Oxidative stress biomarkers in some rat brain structures and peripheral organs underwent cocaine
- PMID: 22791409
- PMCID: PMC3526736
- DOI: 10.1007/s12640-012-9335-6
Oxidative stress biomarkers in some rat brain structures and peripheral organs underwent cocaine
Erratum in
- Neurotox Res. Neurotox Res. 2013 Jan;23(1):103-4
Abstract
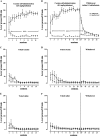
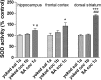
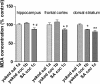
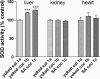
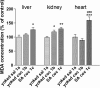
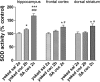
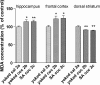
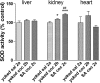
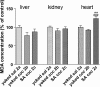
Oxidative stress (OS) generates or intensifies cocaine-evoked toxicity in the brain and peripheral organs. The aim of this study was to examine superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity and lipid peroxidation [measured by malondialdehyde (MDA) levels] in rats during maintenance of cocaine self-administration and after withdrawal by a yoked-triad procedure. Our results indicate that repeated cocaine self-administration provoked an elevation of SOD activity in the hippocampus, frontal cortex, dorsal striatum, and liver. MDA levels were reduced in the brain, increased in the liver, kidney, and heart during maintenance of self-administration, and increased in the kidney in cocaine-yoked rats. In addition, following extinction training, we found enhanced MDA levels and SOD activity in the rat hippocampus, while changes in the activity of OS biomarkers in other brain structures and peripheral tissues were reminiscent of the changes seen during cocaine self-administration. These findings highlight the association between OS biomarkers in motivational processes related to voluntary cocaine intake in rats. OS participates in memory and learning impairments that could be involved in drug toxicity and addiction mechanisms. Therefore, further studies are necessary to address protective mechanisms against cocaine-induced brain and peripheral tissue damage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protective effects of hesperidin and diosmin against acrylamide-induced liver, kidney, and brain oxidative damage in rats.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 Dec;26(34):35151-35162. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-06660-3. Epub 2019 Nov 4. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31686333
-
Changes in endocannabinoid and N-acylethanolamine levels in rat brain structures following cocaine self-administration and extinction training.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2014 Apr 3;50:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2013.12.002. Epub 2013 Dec 12. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 24334211
-
Oxidative Stress Markers and Histological Analysis in Diverse Organs from Rats Treated with a Hepatotoxic Dose of Cr(VI): Effect of Curcumin.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2015 Sep;167(1):130-45. doi: 10.1007/s12011-015-0283-x. Epub 2015 Mar 14. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2015. PMID: 25774041
-
Antioxidant enzymes activity and lipid peroxidation in liver and kidney of rats exposed to cadmium and ethanol.Food Chem Toxicol. 2004 Mar;42(3):429-38. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2003.10.005. Food Chem Toxicol. 2004. PMID: 14871584
-
Studies on fate and toxicity of nanoalumina in male albino rats: Oxidative stress in the brain, liver and kidney.Toxicol Ind Health. 2016 Feb;32(2):200-14. doi: 10.1177/0748233713498462. Epub 2013 Sep 30. Toxicol Ind Health. 2016. PMID: 24081632
Cited by
-
Cocaine and kidney injury: a kaleidoscope of pathology.Clin Kidney J. 2014 Dec;7(6):513-7. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfu092. Epub 2014 Sep 12. Clin Kidney J. 2014. PMID: 25859366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acquisition, Maintenance and Relapse-Like Alcohol Drinking: Lessons from the UChB Rat Line.Front Behav Neurosci. 2017 Apr 4;11:57. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2017.00057. eCollection 2017. Front Behav Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28420969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Withdrawal from cocaine self-administration and yoked cocaine delivery dysregulates glutamatergic mGlu5 and NMDA receptors in the rat brain.Neurotox Res. 2015 Apr;27(3):246-58. doi: 10.1007/s12640-014-9502-z. Epub 2014 Nov 19. Neurotox Res. 2015. PMID: 25408547 Free PMC article.
-
S-Glutathionylation and Redox Protein Signaling in Drug Addiction.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2016;137:87-121. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2015.10.001. Epub 2015 Oct 31. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2016. PMID: 26809999 Free PMC article.
-
Heat shock protein 27 plays a protective role in thoracic aortic dissection by promoting cell proliferation and inhibiting apoptosis.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2017 Nov 28;22:24. doi: 10.1186/s11658-017-0056-y. eCollection 2017. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2017. PMID: 29209372 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berger AJ, Dieudonné S, Ascher P. Glycine uptake governs glycine site occupancy at NMDA receptors of excitatory synapses. J Neurophysiol. 1998;80:3336–3340. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

