Endotoxemia alters tight junction gene and protein expression in the kidney
- PMID: 22791339
- PMCID: PMC3468522
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00023.2012
Endotoxemia alters tight junction gene and protein expression in the kidney
Abstract
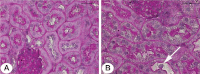
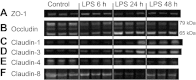
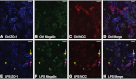
Intact tight junctional (TJ) proteins are required for tubular ion transport and waste excretion. Disruption of TJs may contribute to a decreased glomerular filtration rate in acute kidney injury (AKI) via tubular backleak. The effect of LPS-mediated AKI on murine TJs has not been studied extensively. We hypothesized LPS endotoxin administration to mice would disrupt tubular TJ proteins including zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1), occludin, and claudins. ZO-1 and occludin immunofluorescence 24 h post-LPS revealed a marked change in localization from the usual circumferential fencework pattern to one with substantial fragmentation. Renal ZO-1 expression was significantly reduced 24 h after LPS (decrease of 56.1 ± 7.4%, P < 0.001), with subsequent recovery. ZO-1 mRNA expression was increased 24 h post-LPS (4.34 ± 0.87-fold, P = 0.0019), suggesting disruption of ZO-1 protein is not mediated by transcriptional regulation, but rather by degradation or changes in translation. Similarly, claudin-4 protein expression was decreased despite elevated mRNA. LPS administration resulted in dephosphorylation of occludin and fragmented tubular redistribution. Protein expression of claudin-1, and -3 was increased after LPS. ZO-1, occludin, and claudin-1, -3, and -4 gene expression were increased 48 h after LPS, suggesting a renal response to strengthen TJs following injury. Interestingly, reduced mRNA expression was found only for claudin-8. This study provides further support that LPS-induced AKI is associated with structural injury and is not merely due to hemodynamic changes.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Corneal epithelial tight junctions and their response to lipopolysaccharide challenge.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000 Dec;41(13):4093-100. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000. PMID: 11095601
-
Effects of cigarette smoke on barrier function and tight junction proteins in the bronchial epithelium: protective role of cathelicidin LL-37.Respir Res. 2019 Nov 9;20(1):251. doi: 10.1186/s12931-019-1226-4. Respir Res. 2019. PMID: 31706310 Free PMC article.
-
RhoA/ROCK-2 Pathway Inhibition and Tight Junction Protein Upregulation by Catalpol Suppresses Lipopolysaccaride-Induced Disruption of Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability.Molecules. 2018 Sep 17;23(9):2371. doi: 10.3390/molecules23092371. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30227623 Free PMC article.
-
Moxibustion combined with acupuncture increases tight junction protein expression in Crohn's disease patients.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Apr 28;21(16):4986-96. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i16.4986. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25945013 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Inducible expression of claudin-1-myc but not occludin-VSV-G results in aberrant tight junction strand formation in MDCK cells.J Cell Sci. 2000 Oct;113 Pt 19:3387-98. doi: 10.1242/jcs.113.19.3387. J Cell Sci. 2000. PMID: 10984430
Cited by
-
Protective effect of emodin on intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier integrity in rats with sepsis induced by cecal ligation and puncture.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Jun;19(6):3521-3530. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.8625. Epub 2020 Mar 24. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32346413 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of omega- 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on endothelial tight junction occludin expression in rat aorta during lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2016 Mar;19(3):290-9. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27114799 Free PMC article.
-
Beneficial Effects of Anti-Interleukin-6 Antibodies on Impaired Gastrointestinal Motility, Inflammation and Increased Colonic Permeability in a Murine Model of Sepsis Are Most Pronounced When Administered in a Preventive Setup.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 4;11(4):e0152914. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152914. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27044016 Free PMC article.
-
[Expression and significance of tight junction proteins in the kidney in a mouse model of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2018 Dec;20(12):1055-1062. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2018.12.015. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30572998 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Development of a zebrafish sepsis model for high-throughput drug discovery.Mol Med. 2017 Jul;23:134-148. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2016.00188. Epub 2017 Jun 7. Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28598490 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acharya P, Beckel J, Ruiz WG, Wang E, Rojas R, Birder L, Apodaca G. Distribution of the tight junction proteins ZO-1, occludin, and claudin-4, -8, and -12 in bladder epithelium. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 287: F305–F318, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Al-Lamki RS, Wang J, Skepper JN, Thiru S, Pober JS, Bradley JR. Expression of tumor necrosis factor receptors in normal kidney and rejecting renal transplants. Lab Invest 81: 1503–1515, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Al-Lamki RS, Wang J, Vandenabeele P, Bradley JA, Thiru S, Luo D, Min W, Pober JS, Bradley JR. TNFR1- and TNFR2-mediated signaling pathways in human kidney are cell type-specific and differentially contribute to renal injury. FASEB J 19: 1637–1645, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Amasheh S, Fromm M, Gunzel D. Claudins of intestine and nephron—a correlation of molecular tight junction structure and barrier function. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 201: 133–140, 2011 - PubMed
-
- Amon M, Menger MD, Vollmar B. Heme oxygenase and nitric oxide synthase mediate cooling-associated protection against TNF-alpha-induced microcirculatory dysfunction and apoptotic cell death. FASEB J 17: 175–185, 2003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

