Morphological, phylogenetic and physiological studies of pico-cyanobacteria isolated from the halocline of a saline meromictic lake, Lake Suigetsu, Japan
- PMID: 22791050
- PMCID: PMC4036012
- DOI: 10.1264/jsme2.me11329
Morphological, phylogenetic and physiological studies of pico-cyanobacteria isolated from the halocline of a saline meromictic lake, Lake Suigetsu, Japan
Abstract
Small cyanobacteria (<2 µm, pico-cyanobacteria) are abundant in waters deeper than the oxic-anoxic zone in the halocline of a saline meromictic lake, Lake Suigetsu, Fukui, Japan. We have isolated 101 strains that were grouped into six groups by means of the phycobiliprotein composition and sequence homology of the intergenic spacer between the 16S and 23S rRNA genes. Significant growth was observed under weak green light (1.5 µmol m⁻² s⁻¹, approx. 460 to 600 nm), whereas the cells died under white light at even moderate intensities. The isolates grew in a wide range of salinities (0.2 to 3.2%). Tolerance to sulfide varied: four groups grew in medium containing sulfide, however, two groups did not. None of the isolates were capable of anoxygenic photosynthetic (PS-II independent photosynthetic) growth using sulfide as an electron donor. All groups were included within fresh and brackish water of Synechococcus/Cyanobium clade, but they were not monophyletic in the 16S rRNA gene-based phylogenetic tree. The physiological properties of pico-cyanobacteria showed that they had the ability to survive in unique physicochemical environments in the halocline of this saline meromictic lake.
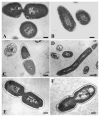
Figures





References
-
- Bossshard PP, Santini Y, Grüter D, Stettler R, Bachofen R. Bacterial diversity and community composition in the chemocline of the meromictic alpine Lake Cadagno as revealed by 16S rDNA analysis. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2000;31:173–182. - PubMed
-
- Craig SR. The distribution and contribution of picoplankton to deep photosynthetic layers in some meromictic lakes. Acta Acad Aboensis. 1987;47:55–81.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions

