Compressed-sensing multispectral imaging of the postoperative spine
- PMID: 22791572
- PMCID: PMC3473176
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.23750
Compressed-sensing multispectral imaging of the postoperative spine
Abstract
Purpose: To apply compressed sensing (CS) to in vivo multispectral imaging (MSI), which uses additional encoding to avoid magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) artifacts near metal, and demonstrate the feasibility of CS-MSI in postoperative spinal imaging.
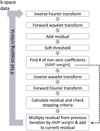
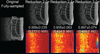
Materials and methods: Thirteen subjects referred for spinal MRI were examined using T2-weighted MSI. A CS undersampling factor was first determined using a structural similarity index as a metric for image quality. Next, these fully sampled datasets were retrospectively undersampled using a variable-density random sampling scheme and reconstructed using an iterative soft-thresholding method. The fully and undersampled images were compared using a 5-point scale. Prospectively undersampled CS-MSI data were also acquired from two subjects to ensure that the prospective random sampling did not affect the image quality.
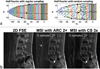
Results: A two-fold outer reduction factor was deemed feasible for the spinal datasets. CS-MSI images were shown to be equivalent or better than the original MSI images in all categories: nerve visualization: P = 0.00018; image artifact: P = 0.00031; image quality: P = 0.0030. No alteration of image quality and T2 contrast was observed from prospectively undersampled CS-MSI.
Conclusion: This study shows that the inherently sparse nature of MSI data allows modest undersampling followed by CS reconstruction with no loss of diagnostic quality.
Copyright © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Investigating the quantitative fidelity of prospectively undersampled chemical shift imaging in muscular dystrophy with compressed sensing and parallel imaging reconstruction.Magn Reson Med. 2014 Dec;72(6):1610-9. doi: 10.1002/mrm.25072. Epub 2013 Dec 17. Magn Reson Med. 2014. PMID: 24347306
-
Smoothly clipped absolute deviation (SCAD) regularization for compressed sensing MRI using an augmented Lagrangian scheme.Magn Reson Imaging. 2013 Oct;31(8):1399-411. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2013.05.010. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Magn Reson Imaging. 2013. PMID: 23891179
-
Compressed sensing for reduction of noise and artefacts in direct PET image reconstruction.Z Med Phys. 2014 Mar;24(1):16-26. doi: 10.1016/j.zemedi.2013.05.003. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Z Med Phys. 2014. PMID: 23756331
-
Evaluation of Variable Density and Data-Driven K-Space Undersampling for Compressed Sensing Magnetic Resonance Imaging.Invest Radiol. 2016 Jun;51(6):410-9. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000231. Invest Radiol. 2016. PMID: 26674209
-
View-Sharing Artifact Reduction With Retrospective Compressed Sensing Reconstruction in the Context of Contrast-Enhanced Liver MRI for Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) Screening.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2019 Apr;49(4):984-993. doi: 10.1002/jmri.26276. Epub 2018 Nov 2. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30390358
Cited by
-
Undersampling patterns in k-space for compressed sensing MRI using two-dimensional Cartesian sampling.Radiol Phys Technol. 2018 Sep;11(3):303-319. doi: 10.1007/s12194-018-0469-y. Epub 2018 Aug 4. Radiol Phys Technol. 2018. PMID: 30078080
-
Clinical utility of accelerated MAVRIC-SL with robust-PCA compared to conventional MAVRIC-SL in evaluation of total hip arthroplasties.Skeletal Radiol. 2022 Mar;51(3):549-556. doi: 10.1007/s00256-021-03848-y. Epub 2021 Jul 5. Skeletal Radiol. 2022. PMID: 34223946 Free PMC article.
-
Improved Single Breath-Hold SSFSE Sequence for Liver MRI Based on Compressed Sensing: Evaluation of Image Quality Compared with Conventional T2-Weighted Sequences.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Sep 6;12(9):2164. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12092164. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36140565 Free PMC article.
-
2D multi-spectral imaging for fast MRI near metal.Magn Reson Med. 2018 Feb;79(2):968-973. doi: 10.1002/mrm.26724. Epub 2017 Apr 25. Magn Reson Med. 2018. PMID: 28444805 Free PMC article.
-
Contrast-Enhanced High-Resolution Intracranial Vessel Wall MRI with Compressed Sensing: Comparison with Conventional T1 Volumetric Isotropic Turbo Spin Echo Acquisition Sequence.Korean J Radiol. 2020 Dec;21(12):1334-1344. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2020.0128. Epub 2020 Aug 4. Korean J Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32767865 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lustig M, Donoho D, Pauly JM. Sparse MRI: The application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging. Magn Reson Med. 2007;58:1182–1195. - PubMed
-
- Koch KM, Lorbiecki JE, Hinks RS, King KF. A multispectral three-dimensional acquisition technique for imaging near metal implants. Magn Reson Med. 2009;61:381–390. - PubMed
-
- Koch KM, Brau AC, Chen W, Gold GE, Hargreaves BA, Koff M, McKinnon GC, Potter HG, King KF. Imaging near metal with a MAVRIC-SEMAC hybrid. Magn Reson Med. 2011;65:71–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

