Interruption of nuclear localization of ATBF1 during the histopathologic progression of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 22791392
- PMCID: PMC3978689
- DOI: 10.1002/hed.23077
Interruption of nuclear localization of ATBF1 during the histopathologic progression of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: The AT-motif binding factor 1 (ATBF1) gene is frequently altered at the genetic level in several types of cancer, but its protein expression and subcellular localization have not been well studied in human cancers, including head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCCs).
Methods: ATBF1 expression and localization were examined in 5 cell lines and 197 clinical specimens of HNSCC, and correlated with pathologic and clinical characteristics.
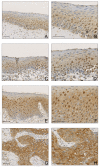
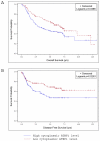
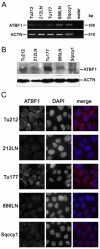
Results: ATBF1 was predominantly localized in the nucleus of hyperplastic squamous epithelium. Whereas nuclear ATBF1 dramatically decreased in invasive tumors (p = .0012), cytoplasmic ATBF1 levels progressively increased from dysplasia to invasive tumors (p < .0001), and the increase correlated with poor survival. Reduced nuclear ATBF1 level was also detected in HNSCC cell lines.
Conclusions: Nuclear localization of ATBF1 is frequently interrupted in HNSCC, and the interruption is significantly associated with the progression of HNSCC. The cytoplasmic ATBF1 level could be useful for predicting patient survival.
Copyright © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60(5):277–300. - PubMed
-
- Miura Y, Tam T, Ido A, et al. Cloning and characterization of an ATBF1 isoform that expresses in a neuronal differentiation-dependent manner. J Biol Chem. 1995;270(45):26840–8. - PubMed
-
- Ido A, Miura Y, Tamaoki T. Activation of ATBF1, a multiple-homeodomain zinc-finger gene, during neuronal differentiation of murine embryonal carcinoma cells. Dev Biol. 1994;163(1):184–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

