Phosphatidylinositol phosphate-dependent regulation of Xenopus ENaC by MARCKS protein
- PMID: 22791334
- PMCID: PMC3468524
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00703.2011
Phosphatidylinositol phosphate-dependent regulation of Xenopus ENaC by MARCKS protein
Abstract
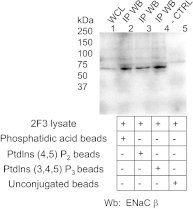
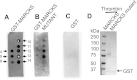
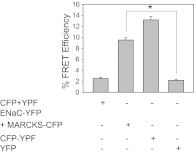
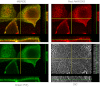
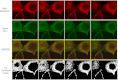
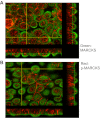
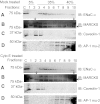
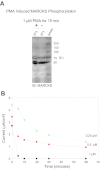
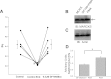
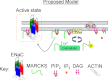
Phosphatidylinositol phosphates (PIPs) are known to regulate epithelial sodium channels (ENaC). Lipid binding assays and coimmunoprecipitation showed that the amino-terminal domain of the β- and γ-subunits of Xenopus ENaC can directly bind to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP(2)), phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP(3)), and phosphatidic acid (PA). Similar assays demonstrated various PIPs can bind strongly to a native myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate (MARCKS), but weakly or not at all to a mutant form of MARCKS. Confocal microscopy demonstrated colocalization between MARCKS and PIP(2). Confocal microscopy also showed that MARCKS redistributes from the apical membrane to the cytoplasm after PMA-induced MARCKS phosphorylation or ionomycin-induced intracellular calcium increases. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer studies revealed ENaC and MARCKS in close proximity in 2F3 cells when PKC activity and intracellular calcium concentrations are low. Transepithelial current measurements from Xenopus 2F3 cells treated with PMA and single-channel patch-clamp studies of Xenopus 2F3 cells treated with a PKC inhibitor altered Xenopus ENaC activity, which suggest an essential role for MARCKS in the regulation of Xenopus ENaC activity.
Figures


References
-
- Aderem A. The MARCKS brothers: a family of protein kinase C substrates. Cell 71: 713–716, 1992 - PubMed
-
- Ali N, Macala LJ, Hayslett JP. Identification and characterization of MARCKS in Xenopus laevis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 234: 143–146, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Alli AA, Gower WR., Jr The C type natriuretic peptide receptor tethers AHNAK1 at the plasma membrane to potentiate arachidonic acid-induced calcium mobilization. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 297: C1157–C1167, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Alli AA, Gower WR., Jr Molecular approaches to examine the phosphorylation state of the C type natriuretic peptide receptor. J Cell Biochem 110: 985–994, 2010 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

