Remission induction in acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 22791508
- PMCID: PMC4052975
- DOI: 10.1007/s12185-012-1121-y
Remission induction in acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
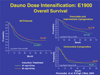
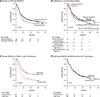
Inducing a complete remission (CR) in patients with acute myeloid leukemia is a prerequisite to long-term disease control with subsequent post-remission consolidation chemotherapy or allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. The use of 7 days of infusional cytarabine and 3 days of daunorubicin or idarubicin (7 + 3) has become the standard of care to induce CR, based on clinical trials conducted in the 1980s. Efforts to improve on the CR rate seen with the 7 + 3 regimen that translates into better overall patient survival have been disappointing. Here we review recent phase III studies of novel induction strategies that show promise in increasing the rate of CR and improving disease outcome.
Figures
References
-
- Preisler H, et al. Comparison of three remission induction regimens and two postinduction strategies for the treatment of acute nonlymphocytic leukemia: a cancer and leukemia group B study. Blood. 1987;69(5):1441–1449. - PubMed
-
- Yates J, et al. Cytosine arabinoside with daunorubicin or adriamycin for therapy of acute myelocytic leukemia: a CALGB study. Blood. 1982;60(2):454–462. - PubMed
-
- Rai KR, et al. Treatment of acute myelocytic leukemia: a study by cancer and leukemia group B. Blood. 1981;58(6):1203–1212. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical