID: 22791024
- PMCID: PMC3432796
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2012.100
Organismal regulation of XBP-1-mediated unfolded protein response during development and immune activation
Abstract
The increased demand on protein folding in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) during bacterial infection activates the unfolded protein response (UPR). OCTR-1--a G protein-coupled catecholamine receptor expressed in neurons--suppresses innate immunity by downregulating a non-canonical UPR pathway and the p38 MAPK pathway. Here, we show that OCTR-1 also regulates the canonical UPR pathway, which is controlled by XBP-1, at the organismal level. Importantly, XBP-1 is not under OCTR-1 control during development, only at the adult stage. Our results indicate that the nervous system temporally controls the UPR pathway to maintain ER homeostasis during development and immune activation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
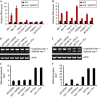
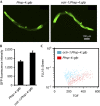
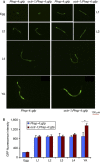
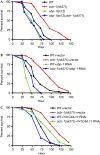
Comment in
-
Cell-nonautonomous control of the UPR.EMBO Rep. 2012 Sep;13(9):767-8. doi: 10.1038/embor.2012.117. Epub 2012 Aug 7. EMBO Rep. 2012. PMID: 22868667 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Walter P, Ron D (2011) The unfolded protein response: from stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science 334: 1081–1086 - PubMed
-
- Ma Y, Hendershot LM (2004) The role of the unfolded protein response in tumour development: friend or foe? Nat Rev Cancer 4: 966–977 - PubMed
-
- Marciniak SJ, Ron D (2006) Endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling in disease. Physiol Rev 86: 1133–1149 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

